Google’s Perspectives feature gives users the ability to see opinions from people across the political and social spectrum, but where exactly are these insights coming from? Data gathered by NewzDash and John Shehata has revealed that YouTube, Twitter and Reddit contribute the largest quantity of perspectives of all.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that 33.6% of the data comes from Twitter alone, making it the single most significant contributer. It’s followed by YouTube with 23.3%, and Reddit with 16.3%. It bears mentioning that no other platform out there was able to crack double figures. TikTok was in fourth place with 3.6%, with Substack rounding off the top five with 2.6%.
As for where Perspectives end up showing up, they appeared after Top Stories around 85.4% of the time. 15.5% of queries pertaining to news pulled Perspectives as well. The NBA’s Twitter page is surprisingly important in this context, reaching a visibility well over 2%. No other single page or profile crossed the 2% threshold with all things having been considered and taken into account.
When you look at the News section on the Google SERP, sports is clearly the top ranking section. That makes the NBA’s prominence understandable, especially considering that the second top ranked section was that of entertainment.
Google is doubling down on Perspectives by giving it an increased presence in the mobile SERP. The dominance of Twitter might be alarming because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up showing misinformation which is becoming increasingly commonplace on that platform after Elon Musk took control.
Finding a way to capitalize on this new addition to the SERP might be crucial for SEO professionals down the line. It remains to be seen whether or not it will have all that positive of an impact on the user experience. Whatever the case may be, Google’s changes are altering the SERP in ways that are difficult to predict, and this might change the landscape of social media as well as search engines in general moving forward.
Chart: NewzDash / John Shehata via X
Read next: World Economic Forum Report Sounds Alarm on AI-Powered Misinformation as Top Short-Term Global Threat
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
"Mr Branding" is a blog based on RSS for everything related to website branding and website design, it collects its posts from many sites in order to facilitate the updating to the latest technology.
To suggest any source, please contact me: Taha.baba@consultant.com
Thursday, January 11, 2024
World Economic Forum Report Sounds Alarm on AI-Powered Misinformation as Top Short-Term Global Threat
The rise of AI has brought many advantages as well as disadvantages to the table. A prime example of the latter is the manner in which it aided malicious actors in the creation of misinformation. According to a report released by the World Economic Forum, this AI powered misinformation is arguably the most significant threat that the world is facing in the short term.
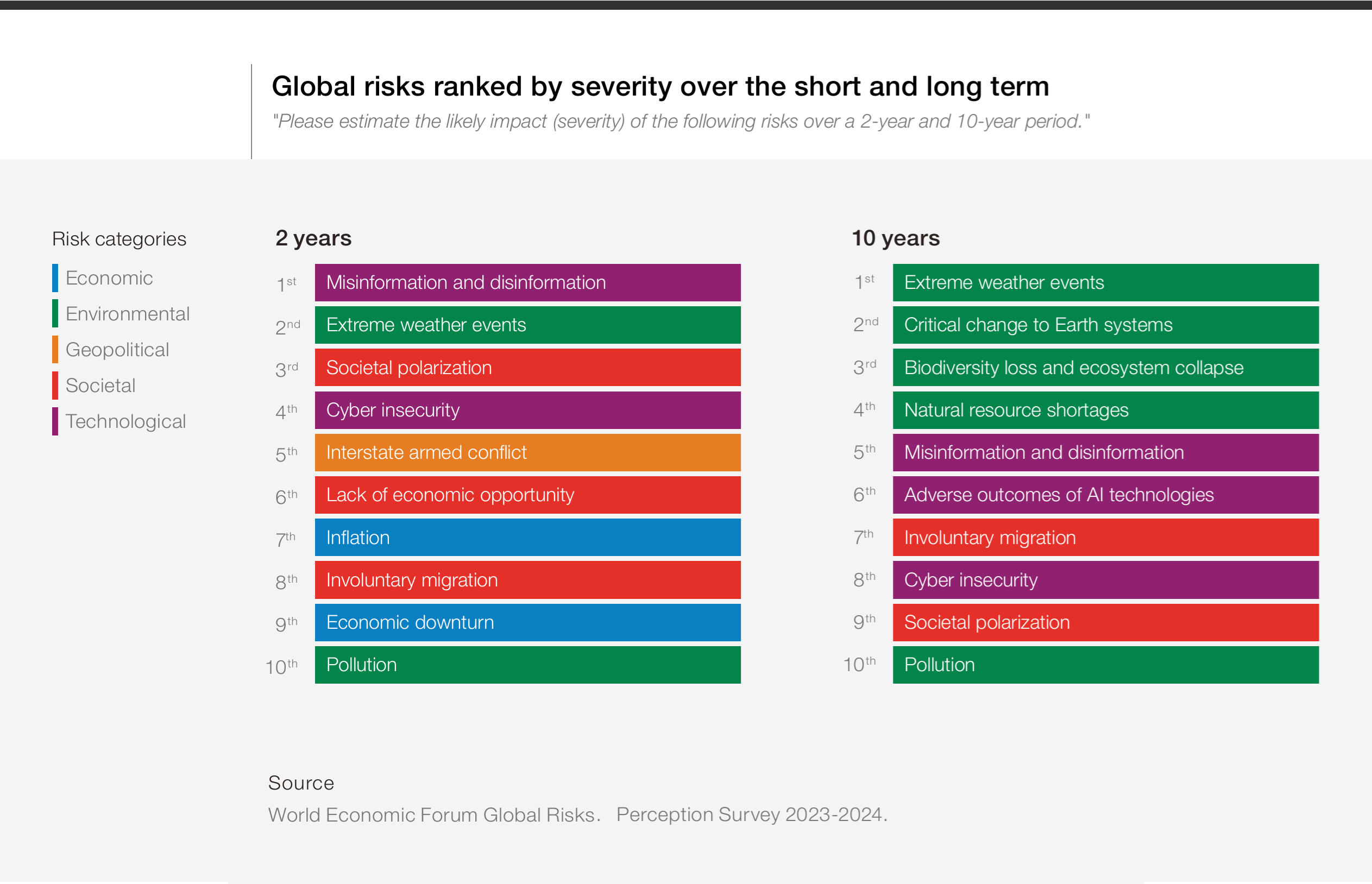
