A new survey from Integral Ad Science (IAS), a media firm known for addressing digital advertising fraud, unveils eighty-seven percent of advertisers are highly concerned about audio ads fraud. Along with this, some vital pieces of information are also gathered by the company, which I will discuss further.
These days programmatic audio ads are gaining publishers' and ad buyers' interest due to their record-breaking consumer engagement capability. The ongoing growth in the volume of online audible stuff is increasing, and everyone is enjoying it. People prefer podcasts, audio blogs, etc., while traveling or doing home chores. Also, streaming audios are popular on mobile phones, and consumers are adopting audio devices such as speakers in their homes.
In response to the enhancement in the audio streaming business, marketers are adding audio to their campaigns to scale up their reach to relevant audiences. As consumers are already used to the audio ad formats, more media experts will adopt audio ads in the current year. The study says digital audio advertisements are expanding the overall performance and brand awareness for sixty-three percent of ad tech marketers surveyed. In addition, the study delves into whether marketers are satisfied with the current audibility metrics and highlights the importance of the third-party verification process in preserving premium quality standards for digital advertising.
The MD of integral Ad Science, Csaba Szabo, believes that with the widespread growth of digital audio content, marketers and advertisers want complete satisfaction with the adequacy of current metrics. About seventy-three percent of media publishers say that programmatic audio ad purchasing is more convenient and a better way to scale brands. Most ad buyers are adopting automated transactions while focusing on good-quality audio ads. Nearly half, almost forty-five percent of publishers said that it's essential to analyze the performance across visual ads, audios, video, etc. For most advertisers, audibility criteria are inadequate as a whole to compare viewability with performance benchmarks.
Furthermore, forty-three percent of mobile marketers would likely serve more frequent audio advertisements, and thirty-one percent of ad buyers would acquire more digital audio ads with integrated third-party support. The verification aids advertisers in tackling ad metrics by sharing in-depth analysis of performance and future novel ideas.
Spotify and IAS are collaborating to establish a third-party verification process to ensure the safety of digital audio ad marketers. So, it is essential to mention that by incorporating third-party support, most tech ad experts will purchase ads.
Read next: Social Media Profiles Are Getting Hacked At Alarming Rates, Confirms New Report
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
"Mr Branding" is a blog based on RSS for everything related to website branding and website design, it collects its posts from many sites in order to facilitate the updating to the latest technology.
To suggest any source, please contact me: Taha.baba@consultant.com
Monday, August 8, 2022
Here’s How China Went From Emerging Economy to Superpower in Just 20 Years
China’s rise to economic might has been a very interesting tale, as the country’s political struggles and turmoil have borne great fruit. Back in 2002, the two dominant economic super powers in the world were the US and the EU, with each having a 19.8% and 19.9% share of the global GDP when looked at with Purchasing Power Parity in mind. With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that both of these regions have seen their powers diminish due to a rapidly rising China.
China’s share of the world’s GDP when adjusted for PPP was around 8.1% in 2002, but 20 years later we are seeing a completely different picture. China now accounts for 18.8% of the world’s GDP, and both the US and the EU have seen a decrease of 4 and 5.1 percentage points respectively. The US now has a 15.8% share of the global economy, and the EU has just 14.8% which is a far cry from the unassailable dominance that they showed in decades prior.
The global recession will likely make the gap wider because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up bringing the economies of the US and the EU to a halt. China, on the other hand, is projected to continue showing modest growth rates which will allow it to cement its place as the world’s foremost super power.
China is not the only country that has been rising rapidly either. India managed to climb its way to an over 7% share of the world’s GDP, and while it is still short of China its growth rate will allow it to get closer to the US and the EU in terms of global GDP share.
The twin powers of China and India might create an entirely new economic paradigm with these two countries now vying for global dominance perhaps similarly to how the US and the Soviet Union were struggling against each other all throughout the 20th century.
 H/T: Statista.
H/T: Statista.
Read next: Gallup Conducted Its Monthly Study On American Fears And Concerns For The Month Of July
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
China’s share of the world’s GDP when adjusted for PPP was around 8.1% in 2002, but 20 years later we are seeing a completely different picture. China now accounts for 18.8% of the world’s GDP, and both the US and the EU have seen a decrease of 4 and 5.1 percentage points respectively. The US now has a 15.8% share of the global economy, and the EU has just 14.8% which is a far cry from the unassailable dominance that they showed in decades prior.
The global recession will likely make the gap wider because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up bringing the economies of the US and the EU to a halt. China, on the other hand, is projected to continue showing modest growth rates which will allow it to cement its place as the world’s foremost super power.
