A few days earlier, Snap Inc. launched a premium subscription service for its users to avail extraordinary features within Snapchat. Since the launch of Snapchat plus (paid service) in late June, it has recorded over a million users in just six weeks. This is exceptional in terms of revenue and the amount is quite affordable that everyone can pay. Right now, per month subscription charges of Snapchat + are 3.99 dollars.
Moving on forward, the app intelligence platform, Appfigures estimated 634,000 dollars of net revenue in just one day, and surprisingly, the revenue reached approximately 7 million dollars in its initial month. After one-time subscription consumers have to repeatedly pay in the coming months to avail of the service. So, according to Appfigures, the revenue hit only $300,000 in August. Comparing the figures from July when the revenue crossed 600,000 dollars it can be said that the peak is no more.
The exact cause of such low figures is not known. However, Snapchat+ is an opportunity for people to enjoy the amazing features of the app. For instance, it enables you to see who rewatched your Snap stories and allows you to change the app icon as well. Furthermore, some handy features are also ready to be rolled out for the paid subscribers which includes story replies, enabling Snapchatters' response more prominent when replying to the stories of public figures (Snap Stars). In addition to it, unique backgrounds, and new and improved Bitmoji characters are also on the way to providing an amazing app experience. Among many other features, the most important one is the launch of Snapchat for desktop, especially designed features for paid subscribers.
Above all, Snapchat Plus is a bundle of diversified features for users and with the paid service, Snapchat aims to generate more revenue than it did ever before. Still, the month isn’t over yet, but looking at the growth of revenue trend in the previous month, revenue had significantly dropped after that peak, so it won’t be difficult to predict that the rest of August would make a difference.
Well, this is certainly not a piece of shocking news for Snap as the initial month of a new service seems appealing to most people and to be very honest it’s not that costly due to which it got so much attention from those who are just curious about this. So, let’s hope in a couple of months, Snapchat will get more subscribers and more people will renew the service once they are used to the features that are exclusively provided to the paid users.
Read next: Snap Inc. May No Longer Continue With Its Pixy Drone As Development Reaches A Standstill
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
"Mr Branding" is a blog based on RSS for everything related to website branding and website design, it collects its posts from many sites in order to facilitate the updating to the latest technology.
To suggest any source, please contact me: Taha.baba@consultant.com
Saturday, August 20, 2022
Snapchat has conducted a survey on what internet privacy means to users on the internet
The internet is a vast place full of opinions, points of view, and judgments. On the internet, a user is subjected to all of them and thrust into their world. On social media apps like Snapchat people are even more variations of the internet and try to maintain privacy settings over their socials so that they can avoid the scrutiny of their peers.
The new rise of private groups on WhatsApp and Facebook provides a testament to this. Also, on Instagram people have started using IG Direct more than tagging people in comments or stories.
With all this happening it makes sense for most of the sharing to go on behind the scenes rather than being the star of the show. But, the real question that comes up is what exactly are the privacy apprehensions of users, and what are the exact key tension points for the users?
Snap Inc. set out to find the answer to this question with their new survey in which more than 13,519 daily social media users were questioned across 11 different markets that belonged to the age group of 13-40.
According to the data released in the report, the key findings of the study were;
77% of respondents consider online privacy as important, while only 72% of respondents are happy with the current level of online privacy that our fav social media apps have to offer.
90% of social media users have it as a priority that the apps they use care about their privacy while they engage on their platform.
Last but not the least, the platform should release features that help the users communicate better all while still having some control as to what information of theirs is available is a huge factor in building the company-consumer trust bridge.
Read next: 7 in 10 consumers feel uncomfortable if their online activity gets leaked to someone they are familiar with
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
The new rise of private groups on WhatsApp and Facebook provides a testament to this. Also, on Instagram people have started using IG Direct more than tagging people in comments or stories.
With all this happening it makes sense for most of the sharing to go on behind the scenes rather than being the star of the show. But, the real question that comes up is what exactly are the privacy apprehensions of users, and what are the exact key tension points for the users?
Snap Inc. set out to find the answer to this question with their new survey in which more than 13,519 daily social media users were questioned across 11 different markets that belonged to the age group of 13-40.
According to the data released in the report, the key findings of the study were;
77% of respondents consider online privacy as important, while only 72% of respondents are happy with the current level of online privacy that our fav social media apps have to offer.
90% of social media users have it as a priority that the apps they use care about their privacy while they engage on their platform.
Last but not the least, the platform should release features that help the users communicate better all while still having some control as to what information of theirs is available is a huge factor in building the company-consumer trust bridge.
Read next: 7 in 10 consumers feel uncomfortable if their online activity gets leaked to someone they are familiar with
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Microsoft’s Bing Says It Comes Across Billions Of ‘Unseen URLs’ On A Daily Basis
A new report by Fabrice Canel has gone on to shed light on a very interesting finding regarding Bing. And that’s related to how it manages to come across billions of unseen URLs on a daily basis.