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that this Global Risks Report has highlighted environmental concerns as the biggest long term threats. In spite of the fact that this is the case, misinformation is the most significant risk over the next two years.
This data comes from a survey of 1,500 decision makers, policy experts and industry titans, and they all seem to agree that misinformation as well as disinformation will be major concerns with all things having been considered and taken into account. Extreme weather events came in second, followed by an increase in social polarization.
As for risks that will become apparent over a ten year period, extreme weather events topped the list because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up bringing society to a standstill. The top four long term issues were all related to the environment. Extreme weather events were followed by critical changes to global ecosystems, a collapse in biodiversity as well as shortages in essential resources procured from the natural environment.
2024 will be a litmus test for the Age of AI, with a number of major elections taking place. The US will decide its next president, and there’s a high level of likelihood that Donald Trump may very well return to the White House. The UK, India, Pakistan and Indonesia are also heading to the polls, and AI might make it harder to separate truth from falsehood than might have been the case otherwise. It will be interesting to see where things go from here on out, since the results of these elections will have long term consequences.
Image: WEF
Read next: Microsoft is Making Batteries With AI, Here’s What You Need to Know
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that this Global Risks Report has highlighted environmental concerns as the biggest long term threats. In spite of the fact that this is the case, misinformation is the most significant risk over the next two years.
This data comes from a survey of 1,500 decision makers, policy experts and industry titans, and they all seem to agree that misinformation as well as disinformation will be major concerns with all things having been considered and taken into account. Extreme weather events came in second, followed by an increase in social polarization.
As for risks that will become apparent over a ten year period, extreme weather events topped the list because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up bringing society to a standstill. The top four long term issues were all related to the environment. Extreme weather events were followed by critical changes to global ecosystems, a collapse in biodiversity as well as shortages in essential resources procured from the natural environment.
2024 will be a litmus test for the Age of AI, with a number of major elections taking place. The US will decide its next president, and there’s a high level of likelihood that Donald Trump may very well return to the White House. The UK, India, Pakistan and Indonesia are also heading to the polls, and AI might make it harder to separate truth from falsehood than might have been the case otherwise. It will be interesting to see where things go from here on out, since the results of these elections will have long term consequences.