China is not the only country that has been rising rapidly either. India managed to climb its way to an over 7% share of the world’s GDP, and while it is still short of China its growth rate will allow it to get closer to the US and the EU in terms of global GDP share.
The twin powers of China and India might create an entirely new economic paradigm with these two countries now vying for global dominance perhaps similarly to how the US and the Soviet Union were struggling against each other all throughout the 20th century.
 H/T: Statista.
H/T: Statista.Read next: Gallup Conducted Its Monthly Study On American Fears And Concerns For The Month Of July
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
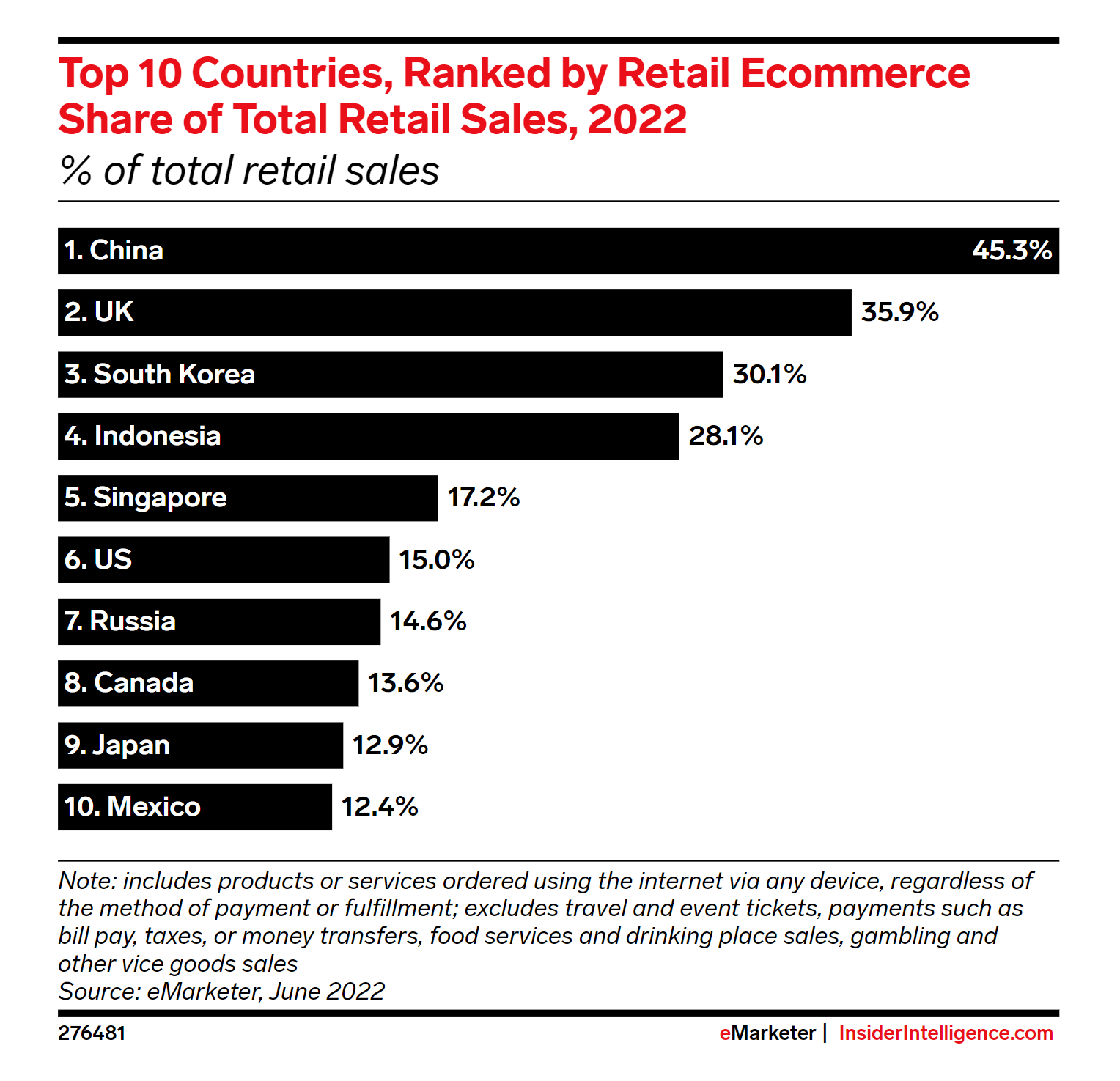
Let's Take A Look At How Much E-commerce Is Affecting The Economies Of Different Countries
With the e-commerce business being so in fashion nowadays, a breakdown was also on its way. As we know, China is the biggest contributor to e-commerce services with roughly 45.3% of online sales occurring this year on different platforms. The UK is next to China in its second spot, with over 35.9% of online sales happening this year and the third spot is South Korea, where 30.1% of online retail sales happened this year via e-commerce. The other countries following them are Indonesia, Singapore, the US, Russia, Canada, Japan, and Mexico respectively.