That’s clearly a significant amount of new URLs for anyone to notice in just one day, what do you think?
However, the world wide web is huge and there is plenty of content out there. It’s not necessary that everything you see is of the same standard. Some are definitely far more superior than others and that’s why you’ll even find junk, AI content, gibberish, and just things that no longer make sense anymore.
The news was explained through Fabrice’s Twitter social media handle, which claims that most of these types of content are beyond useless. He even went about enlisting examples that comprise duplicated material, things scraped upon the surface and those things that are simply generated through automated means.
Some of the URLs pertain to spam, junk, and more. And while Bing Searches are definitely coming across billions of such URLs on a daily basis, we’ve got great doubts on whether or not it actually indexes them or not at all.
Fabrice agrees that most of it is pretty useless and as you can expect, the news did manage to get plenty of viewers commenting on how Bing struggles with regular tasks and this would only make things worse.
Read next: Study shows shoppers are more likely to buy products from brands that offer a personalized experience
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
That’s clearly a significant amount of new URLs for anyone to notice in just one day, what do you think?
However, the world wide web is huge and there is plenty of content out there. It’s not necessary that everything you see is of the same standard. Some are definitely far more superior than others and that’s why you’ll even find junk, AI content, gibberish, and just things that no longer make sense anymore.
The news was explained through Fabrice’s Twitter social media handle, which claims that most of these types of content are beyond useless. He even went about enlisting examples that comprise duplicated material, things scraped upon the surface and those things that are simply generated through automated means.
Some of the URLs pertain to spam, junk, and more. And while Bing Searches are definitely coming across billions of such URLs on a daily basis, we’ve got great doubts on whether or not it actually indexes them or not at all.
Fabrice agrees that most of it is pretty useless and as you can expect, the news did manage to get plenty of viewers commenting on how Bing struggles with regular tasks and this would only make things worse.
Read next: Study shows shoppers are more likely to buy products from brands that offer a personalized experience
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
Friday, August 19, 2022
Flashpoint’s report shows data theft incidents take place frequently due to hacking
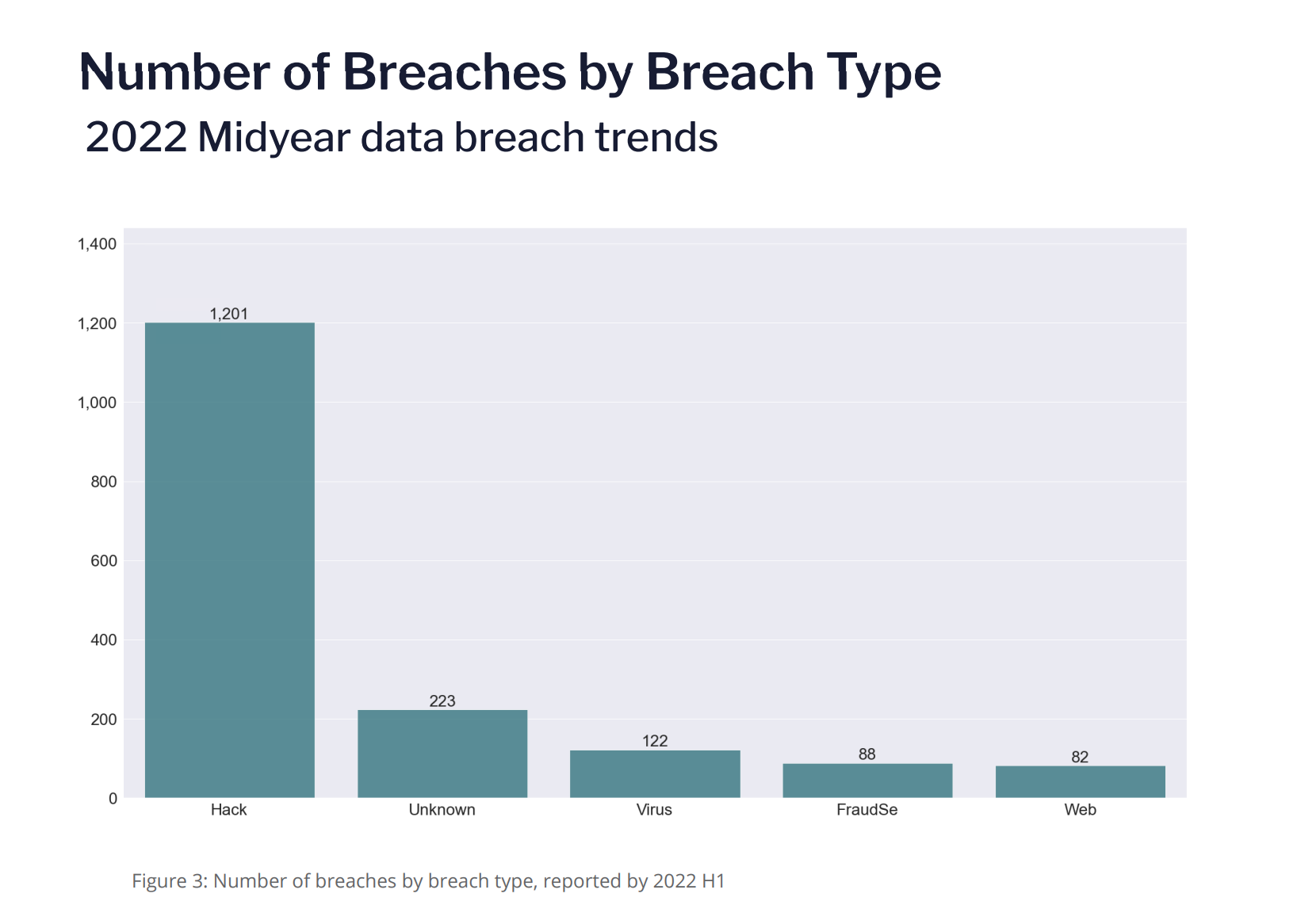
Flashpoint, a global platform dealing in risk intelligence for organizations, release a report which says during the first half of 2022, the most serious breaches dropped as compared to last year. The report shows that 1,980 breaches occurred due to glitches and web-related errors have fallen from 27.3 billion in 2021 to 1.4 billion in 2022.
While this indicates that businesses would have set their priorities to prevent data breaches and still organizations need to become active in dealing with cyber threats efficiently. Most of the data breaches recognized in the report are due to hacking, with 60 percent of cybercrimes aroused from illegitimate access to software systems. This is essentially crucial to take steps to minimize web exposure as well as organizations will need to pay attention to stopping cybercriminals. Moreover, security teams within organizations need to focus on vulnerability management strategies with improved intelligence. Talking about vulnerability management, it is the cyber activity that is based on efficient assessment and detailed report of susceptible actions in IT. Vulnerability is the major issue that organizations are worried about. Because of this organizations must become proactive in closing loopholes and insecure setups.