Image: WEF
Read next: Microsoft is Making Batteries With AI, Here’s What You Need to Know
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Wednesday, January 10, 2024
Microsoft is Making Batteries With AI, Here’s What You Need to Know
Batteries are quickly becoming the name of the game, especially given how central they are to renewable energy as well as electric vehicles. It appears that Microsoft is leveraging AI and quantum computing to create the most powerful battery they can, and the tech juggernaut is collaborating with the Department of Energy in order to get to the finish line.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that this collaboration will take place over several years. Microsoft is trying to use the Azure Quantum platform in order to speed up the process by which research is conducted, so there is a high level of likelihood that decades of studies can be done within the span of a few years.
Image: Microsoft / YT
It bears mentioning that this project has already seen a few successes in its short lifetime. The AI was able to comb through 32 million chemical combinations that would make for an ideal battery and narrow it down to just 500,000 with all things having been considered and taken into account. The Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory is currently in the process of testing out the best candidates in its advanced simulations.
Material science research is proving to be fertile ground in which the capabilities of AI can be tested out. Google is yet another tech titan that managed to discover 2 million materials that can be used in this context with its GNoME AI. Its Deep Mind division is managing this project, and it will be interesting to see what other results it yields in the long run.
These two projects are competing with each other, with Google trying to come up with new chemical compositions and Microsoft utilizing AI to explore currently known molecular structures. No matter ends up winning this race, the truth of the situation is that these projects are revealing just how critical both cloud computing and AI are becoming in the realm of scientific discovery. It may be the key that helps us solve the climate change crisis once and for all.
Read next: Apple Makes Striking Confession To The EU About Operating Five Different App Stores
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that this collaboration will take place over several years. Microsoft is trying to use the Azure Quantum platform in order to speed up the process by which research is conducted, so there is a high level of likelihood that decades of studies can be done within the span of a few years.
Image: Microsoft / YT