E-commerce is the most emerging source of income right now in the world right now and every country is breaking their sweat into making it a larger part of their economies. And right now China is exceeding every country in being the biggest part of e-commerce. China is the top country that has the largest e-commerce sales for retails this year. With over $2.879 trillion this year, it has become the top country for e-commerce services. China is the biggest e-commerce market that is led by different groups. The well-known being Ali Baba and the other companies associated with it. China is getting bigger and bigger in online marketing and leaving all these countries behind.
The next in the race is the United Kingdom(England, Scotland, Ireland, and Wales). This year the US is in the race to earn more than a trillion dollars with its e-commerce marketing getting higher and higher. Its sales can reach up to $1.050 trillion this year, all because of the effort the country is putting to make its online economy grow. Most of the reports are saying that e-commerce is going to be up to 15% of the online retail sales of the United States economy. USA buyers are slowly adapting to buying things online as it was not a much-done activity before covid-19. That being said, covid-19 is one of the big reasons for shoppers to buy most things online. The future of e-commerce is bright and it is going to stay here for infinity.
H/T: eMarketer
Read next: Many mobile app gaming genres have started facing a decline in their app downloads in the first half of 2022
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
E-commerce is the most emerging source of income right now in the world right now and every country is breaking their sweat into making it a larger part of their economies. And right now China is exceeding every country in being the biggest part of e-commerce. China is the top country that has the largest e-commerce sales for retails this year. With over $2.879 trillion this year, it has become the top country for e-commerce services. China is the biggest e-commerce market that is led by different groups. The well-known being Ali Baba and the other companies associated with it. China is getting bigger and bigger in online marketing and leaving all these countries behind.
The next in the race is the United Kingdom(England, Scotland, Ireland, and Wales). This year the US is in the race to earn more than a trillion dollars with its e-commerce marketing getting higher and higher. Its sales can reach up to $1.050 trillion this year, all because of the effort the country is putting to make its online economy grow. Most of the reports are saying that e-commerce is going to be up to 15% of the online retail sales of the United States economy. USA buyers are slowly adapting to buying things online as it was not a much-done activity before covid-19. That being said, covid-19 is one of the big reasons for shoppers to buy most things online. The future of e-commerce is bright and it is going to stay here for infinity.
H/T: eMarketer
Read next: Many mobile app gaming genres have started facing a decline in their app downloads in the first half of 2022
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Twitter Finally Fixes Security Vulnerability That Exposed User Data Of Over 5 Million Accounts
The statement 'better late than never' surely applies to Twitter’s behavior as the company was finally seen finding a solution to a security vulnerability issue that is the latest to strike the firm in recent years.
Twitter revealed how it got to the bottom of a bug that was exposing user data belonging to nearly 5.4 million accounts on the app. A number of threat actors managed to bypass the app’s security checkpoints and compile sensitive data.
This information was then being offered for sale at a top cybercrime forum, the company’s new report revealed.
More details proved how the security threat enabled any individual to break in by simply adding relevant information pertaining to user accounts. Hence, that could be possible with the simple addition of an email ID or perhaps a phone number of the known user.
Then, the details were checked if they were indeed linked to an account on the app and if yes, the technique went about exposing the user identities of countless accounts.
We came to know of all this on Friday when Twitter revealed the shocking news through a blog post that shed light on the matter.
The statement mentioned that any user who submitted their email IDs or number to the app’s systems would be liable for having their identities exposed as the Twitter system was built in a way that would allow this.
Therefore, it warned against such practices and told people to be aware, making sure they were in the loop of what was going on.
Interestingly, the company revealed how they had actually gone about fixing the bug linked to the same problem in January of this year. But six months down the line, the fact that we’re still speaking about this means that things were either not done properly or the bug really managed to reappear.
The bug’s details and its entrance into Twitter’s codebase were outlined by one researcher who was awarded $6000 for making the discovery. After that, a report was generated that spoke in detail about how the threat was a serious one to all account holders on the app.
