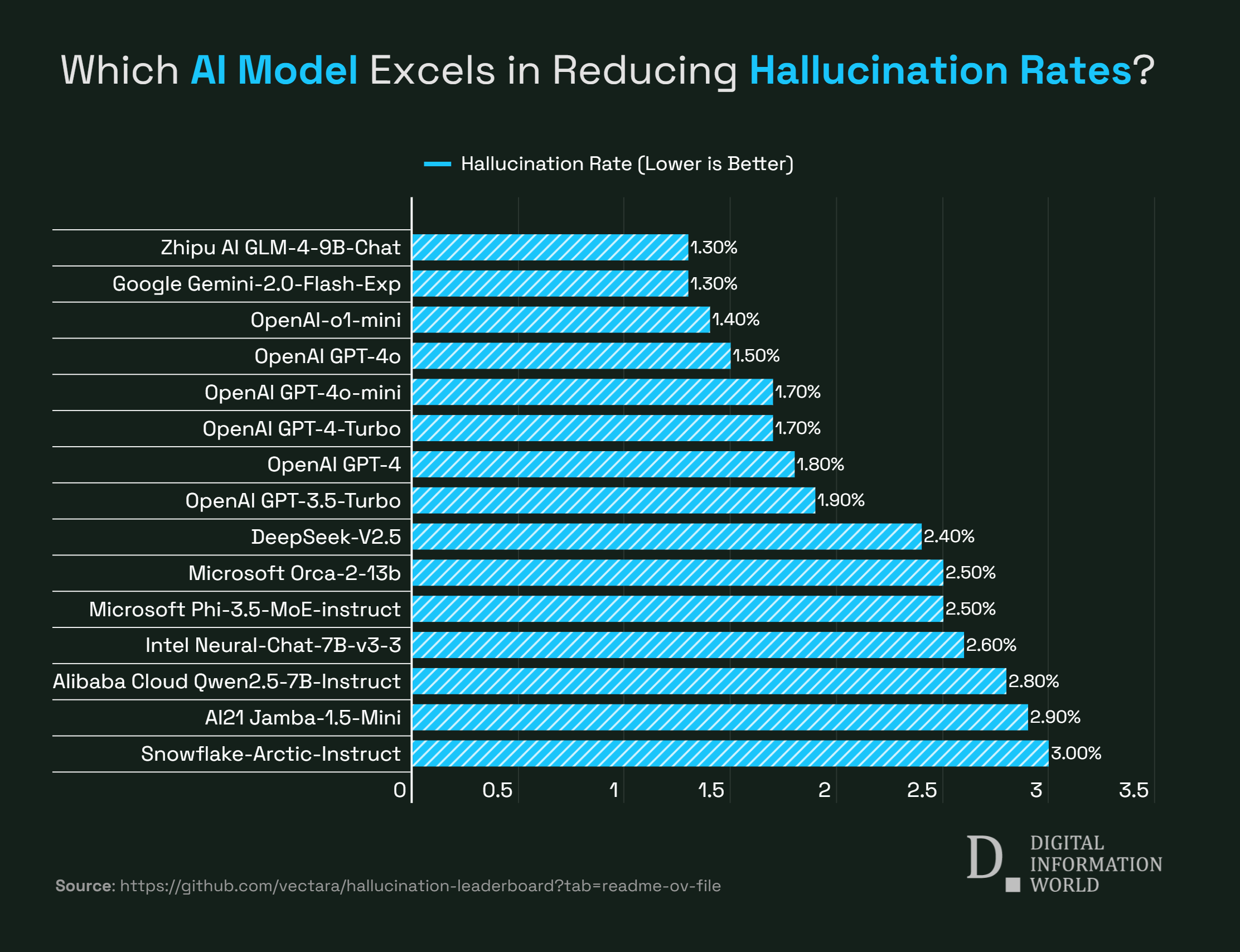
The top third LLM with least hallucination levels is OpenAI’s o1-mini with 1.4% hallucination rate. With a hallucination rate of 1.5%, GPT-4o is the fourth model with least hallucination. GPT-4o-mini and GPT-4-Turbo have hallucination rates of 1.7%. It was observed that more specialized and smaller models have the lowest hallucination rates. OpenAI’s GPT-4 has a hallucination rate of 1.8%, while GPT-3.5-Turbo has a hallucination rate of 1.9%.