Material science research is proving to be fertile ground in which the capabilities of AI can be tested out. Google is yet another tech titan that managed to discover 2 million materials that can be used in this context with its GNoME AI. Its Deep Mind division is managing this project, and it will be interesting to see what other results it yields in the long run.
These two projects are competing with each other, with Google trying to come up with new chemical compositions and Microsoft utilizing AI to explore currently known molecular structures. No matter ends up winning this race, the truth of the situation is that these projects are revealing just how critical both cloud computing and AI are becoming in the realm of scientific discovery. It may be the key that helps us solve the climate change crisis once and for all.
Read next: Apple Makes Striking Confession To The EU About Operating Five Different App Stores
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
How Effective Are AI Content Detectors?
Ever since ChatGPT made it far easier to create written content than might have been the case otherwise, a slew of AI content detectors have popped up. Many have begun using these detectors because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up allowing them to spot AI generated content. Even so, how effective are these content detectors? A study conducted by the Department of Computer Science at Southern Methodist University tried to come up with answers.
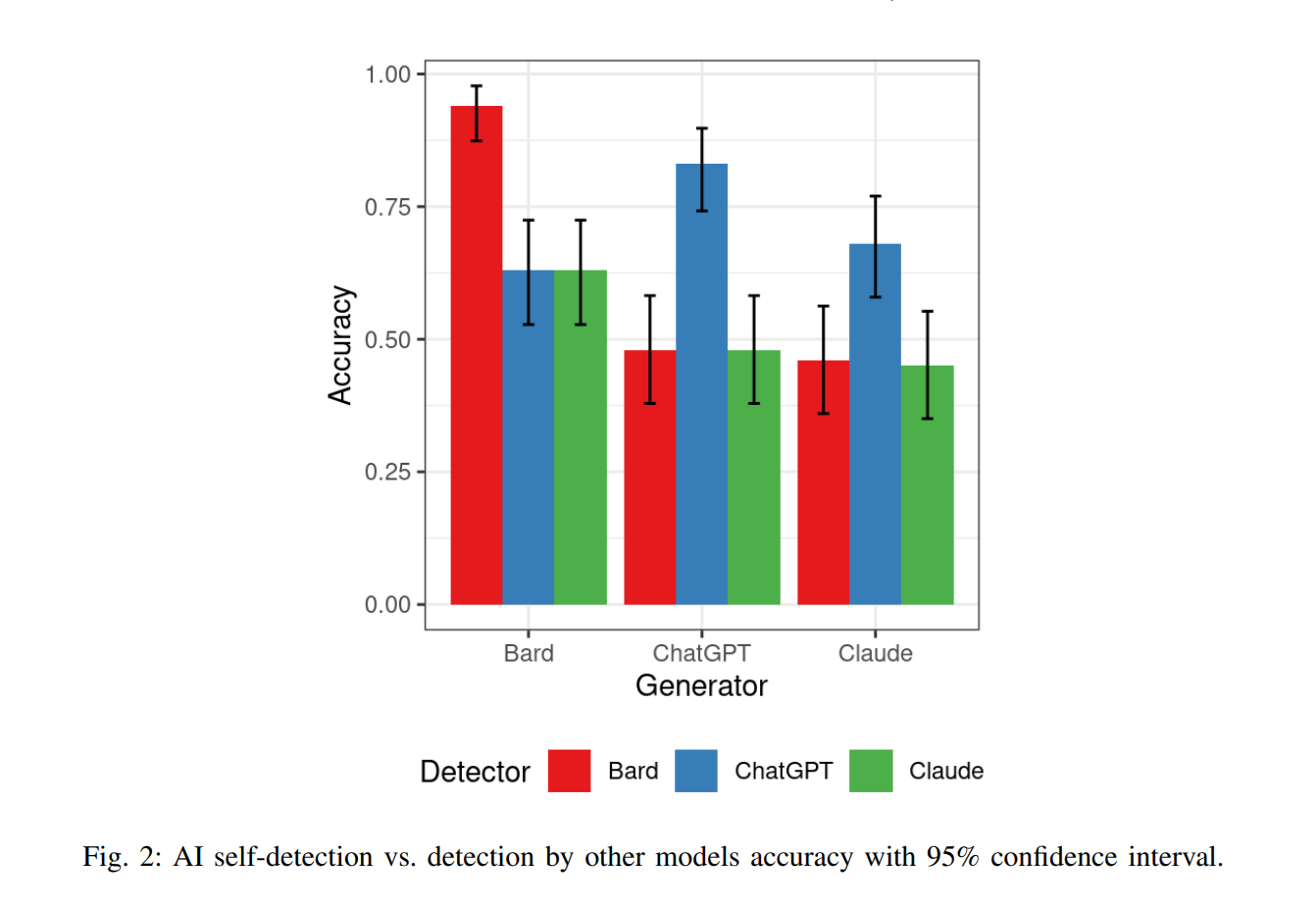
Researchers analyzed Claude, Bard as well as ChatGPT in order to ascertain which of them were easier to detect. With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that Claude actually provided content that evaded detection for the most part. As for ChatGPT and Bard, they were better at detecting their own content, but they weren’t quite as good as Claude when it came to avoiding detection by third party tools.
The manner in which AI content detectors function is that they look for artifacts, or in other words, signs that a piece of content was made using large language models. Each LLM comes with its own unique set of artifacts, all of which can contribute to them becoming more or less challenging to pinpoint with all things having been considered and taken into account.
The way this study was conducted involved generating a 250 word piece of content for around 50 topics or so. The three AI models that were being analyzed were then asked to paraphrase this content, and fifty human generated essays were also factored into the equation.
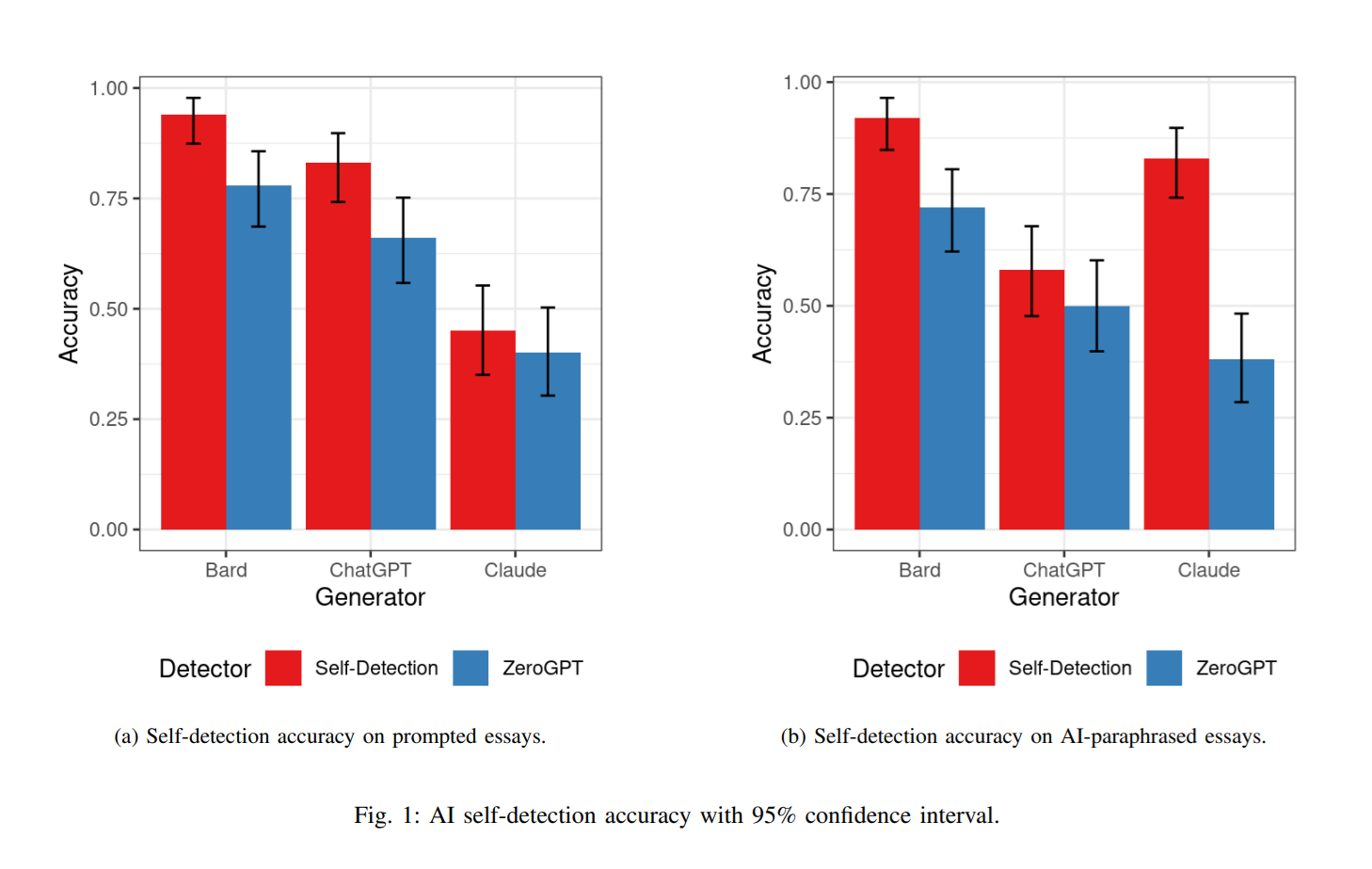