Therefore, private account holders were the most at risk and their information would potentially be used to make an entire database.
We can best recall this incident to be similar to that seen during the later part of 2019, where one security analyst was able to align phone numbers of almost 17 million users and link them to respective accounts on the app.
But in this case, we certainly feel the warning by the researcher had come a tad bit too late as that six-month period was enough for the bug to extract user account details of more than 5 million users which is actually a lot of information.
Twitter revealed recently how it only came to know about all of this type of exploitation thanks to a press release that was released last month.
It spoke about Twitter account holders’ data being up for sale on an online forum and that really raised the alarm for many as the site was a renowned cybercrime destination.
Common people whose data was sold included the likes of celebs and firms as well as other sought-after personalities from the world of gaming and social media today.
Twitter says they are now busy informing all of their relevant account holders that may have been affected by the bug.
Clearly, this is one massive incident that has really struck the app greatly in recent times with many users shocked at how easily the bug managed to defeat the security protocols in place.
Read next: Twitter Lawyers Hit Back At Elon Musk Saying His Tool Once Classified Him As A Bot
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
Twitter revealed how it got to the bottom of a bug that was exposing user data belonging to nearly 5.4 million accounts on the app. A number of threat actors managed to bypass the app’s security checkpoints and compile sensitive data.
This information was then being offered for sale at a top cybercrime forum, the company’s new report revealed.
More details proved how the security threat enabled any individual to break in by simply adding relevant information pertaining to user accounts. Hence, that could be possible with the simple addition of an email ID or perhaps a phone number of the known user.
Then, the details were checked if they were indeed linked to an account on the app and if yes, the technique went about exposing the user identities of countless accounts.
We came to know of all this on Friday when Twitter revealed the shocking news through a blog post that shed light on the matter.
The statement mentioned that any user who submitted their email IDs or number to the app’s systems would be liable for having their identities exposed as the Twitter system was built in a way that would allow this.
Therefore, it warned against such practices and told people to be aware, making sure they were in the loop of what was going on.
Interestingly, the company revealed how they had actually gone about fixing the bug linked to the same problem in January of this year. But six months down the line, the fact that we’re still speaking about this means that things were either not done properly or the bug really managed to reappear.
The bug’s details and its entrance into Twitter’s codebase were outlined by one researcher who was awarded $6000 for making the discovery. After that, a report was generated that spoke in detail about how the threat was a serious one to all account holders on the app.
Therefore, private account holders were the most at risk and their information would potentially be used to make an entire database.
We can best recall this incident to be similar to that seen during the later part of 2019, where one security analyst was able to align phone numbers of almost 17 million users and link them to respective accounts on the app.
But in this case, we certainly feel the warning by the researcher had come a tad bit too late as that six-month period was enough for the bug to extract user account details of more than 5 million users which is actually a lot of information.
Twitter revealed recently how it only came to know about all of this type of exploitation thanks to a press release that was released last month.
It spoke about Twitter account holders’ data being up for sale on an online forum and that really raised the alarm for many as the site was a renowned cybercrime destination.
Common people whose data was sold included the likes of celebs and firms as well as other sought-after personalities from the world of gaming and social media today.
Twitter says they are now busy informing all of their relevant account holders that may have been affected by the bug.
Clearly, this is one massive incident that has really struck the app greatly in recent times with many users shocked at how easily the bug managed to defeat the security protocols in place.
Read next: Twitter Lawyers Hit Back At Elon Musk Saying His Tool Once Classified Him As A Bot
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
Twitter Lawyers Hit Back At Elon Musk Saying His Tool Once Classified Him As A Bot
We all know by now that Twitter is not happy with billionaire Elon Musk for failing to fulfill his promises and acquire the company for $44 billion.
Therefore, they’ve dragged the Tesla and SpaceX CEO to court with a lawsuit holding him accountable for his wrongful actions. But now, more details are surfacing regarding the legal proceedings including an in-depth analysis of what tools Musk was using to back up his accusations.
Let’s do a quick recap before we proceed to make sure everyone’s on the same page. Musk continues to allege Twitter lied about the actual number of bot accounts, calling them out for undercounting and painting a picture that was far from reality.
Twitter denied the accusations and even provided Musk with details on how the figures were reached and any other relevant information that would be needed to help reassure him that what they were doing was right.
Again, that wasn’t good enough for Musk and his legal team who continually stand by their claims and now want to exit the deal.
But Twitter’s lawyers are hitting back at the world’s richest man by finding fault in the tools that were used to calculate the company’s spam and bot accounts. According to them, the tool that Musk was using had even classified his account as a bot so there shouldn’t be much reliance on that factor.
