[ This is a content summary only. Visit our website https://ift.tt/1b4YgHQ for full links, other content, and more! ]
by Daniyal Malik via Digital Information World
"Mr Branding" is a blog based on RSS for everything related to website branding and website design, it collects its posts from many sites in order to facilitate the updating to the latest technology.
To suggest any source, please contact me: Taha.baba@consultant.com
Android is the most popular mobile operating system in the world today, running on billions of active devices, which include phones, tablets, smart TVs, and various home appliances. So it should come as no surprise that knowing how to create native apps for it can open up a world of opportunities. You could, for instance, create a new income stream for yourself by publishing paid apps or apps with in-app purchases on Google Play. Or you could have an extremely lucrative career developing Android apps for your clients.
But to develop Android apps, you're going to need the right tools installed on your computer. In this tutorial, I'll show you how to install them, configure them, and use them to build and run a very simple Android app.
Note that you can use these same techniques to start an app using one of the premium app templates available from CodeCanyon—an online marketplace that has hundreds of Android app templates, which are very feature-rich and tailored to every domain. You can save days, even months, of effort by using one of them.
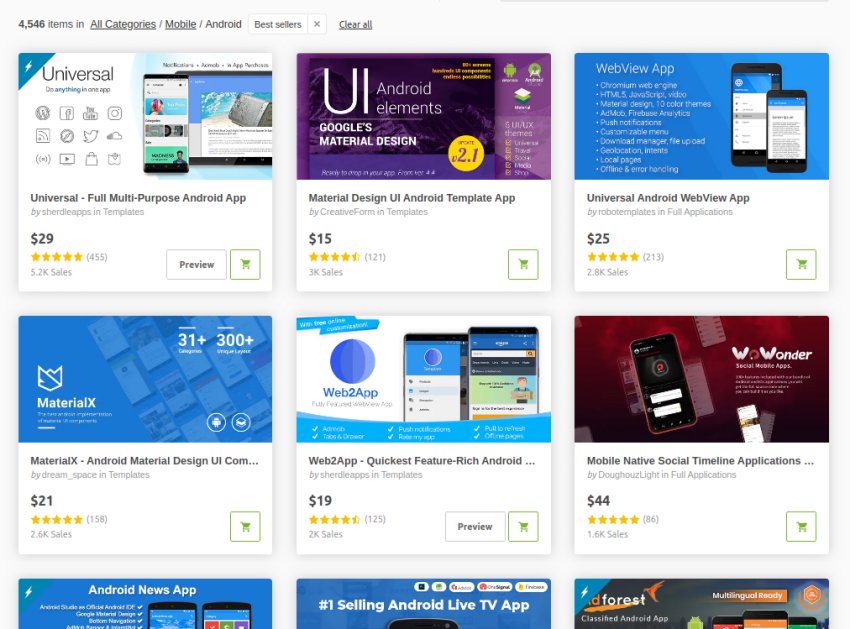
To be able to follow this step-by-step tutorial, all you need is a decent Internet connection and a computer that's running Windows 7 or higher. For an optimal experience, your computer should have at least 4 GB of RAM and about 5 GB of free disk space.
Android Studio is the official integrated development environment for native Android app development. With powerful features such as intelligent code completion, static code analysis, a visual layout editor, and cloud integration, it offers a very pleasant and intuitive development experience.
Android Studio is free and open source. So go ahead and open the Android Developers website, and click on the Download Android Studio button to download its latest stable version.

Once the download's complete, you'll have an executable file with a name that looks like this: android-studio-ide-191.6010548-windows.exe. The numbers in the filename may, however, be different, depending on the version of Android Studio you downloaded.
Double click on the file to start the installation wizard. In the dialog that pops up, press the Next button to proceed.

In the next screen, you'll be asked to select the components you want to install. Here's where you need to decide if you'll be needing an Android emulator, which is also often referred to as an Android virtual device, or AVD for short. Even if you have a real Android device, it's usually a good idea to have an AVD as well.

You'll then be prompted to specify where you want to install Android Studio. To go ahead with the default location, you can simply press Next.
Finally, you'll be asked if you want to add a shortcut for Android Studio in your Start menu. I suggest you don't change the defaults and directly press the Install button to start the installation.
Once the installation's complete, make sure that the Start Android Studio option is checked and press the Finish button.

Android Studio, fundamentally, is a code editor. It can't build and run Android applications by itself. It depends on the Android SDK, which is short for the Android software development kit, to be able to do that. Therefore, as soon as Android Studio starts for the first time, it will ask you to install the SDK.
The first time Android Studio starts, you should see a welcome dialog that looks like this:

Press the Next button to proceed. In the next screen, you'll be prompted to select the type of setup you want for the SDK. For now, choose the Standard option, which gets you all the important SDK components, and press Next.
You can then choose whether you want a dark or light UI theme for your IDE. Select Darcula if you prefer the dark theme.