It is important for AI systems to show low levels of hallucination for them to work properly, especially in high-stake applications in healthcare, finance and law. Smaller models are slowly reducing hallucinations in their AI models, with Mistral 8×7B models reducing hallucinations in their AI generated texts.
| Model | Hallucination Rate | Factual Consistency Rate | Answer Rate | Average Summary Length (Words) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhipu AI GLM-4-9B-Chat | 1.3 % | 98.7 % | 100.0 % | 58.1 |
| Google Gemini-2.0-Flash-Exp | 1.3 % | 98.7 % | 99.9 % | 60 |
| OpenAI-o1-mini | 1.4 % | 98.6 % | 100.0 % | 78.3 |
| GPT-4o | 1.5 % | 98.5 % | 100.0 % | 77.8 |
| GPT-4o-mini | 1.7 % | 98.3 % | 100.0 % | 76.3 |
| GPT-4-Turbo | 1.7 % | 98.3 % | 100.0 % | 86.2 |
| GPT-4 | 1.8 % | 98.2 % | 100.0 % | 81.1 |
| GPT-3.5-Turbo | 1.9 % | 98.1 % | 99.6 % | 84.1 |
| DeepSeek-V2.5 | 2.4 % | 97.6 % | 100.0 % | 83.2 |
| Microsoft Orca-2-13b | 2.5 % | 97.5 % | 100.0 % | 66.2 |
| Microsoft Phi-3.5-MoE-instruct | 2.5 % | 97.5 % | 96.3 % | 69.7 |
| Intel Neural-Chat-7B-v3-3 | 2.6 % | 97.4 % | 100.0 % | 60.7 |
| Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct | 2.8 % | 97.2 % | 100.0 % | 71 |
| AI21 Jamba-1.5-Mini | 2.9 % | 97.1 % | 95.6 % | 74.5 |
| Snowflake-Arctic-Instruct | 3.0 % | 97.0 % | 100.0 % | 68.7 |
| Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct | 3.0 % | 97.0 % | 100.0 % | 67.9 |
| Microsoft Phi-3-mini-128k-instruct | 3.1 % | 96.9 % | 100.0 % | 60.1 |
| OpenAI-o1-preview | 3.3 % | 96.7 % | 100.0 % | 119.3 |
| Google Gemini-1.5-Flash-002 | 3.4 % | 96.6 % | 99.9 % | 59.4 |
| 01-AI Yi-1.5-34B-Chat | 3.7 % | 96.3 % | 100.0 % | 83.7 |
| Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct | 3.9 % | 96.1 % | 99.6 % | 85.7 |
| Microsoft Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct | 4.0 % | 96.0 % | 100.0 % | 86.8 |
| Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct | 4.0 % | 96.0 % | 100.0 % | 85.3 |
| Microsoft Phi-3.5-mini-instruct | 4.1 % | 95.9 % | 100.0 % | 75 |
| Mistral-Large2 | 4.1 % | 95.9 % | 100.0 % | 77.4 |
| Llama-3-70B-Chat-hf | 4.1 % | 95.9 % | 99.2 % | 68.5 |
| Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct | 4.2 % | 95.8 % | 100.0 % | 73.9 |
| Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct | 4.2 % | 95.8 % | 100.0 % | 74.8 |
| Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct | 4.3 % | 95.7 % | 100.0 % | 80 |
| Llama-3.2-90B-Vision-Instruct | 4.3 % | 95.7 % | 100.0 % | 79.8 |
| XAI Grok | 4.6 % | 95.4 % | 100.0 % | 91 |
| Anthropic Claude-3-5-sonnet | 4.6 % | 95.4 % | 100.0 % | 95.9 |
| Qwen2-72B-Instruct | 4.7 % | 95.3 % | 100.0 % | 100.1 |
| Mixtral-8x22B-Instruct-v0.1 | 4.7 % | 95.3 % | 99.9 % | 92 |
| Anthropic Claude-3-5-haiku | 4.9 % | 95.1 % | 100.0 % | 92.9 |
| 01-AI Yi-1.5-9B-Chat | 4.9 % | 95.1 % | 100.0 % | 85.7 |
| Cohere Command-R | 4.9 % | 95.1 % | 100.0 % | 68.7 |
| Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct | 5.0 % | 95.0 % | 100.0 % | 79.6 |
| Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct | 5.4 % | 94.6 % | 100.0 % | 71 |
| Cohere Command-R-Plus | 5.4 % | 94.6 % | 100.0 % | 68.4 |
| Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct | 5.5 % | 94.5 % | 100.0 % | 67.3 |
| Llama-2-70B-Chat-hf | 5.9 % | 94.1 % | 99.9 % | 84.9 |
| IBM Granite-3.0-8B-Instruct | 6.5 % | 93.5 % | 100.0 % | 74.2 |
| Google Gemini-1.5-Pro-002 | 6.6 % | 93.7 % | 99.9 % | 62 |
| Google Gemini-1.5-Flash | 6.6 % | 93.4 % | 99.9 % | 63.3 |
| Microsoft phi-2 | 6.7 % | 93.3 % | 91.5 % | 80.8 |
| Google Gemma-2-2B-it | 7.0 % | 93.0 % | 100.0 % | 62.2 |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct | 7.0 % | 93.0 % | 100.0 % | 70.4 |
| Llama-3-8B-Chat-hf | 7.4 % | 92.6 % | 99.8 % | 79.7 |
| Google Gemini-Pro | 7.7 % | 92.3 % | 98.4 % | 89.5 |
| 01-AI Yi-1.5-6B-Chat | 7.9 % | 92.1 % | 100.0 % | 98.9 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 7.9 % | 92.1 % | 100.0 % | 72.2 |
| databricks dbrx-instruct | 8.3 % | 91.7 % | 100.0 % | 85.9 |
| Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct | 8.3 % | 91.7 % | 100.0 % | 81.8 |
| Cohere Aya Expanse 32B | 8.5 % | 91.5 % | 99.9 % | 81.9 |
| IBM Granite-3.0-2B-Instruct | 8.8 % | 91.2 % | 100.0 % | 81.6 |
| Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 | 9.5 % | 90.5 % | 100.0 % | 98.4 |
| Google Gemini-1.5-Pro | 9.1 % | 90.9 % | 99.8 % | 61.6 |
| Anthropic Claude-3-opus | 10.1 % | 89.9 % | 95.5 % | 92.1 |
| Google Gemma-2-9B-it | 10.1 % | 89.9 % | 100.0 % | 70.2 |
| Llama-2-13B-Chat-hf | 10.5 % | 89.5 % | 99.8 % | 82.1 |
| AllenAI-OLMo-2-13B-Instruct | 10.8 % | 89.2 % | 100.0 % | 82 |
| AllenAI-OLMo-2-7B-Instruct | 11.1 % | 88.9 % | 100.0 % | 112.6 |
| Mistral-Nemo-Instruct | 11.2 % | 88.8 % | 100.0 % | 69.9 |
| Llama-2-7B-Chat-hf | 11.3 % | 88.7 % | 99.6 % | 119.9 |
| Microsoft WizardLM-2-8x22B | 11.7 % | 88.3 % | 99.9 % | 140.8 |
| Cohere Aya Expanse 8B | 12.2 % | 87.8 % | 99.9 % | 83.9 |
| Amazon Titan-Express | 13.5 % | 86.5 % | 99.5 % | 98.4 |
| Google PaLM-2 | 14.1 % | 85.9 % | 99.8 % | 86.6 |
| Google Gemma-7B-it | 14.8 % | 85.2 % | 100.0 % | 113 |
| Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct | 15.8 % | 84.2 % | 100.0 % | 70.7 |
| Qwen-QwQ-32B-Preview | 16.1 % | 83.9 % | 100.0 % | 201.5 |
| Anthropic Claude-3-sonnet | 16.3 % | 83.7 % | 100.0 % | 108.5 |
| Google Gemma-1.1-7B-it | 17.0 % | 83.0 % | 100.0 % | 64.3 |
| Anthropic Claude-2 | 17.4 % | 82.6 % | 99.3 % | 87.5 |
| Google Flan-T5-large | 18.3 % | 81.7 % | 99.3 % | 20.9 |
| Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1 | 20.1 % | 79.9 % | 99.9 % | 90.7 |
| Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 20.7 % | 79.3 % | 100.0 % | 71.5 |
| Apple OpenELM-3B-Instruct | 24.8 % | 75.2 % | 99.3 % | 47.2 |
| Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct | 25.2 % | 74.8 % | 100.0 % | 72.6 |
| Google Gemma-1.1-2B-it | 27.8 % | 72.2 % | 100.0 % | 66.8 |
| TII falcon-7B-instruct | 29.9 % | 70.1 % | 90.0 % | 75.5 |
Read next:
• WhatsApp Beta Tests Personalized AI Chatbots – A Sneak Peek at What’s Coming!
• Researchers Explore How Personality and Integrity Shape Trust in AI Technology
• China’s AI Chatbot Market Sees ByteDance’s Doubao Leading Through Innovation and Accessibility
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World