Thanks to a recent article published by the Washington Post yesterday, Twitter shed light on the tool that was linked to an internet service offered publicly called Botometer.
This was used to determine an estimated number of fake profiles seen on the app, which the firm finds beyond amusing.
Putting more emphasis on the actual working of the Botometer, we know that this method finds fake accounts through a means that’s very different from the method used by the platform Twitter.
Digging deep down into its mechanism of action through the website from which its creators had developed it, the lawyers found that the tool uses machine learning for its algorithm to try and get a score to see which profiles are more likely to be a bot than others. And this is in regard to the activity seen on the app.
Musk has continually accused the firm of arguing and misleading him and his team and investors regarding spam accounts and bots. They feel as if they’ve been misled and not given an accurate picture of the firm’s prospects.
According to the Tesla and SpaceX CEO, the platform actually also failed to outline the right number of users on the app, which it feels has been exaggerated by nearly 65 million than what the reality truly is.
It also mentioned how about 16 million viewers visit the app on a daily basis and see the ads projected on Twitter.
In addition, Musk’s lawsuit adds how this was a strategy from day one used by the company to distract potential investors from the truth and secure a deal it feels is based on nothing but lies.
The court battle will begin in October when both sides will put their arguments forward and we think it’s going to be exciting to see who comes out on top.
Read next: Twitter Rolls Out A Location Spotlight Feature That Helps Users Find Businesses Easily
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
Therefore, they’ve dragged the Tesla and SpaceX CEO to court with a lawsuit holding him accountable for his wrongful actions. But now, more details are surfacing regarding the legal proceedings including an in-depth analysis of what tools Musk was using to back up his accusations.
Let’s do a quick recap before we proceed to make sure everyone’s on the same page. Musk continues to allege Twitter lied about the actual number of bot accounts, calling them out for undercounting and painting a picture that was far from reality.
Twitter denied the accusations and even provided Musk with details on how the figures were reached and any other relevant information that would be needed to help reassure him that what they were doing was right.
Again, that wasn’t good enough for Musk and his legal team who continually stand by their claims and now want to exit the deal.
But Twitter’s lawyers are hitting back at the world’s richest man by finding fault in the tools that were used to calculate the company’s spam and bot accounts. According to them, the tool that Musk was using had even classified his account as a bot so there shouldn’t be much reliance on that factor.
Thanks to a recent article published by the Washington Post yesterday, Twitter shed light on the tool that was linked to an internet service offered publicly called Botometer.
This was used to determine an estimated number of fake profiles seen on the app, which the firm finds beyond amusing.
Putting more emphasis on the actual working of the Botometer, we know that this method finds fake accounts through a means that’s very different from the method used by the platform Twitter.
Digging deep down into its mechanism of action through the website from which its creators had developed it, the lawyers found that the tool uses machine learning for its algorithm to try and get a score to see which profiles are more likely to be a bot than others. And this is in regard to the activity seen on the app.
Musk has continually accused the firm of arguing and misleading him and his team and investors regarding spam accounts and bots. They feel as if they’ve been misled and not given an accurate picture of the firm’s prospects.
According to the Tesla and SpaceX CEO, the platform actually also failed to outline the right number of users on the app, which it feels has been exaggerated by nearly 65 million than what the reality truly is.
It also mentioned how about 16 million viewers visit the app on a daily basis and see the ads projected on Twitter.
In addition, Musk’s lawsuit adds how this was a strategy from day one used by the company to distract potential investors from the truth and secure a deal it feels is based on nothing but lies.
The court battle will begin in October when both sides will put their arguments forward and we think it’s going to be exciting to see who comes out on top.