Zero shot prompting was then utilized for the purposes of self detection by these AI models. Bard had the highest level of accuracy when detecting its own content, followed by ChatGPT and Claude in dead last.
As for ZeroGPT, an AI content detector offered by Open AI, it detected Bard content around 75% of the time. It was slightly less effective at detecting GPT generated content, and Claude managed to trick it into believing the content wasn’t AI generated the most times out of all the models.
One thing that must be mentioned here is that ChatGPT’s self detection hovered at around 50%. This seems to suggest that it has the same accuracy rate as guessing, which was considered to be a failure in the context of this study. The self detection of paraphrased content yielded even more interesting results. Claude registered a much higher self detection score, and it also had the lowest accuracy score when being detected by ZeroGPT.
In the end, researchers concluded that ChatGPT is able to detect content that it was used to generate, but it appears to be less effective at registering paraphrased content. Bard was able to perform reasonably well in both cases, but each of these models were far outstripped by Claude.
Claude was able to outsmart not only other AI models, but also its own detection. This seems to suggest that it had the fewest artifacts that could be used to determine the origin of is content. More study will be needed to obtain further evidence, but the signs are pointing to Claude being the most reliable text generator of all.
Read next: AI Systems Are Facing Increasing Threats According to This Report
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Researchers analyzed Claude, Bard as well as ChatGPT in order to ascertain which of them were easier to detect. With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that Claude actually provided content that evaded detection for the most part. As for ChatGPT and Bard, they were better at detecting their own content, but they weren’t quite as good as Claude when it came to avoiding detection by third party tools.
The manner in which AI content detectors function is that they look for artifacts, or in other words, signs that a piece of content was made using large language models. Each LLM comes with its own unique set of artifacts, all of which can contribute to them becoming more or less challenging to pinpoint with all things having been considered and taken into account.
The way this study was conducted involved generating a 250 word piece of content for around 50 topics or so. The three AI models that were being analyzed were then asked to paraphrase this content, and fifty human generated essays were also factored into the equation.