Finally, you'll be able to see the actual SDK components that're going to be installed. Press the Finish button to download and install them.

After all the components are installed, Android Studio is ready to be used. So you'll be taken to the following welcome screen:

If you have a real Android device handy and want to use it instead of a virtual device, you're free to skip this step.
Even though you now have all the tools required to run an Android virtual device, you still need to create one. So open the Configure menu you see near the bottom of the welcome dialog and select the AVD Manager option. In the dialog that pops up, click on the Create Virtual Device... button.
You'll now be prompted to select a hardware profile for your virtual device. This profile, among other specifications, decides the screen size, the resolution, and pixel density of your AVD.

To make it easy for you, Android Studio has profiles that emulate various popular phones, such as Pixel, Pixel 2, and Pixel 3 XL. As you may have guessed, the profiles that sport the Google Play icon are ones that can run Google Play. For now, I suggest you choose the Pixel 2 profile and press Next.
In the next screen, you must specify the version of Android that must be installed on the AVD. You can choose any version you prefer, but you must have that version's system image available on your computer. So, usually, you'll have to first click on the Download button shown beside the version, and then select the version.

In the final screen of the wizard, give a name to your AVD and press the Finish button.

To make sure that Android Studio and all the SDK components are installed and configured correctly, let us now try to create and run a new Android Studio project.
Start by clicking on the Start a new Android Studio project button in the welcome screen.
Android Studio offers several templates you can use to avoid starting your project from scratch. For now, choose the Empty Activity template and press Next.

You can think of an activity as a screen of your app. Most apps have several activities, and thus several screens. By choosing the Empty Activity template, you're creating an app with one screen that has nothing but a "Hello World" label inside it.
In the next screen, give a name to your project and press the Finish button.

Android Studio may take a few minutes to prepare the project and download additional dependencies, such as Gradle, which serves as the default build toolkit.
Once the project's ready, press Shift + F10 to build and run it. Alternatively, you can open the Run menu and select Run 'app'.
If you followed all the steps in this tutorial, the project should build successfully. Furthermore, Android Studio should be able to automatically launch the AVD you created and run the project on it.

In this tutorial, you learned how to install Android Studio and all the SDK components it needs. You also learned how to create, build, and run an Android Studio project.
The default templates offered by Android Studio are very basic and provide minimal, generic functionality. CodeCanyon is an online marketplace that has hundreds of additional templates, which are way more feature rich and domain-specific too. You can save days, even months, of effort by using one of them.

If you have trouble deciding which template on CodeCanyon is right for you, these articles should help:




In this article, I'll show you how to use PHP code in your HTML pages. It’s aimed to PHP beginners who are trying to strengthen their grip on the world's most popular server-side scripting language.
Again, PHP is a server-side scripting language. That means a PHP script is executed on the server, the output is built on the server, and the result is finally sent as HTML to the client browser for rendering. It's natural to mix PHP and HTML in a script, but as a beginner, it’s tricky to know how to combine the PHP code with the HTML code.
Today, we’re going to discuss a couple of different ways you could choose from when you want to use PHP in HTML. I assume that you have a working installation of PHP so that you can run the examples provided in this article.
Broadly speaking, when it comes to use PHP in HTML, there are two different approaches. The first is to embed the PHP code in your HTML file itself with the .html extension—this requires a special consideration which we’ll discuss in a moment. The other option, the preferred way, is to combine PHP and HTML tags in .php files.
Since PHP is a server-side scripting language, the code is interpreted and run on the server side. For example, if you add the following code in your index.html file, it won’t run out of the box.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Embed PHP in a .html File</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><?php echo "Hello World" ?></h1>
</body>
</html>
First of all, don’t worry if you haven’t seen this kind of mixed PHP and HTML code before, as we’ll discuss it in detail throughout this article. The above example outputs following in your browser:
<?php echo "Hello World" ?>
So as you can see, by default, PHP tags in your .html document are not detected, and they're just considered plain-text, outputting without parsing. That's because the server is usually configured to run PHP only for files with the .php extension.
If you want to run your HTML files as PHP, you can tell the server to run your .html files as PHP files, but it's a much better idea to put your mixed PHP and HTML code into a file with the .php extension.
That's what I'll show you in this tutorial.
When it comes to integrating PHP code with HTML content, you need to enclose the PHP code with the PHP start tag <?php and the PHP end tag ?>. The code wrapped between these two tags is considered to be PHP code, and thus it'll be executed on the server side before the requested file is sent to the client browser.
Let’s have a look at a very simple example which displays a message by the PHP code. Create the index.php file with the following contents under your document root.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>How to put PHP in HTML - Simple Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><?php echo "This message is from server side." ?></h1>
</body>
</html>
The important thing in the above example is that the PHP code is wrapped by the PHP tags.
The output of the above example looks like this:

And, if you look at the view source of the page, it should look like this:

As you can see, the PHP code is parsed and executed on the server side, and it's merged with HTML before the page is sent to the client browser.
Let’s have a look at another example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>How to put PHP in HTML- Date Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>This is pure HTML message.</div>
<div>Next, we’ll display today’s date and day by PHP!</div>
<div>
Today’s date is <b><?php echo date('Y/m/d') ?></b> and it’s a <b><?php echo date(‘l’) ?></b> today!
</div>
<div>Again, this is static HTML content.</div>
</body>
</html>
This will output the current date and time, so as you can see you can use PHP code in between the HTML tags to produce dynamic output from the server. It’s important to remember that whenever the page is executed on the server side, all the code between the <?php and ?> tags will be interpreted as PHP and the output will be embedded with the HTML tags.
In fact, there’s another way you could write the above example as shown in the following snippet.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>How to put PHP in HTML- Date Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>This is pure HTML message.</div>
<div>Next, we’ll display today’s date and day by PHP!</div>
<div>
<?php
echo 'Today’s date is <b>' . date('Y/m/d') . '</b> and it’s a <b>'.date('l').'</b> today!';
?>
</div>
<div>Again, this is static HTML content.</div>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, we’ve used the concatenation feature of PHP which allows you to join different strings into one string. And finally, we’ve used the echo construct to display the concatenated string.
The output is same irrespective of the method you use as shown in the following screenshot.

And that brings another question: which is the best way? Should you use the concatenation feature or insert separate PHP tags in between the HTML tags? I would say, it really depends, there’s no strict rule which forces you to use one of these methods. Personally, I feel that the placeholder method is more readable compared to the concatenation method.
The overall structure of the PHP page combined with HTML and PHP code should look like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>...</title>
</head>
<body>
HTML...
<?php PHP code ... ?>
HTML...
<?php PHP code ... ?>
HTML...
</body>
</html>
Iterating through the arrays to produce HTML content is one of the most common tasks you'll encounter while writing PHP scripts. In this section, we’ll see how you could iterate through the an array of items and and generate output.
In most of the cases, you’ll need to display array content which you’ve populated from the database or some other sources. In this example, for the sake of simplicity, we’ll initialize the array with different values in the beginning of the script itself.
Go ahead and create a PHP file with the following contents.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>How to put PHP in HTML - foreach Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
$employees = array(‘John’, ‘Michelle’, ‘Mari’, ‘Luke’, ‘Nellie’);
?>
<h1>List of Employees</h1>
<ul>
<?php foreach ($employees as $employee) { ?>
<li><?php echo $employee ?></li>
<?php } ?>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
Firstly, we’ve initialized the array in the beginning of our script. Next, we’ve used the foreach construct to iterate through the array values. And finally, we’ve used the echo construct to display the array element value.
And the output should look like this:

The same example with a while loop looks like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>How to put PHP in HTML - foreach Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
$employees = array(‘John’, ‘Michelle’, ‘Mari’, ‘Luke’, ‘Nellie’);
$total = count($employees);
?>
<h1>List of Employees</h1>
<ul>
<?php
$i = 0;
?>
<?php while ($i < $total) { ?>
<li><?php echo $employees[$i] ?></li>
<?php ++$i ?>
<?php } ?>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
And the output will be the same. So that’s how you can use foreach and while loops to generate HTML content based on PHP arrays.
In the next and last section, we’ll see how you could use PHP short tags syntax.
In the examples we’ve discussed so far, we’ve used the <?php as a starting tag everywhere. In fact, PHP comes with a variation of that <?= which you could use as a short-hand syntax when you want to display a string or value of the variable.
Let’s revise the example with the short-hand syntax which we discussed earlier.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>How to put PHP in HTML - Simple Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><?= "This message is from server side." ?></h1>
</body>
</html>
As you can see, we can omit the echo or print construct while displaying a value by using the short-hand syntax. The short-hand syntax is short and readable when you want to display something with echo or print.
So these are different ways you can use to add PHP in HTML content. As a beginner, you can learn from trying different ways to do things, and it's fun too!
Today we discussed how you can mix PHP and HTML to create dynamic HTML. We discussed different methods with a few handful of examples to see how things work.
Feel free to use the feed below to ask if you’ve any queries and I’ll be happy to answer them!
Explore thousands of the best PHP scripts ever created on CodeCanyon. With a low-cost one time payment, you can purchase these high-quality WordPress plugins and improve your website experience for you and your visitors.

Here are a few of the best-selling and up-and-coming PHP scripts available from CodeCanyon for 2020.