Read next: Twitter Rolls Out A Location Spotlight Feature That Helps Users Find Businesses Easily
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
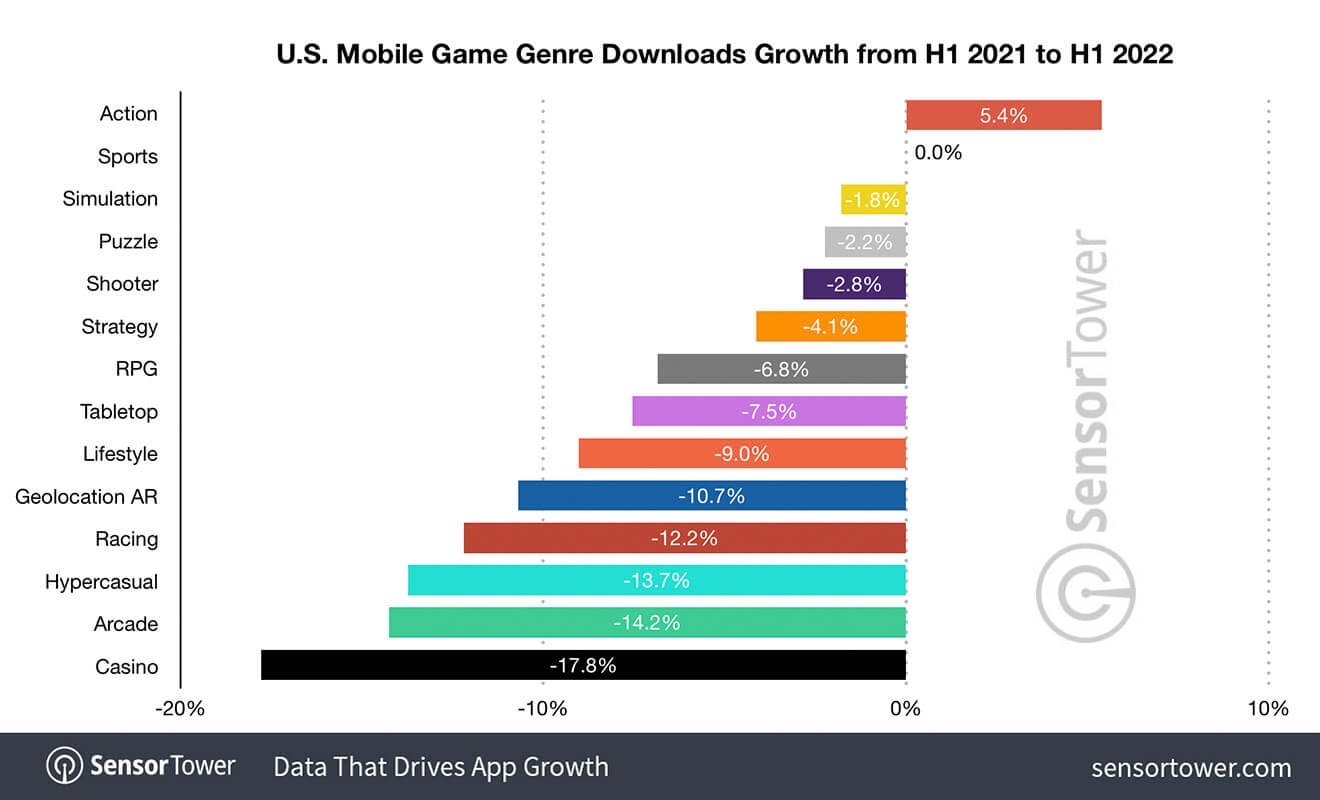
Many mobile app gaming genres have started facing a decline in their app downloads in the first half of 2022
Games of all types have always been a family favorite. Somewhere between playing board games with siblings and cousins at grandma's house to playing them online with friends, we all grew up. Ever since board games like monopoly were invented, games have always been a great source of entertainment and fun for the family, however, our topic for today is how some types of mobile games both online and offline through different genres have been seeing a decline in their revenue.
In the first half of 2022, according to data from SensorTower, most mobile apps spread across many genres have seen a huge downfall in in-app spending of players and the downloads of their app.
In the first half of the year, it was revealed that the gaming market fell by 9.6 percent after comparing it year by year and resulting in an end value of 11.4 billion dollars.
All of this data was collected using Sensor Tower's Game Taxonomy and Game Intelligence features. Now what these two features do is not very interesting but very useful instead. These two features separate and then sort games into their specific genres and sub-genres that they belong to. Then that data is used by expert analysts to check trends.
The fastest rising genre of this half of the year was Arcade with the player spending amount shooting up 14.8 years over year to almost over $176 million. The largest sub-genre of Arcade was Idler which generated almost 88 million dollars going up 35.3 percent when compared year by year.
The second most growing genre of mobile games was Tabletop, which saw an increase of approximately 1 percent and came close to total revenue of 388.8 million dollars.
All other mobile game genres except these two saw a huge decrease in either their player spending or the downloads of their apps and sometimes apps faced both at the same time.
Read next: Children between the ages of 10-12 are spending the most on video games, survey reveals
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
In the first half of 2022, according to data from SensorTower, most mobile apps spread across many genres have seen a huge downfall in in-app spending of players and the downloads of their app.