Zero shot prompting was then utilized for the purposes of self detection by these AI models. Bard had the highest level of accuracy when detecting its own content, followed by ChatGPT and Claude in dead last.
As for ZeroGPT, an AI content detector offered by Open AI, it detected Bard content around 75% of the time. It was slightly less effective at detecting GPT generated content, and Claude managed to trick it into believing the content wasn’t AI generated the most times out of all the models.
One thing that must be mentioned here is that ChatGPT’s self detection hovered at around 50%. This seems to suggest that it has the same accuracy rate as guessing, which was considered to be a failure in the context of this study. The self detection of paraphrased content yielded even more interesting results. Claude registered a much higher self detection score, and it also had the lowest accuracy score when being detected by ZeroGPT.
In the end, researchers concluded that ChatGPT is able to detect content that it was used to generate, but it appears to be less effective at registering paraphrased content. Bard was able to perform reasonably well in both cases, but each of these models were far outstripped by Claude.
Claude was able to outsmart not only other AI models, but also its own detection. This seems to suggest that it had the fewest artifacts that could be used to determine the origin of is content. More study will be needed to obtain further evidence, but the signs are pointing to Claude being the most reliable text generator of all.
Read next: AI Systems Are Facing Increasing Threats According to This Report
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Tuesday, January 9, 2024
AI Systems Are Facing Increasing Threats According to This Report
As AI systems continue to grow, so too does the threat landscape targeting them. The National Institute of Standards and Technology just released a report stating that malicious actors are using adversarial machine learning in order to circumvent these systems. Based on the findings presented in this report, this threat is likely going to grow in the near future with all things having been considered and taken into account.
One example of an attack that can be conducted is known as data poisoning. This is when malicious actors sabotage training data for AI models, and this type of attack requires hardly any financial resources due to its ability to scale. Backdoor attacks are also dangerous because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up leaving triggers in the training data which would allow malicious actors secret entry into the database by inducing misclassifications.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that these attacks can be extremely difficult to ward off. They are just two of the many examples of AI based threats that can compromise a wide range of systems in the long run, and many of the risks have to do with privacy as well.
Using something called membership inference, malicious actors can figure out if a string of data was used to train a particular AI. Yet again, there is no consensus on how systems can be protected from such incursions. This casts some doubts on the ability of AI to transform industries in the way that many are expecting.
The nascent stage that this tech is still within the confines of requires a deep understanding of where the threats might lie. In spite of the fact that this is the case, many companies that are investing in AI systems aren’t doing all that much to mitigate the risk of attack. A reactive approach will only lead to malicious actors gaining a foothold. As a result of the fact that this is the case, researchers are urging decision makers to adopt a proactive approach using this report.
Photo: Digital Information World - AIgen
Read next: Google is Planning to Crack Down on Search Spam
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
One example of an attack that can be conducted is known as data poisoning. This is when malicious actors sabotage training data for AI models, and this type of attack requires hardly any financial resources due to its ability to scale. Backdoor attacks are also dangerous because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up leaving triggers in the training data which would allow malicious actors secret entry into the database by inducing misclassifications.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that these attacks can be extremely difficult to ward off. They are just two of the many examples of AI based threats that can compromise a wide range of systems in the long run, and many of the risks have to do with privacy as well.
Using something called membership inference, malicious actors can figure out if a string of data was used to train a particular AI. Yet again, there is no consensus on how systems can be protected from such incursions. This casts some doubts on the ability of AI to transform industries in the way that many are expecting.
The nascent stage that this tech is still within the confines of requires a deep understanding of where the threats might lie. In spite of the fact that this is the case, many companies that are investing in AI systems aren’t doing all that much to mitigate the risk of attack. A reactive approach will only lead to malicious actors gaining a foothold. As a result of the fact that this is the case, researchers are urging decision makers to adopt a proactive approach using this report.
Photo: Digital Information World - AIgen
Read next: Google is Planning to Crack Down on Search Spam
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Search Snippets Come From Page Content, Google Clarifies
Search snippets have become a useful way for SEO professionals to get ahead, but in spite of the fact that this is the case, they have also caused a considerable amount of confusion. When Google released documentation pertaining to these snippets, people were led to believe that they were gleaned from meta descriptions in the HTML code as well as structured data.
Search giant Google has now set the record straight. The tech juggernaut has clarified that the content present within these snippets is sourced largely from the content contained within pages rather than what SEOs initially assumed.