In the first half of the year, it was revealed that the gaming market fell by 9.6 percent after comparing it year by year and resulting in an end value of 11.4 billion dollars.
All of this data was collected using Sensor Tower's Game Taxonomy and Game Intelligence features. Now what these two features do is not very interesting but very useful instead. These two features separate and then sort games into their specific genres and sub-genres that they belong to. Then that data is used by expert analysts to check trends.
The fastest rising genre of this half of the year was Arcade with the player spending amount shooting up 14.8 years over year to almost over $176 million. The largest sub-genre of Arcade was Idler which generated almost 88 million dollars going up 35.3 percent when compared year by year.
The second most growing genre of mobile games was Tabletop, which saw an increase of approximately 1 percent and came close to total revenue of 388.8 million dollars.
All other mobile game genres except these two saw a huge decrease in either their player spending or the downloads of their apps and sometimes apps faced both at the same time.
Read next: Children between the ages of 10-12 are spending the most on video games, survey reveals
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
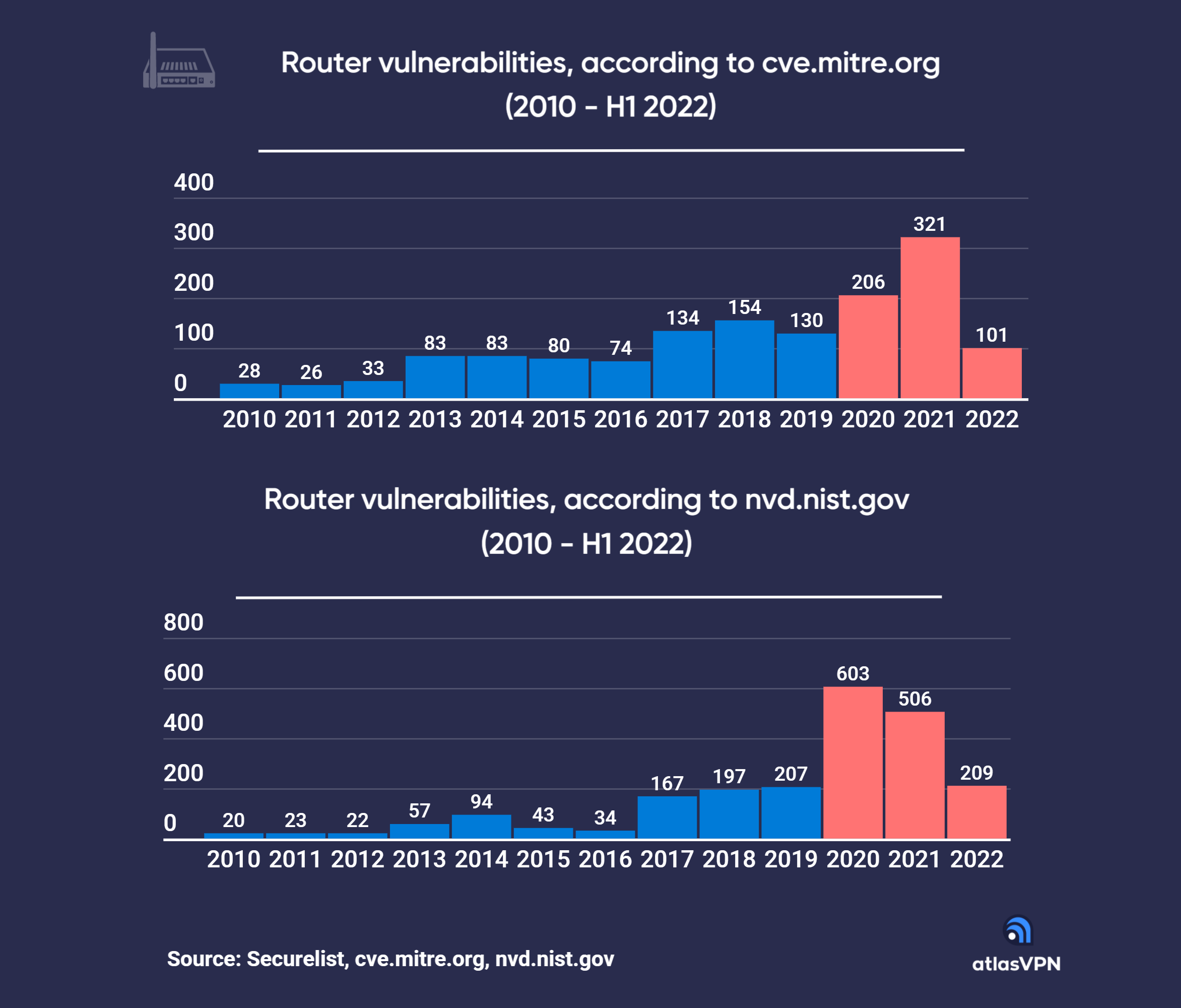
Altas VPN Reveals That 2020 Was The Worst Year For Router-Oriented Cybersecurity Threats
A study by Atlas VPN reveals that a record number of routers with cybersecurity vulnerabilities were identified in the past few years.
My writing about cybersecurity threats has almost become a chore at this point; there are just so many vulnerabilities out there, and many can be dealt with if everyone just paid a tad bit more attention than they currently do. The Google Play store, for example, keeps letting in malware disguised as apps; unaware individuals download them, even if someone familiar with the internet needs only to take a single glance at the copy-paste reviews and the terrible grammar to know that something’s wrong. However, Google refuses to put in the necessary legwork and people suffer. Cases of cybersecurity breaches just seem to be increasing at an alarmingly exponential rate, with incremental damages due to more and more personal information being stored online. People have their literal social security details available on their phones, and yet refuse to download password managers or go through the minute annoyance of two-factor authentication. At some point, it’s just shooting oneself in the foot to not invest in security options. Then again, the average individual should be blamed less for falling into security traps when we can hold the corporations behind building such fragile equipment accountable.
To make matters worse, cybercriminals seem to be exceeding their chosen career paths with every coming day. Lockdown probably helped out a ton, since it forced everyone to shift towards online work and gave such seedy individuals more time to find new loopholes in pre-existing systems. Android isn’t infallible, Apple isn’t infallible, and routers certainly aren’t. The Atlas VPN study utilized data from Kaspersky, which itself relied on many government sources for information. The figures we’re looking at may vary in the specifics but paint the same general picture. That is to say that since 2010, there has been a massive uptick in router vulnerabilities being exposed by cyber criminals.
In all data compilations, 2017 seems to be a real tipping point for cybersecurity threats, with a second, much more significant uptick being noted in 2020. While I can’t exactly speak for the former, the latter makes sense for reasons that I’ve highlighted above. All sources agree that 2020 was the worst year in terms of router-oriented cybersecurity threats (and I’d wager cybersecurity threats in general as well). However, there is some good news: 2022 seems to be much, much better than 2020, even if conditions are much worse than in preceding years.
Read next: Apple Plans To Wipe Out Passwords Forever As Company Puts Its Passkeys Into The Spotlight
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
My writing about cybersecurity threats has almost become a chore at this point; there are just so many vulnerabilities out there, and many can be dealt with if everyone just paid a tad bit more attention than they currently do. The Google Play store, for example, keeps letting in malware disguised as apps; unaware individuals download them, even if someone familiar with the internet needs only to take a single glance at the copy-paste reviews and the terrible grammar to know that something’s wrong. However, Google refuses to put in the necessary legwork and people suffer. Cases of cybersecurity breaches just seem to be increasing at an alarmingly exponential rate, with incremental damages due to more and more personal information being stored online. People have their literal social security details available on their phones, and yet refuse to download password managers or go through the minute annoyance of two-factor authentication. At some point, it’s just shooting oneself in the foot to not invest in security options. Then again, the average individual should be blamed less for falling into security traps when we can hold the corporations behind building such fragile equipment accountable.
To make matters worse, cybercriminals seem to be exceeding their chosen career paths with every coming day. Lockdown probably helped out a ton, since it forced everyone to shift towards online work and gave such seedy individuals more time to find new loopholes in pre-existing systems. Android isn’t infallible, Apple isn’t infallible, and routers certainly aren’t. The Atlas VPN study utilized data from Kaspersky, which itself relied on many government sources for information. The figures we’re looking at may vary in the specifics but paint the same general picture. That is to say that since 2010, there has been a massive uptick in router vulnerabilities being exposed by cyber criminals.
In all data compilations, 2017 seems to be a real tipping point for cybersecurity threats, with a second, much more significant uptick being noted in 2020. While I can’t exactly speak for the former, the latter makes sense for reasons that I’ve highlighted above. All sources agree that 2020 was the worst year in terms of router-oriented cybersecurity threats (and I’d wager cybersecurity threats in general as well). However, there is some good news: 2022 seems to be much, much better than 2020, even if conditions are much worse than in preceding years.
Read next: Apple Plans To Wipe Out Passwords Forever As Company Puts Its Passkeys Into The Spotlight
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)