Google automatically detects what content on a given page would be appropriate to use within the context of a search snippet. The company has altered the document to avoid further confusion, and it bears mentioning that all mentions of rich results have also been removed
These changes are important because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up determining how content will be structured on a page. Now that SEOs are aware that HTML elements are not part of the equation, they will be less likely to focus on them when trying to get content included in snippets.
One thing that must be clarified here is that HTML elements aren’t entirely ignored. They are used on occasion, but by and large Google relies on page content for snippets so that they can be made more accurate and useful to searchers than might have been the case otherwise.
If the meta description happens to offer a more suitable summary of the contents of a page, it might end up being used instead. Website owners would do well to keep this at the forefront of their minds with all things having been considered and taken into account. It can have an enormous impact on the manner in which their sites appear on the SERP, something that can drive considerable traffic and ensure organic growth without requiring any manipulation of meta descriptions and the like.
Photo: Digital Information World - AIgen
Read next: Google is Planning to Crack Down on Search Spam
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Search giant Google has now set the record straight. The tech juggernaut has clarified that the content present within these snippets is sourced largely from the content contained within pages rather than what SEOs initially assumed.
Google automatically detects what content on a given page would be appropriate to use within the context of a search snippet. The company has altered the document to avoid further confusion, and it bears mentioning that all mentions of rich results have also been removed
These changes are important because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up determining how content will be structured on a page. Now that SEOs are aware that HTML elements are not part of the equation, they will be less likely to focus on them when trying to get content included in snippets.
One thing that must be clarified here is that HTML elements aren’t entirely ignored. They are used on occasion, but by and large Google relies on page content for snippets so that they can be made more accurate and useful to searchers than might have been the case otherwise.
If the meta description happens to offer a more suitable summary of the contents of a page, it might end up being used instead. Website owners would do well to keep this at the forefront of their minds with all things having been considered and taken into account. It can have an enormous impact on the manner in which their sites appear on the SERP, something that can drive considerable traffic and ensure organic growth without requiring any manipulation of meta descriptions and the like.
Photo: Digital Information World - AIgen
Read next: Google is Planning to Crack Down on Search Spam
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Google is Planning to Crack Down on Search Spam
Google has a major spam problem, with many examples popping up of top ranking sites being replete with affiliate links and irrelevant content. This poses a problem due to how untrustworthy Google will become if its SERP consists solely of websites that are trying to game the algorithm with all things having been considered and taken into account. However, it turns out that Google is developing a strategy that will make spam far less commonplace than might have been the case otherwise.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that Google Search Liaison Danny Sullivan took to X, formerly known as Twitter, to announce that the company is finally cracking down on the problem. In spite of the fact that this is the case, he hasn’t really provided a timeline for the implementation of this solution.
Solving the issue is essential because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up restoring user trust in the search engine. Sullivan has stated that the solution will take time, and that users need to wait and see what Google has in store.
Responding to a post about a particularly spam heavy site, the search liaison suggested that it was a one off issue. The site in question didn’t appear to know about the content that was being pointed out, so according to Google, it was a case of accidental spam rather than malicious intent.
The main issue here is that top ranking sites are full of spam. Since most users rarely ever go past the top two or three sites, this might bring down the quality of the entire SERP if steps aren’t taken fast.
Photo: Digital Information World - AIgen
Read next: Meta's Threads Tests Much-Needed Changes Including Trending Topics And Chronologically Filtered Search Results
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that Google Search Liaison Danny Sullivan took to X, formerly known as Twitter, to announce that the company is finally cracking down on the problem. In spite of the fact that this is the case, he hasn’t really provided a timeline for the implementation of this solution.
Solving the issue is essential because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up restoring user trust in the search engine. Sullivan has stated that the solution will take time, and that users need to wait and see what Google has in store.
Responding to a post about a particularly spam heavy site, the search liaison suggested that it was a one off issue. The site in question didn’t appear to know about the content that was being pointed out, so according to Google, it was a case of accidental spam rather than malicious intent.
- Also read: TikTok Removes User Ability To Search For Specific Hashtags Trends Through Its Creative Center Tools
The main issue here is that top ranking sites are full of spam. Since most users rarely ever go past the top two or three sites, this might bring down the quality of the entire SERP if steps aren’t taken fast.
Photo: Digital Information World - AIgen
Read next: Meta's Threads Tests Much-Needed Changes Including Trending Topics And Chronologically Filtered Search Results
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)