Flashpoint’s study also reveals that only 23 percent of data breaches initiated from within the victim enterprise and mostly (61 percent) of breaches were mainly due to data handling errors. The state of data breach intelligence study identified 54 breaches aroused from Turncloak (malicious insider) referring to someone who illegally uses credentials for financial or personal benefits. In addition, the occurrence of ordinary events of cybercrime to minor stealing of credit card data from people during purchasing.
Finally, Flashpoint’s mid-year report depicts how firms should learn security measures accordingly and address the significant threats that often take place when defending against, or getting back to normal circumstances after a data breach.
Read next: 265 Brands Impersonated in Credential Phishing Attacks in the First Half of 2022
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
While this indicates that businesses would have set their priorities to prevent data breaches and still organizations need to become active in dealing with cyber threats efficiently. Most of the data breaches recognized in the report are due to hacking, with 60 percent of cybercrimes aroused from illegitimate access to software systems. This is essentially crucial to take steps to minimize web exposure as well as organizations will need to pay attention to stopping cybercriminals. Moreover, security teams within organizations need to focus on vulnerability management strategies with improved intelligence. Talking about vulnerability management, it is the cyber activity that is based on efficient assessment and detailed report of susceptible actions in IT. Vulnerability is the major issue that organizations are worried about. Because of this organizations must become proactive in closing loopholes and insecure setups.
Flashpoint’s study also reveals that only 23 percent of data breaches initiated from within the victim enterprise and mostly (61 percent) of breaches were mainly due to data handling errors. The state of data breach intelligence study identified 54 breaches aroused from Turncloak (malicious insider) referring to someone who illegally uses credentials for financial or personal benefits. In addition, the occurrence of ordinary events of cybercrime to minor stealing of credit card data from people during purchasing.
Finally, Flashpoint’s mid-year report depicts how firms should learn security measures accordingly and address the significant threats that often take place when defending against, or getting back to normal circumstances after a data breach.
Read next: 265 Brands Impersonated in Credential Phishing Attacks in the First Half of 2022
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Google’s stopwatch functionality is working again after a month of mysterious disappearance
Complains have been roaming around on Twitter that the ability to set the timer on Google is broken. A while ago, the company developed a popular feature of a stopwatch to allow people to set timers while searching for their queries, such as "10 minutes timer". Last month, several users reported that the feature has gone missing. But, the good news is that the bug is fixed now and the stopwatch and timer car is working again, informed Google's Danny Sullivan.
A month ago, when people were searching for a stopwatch or timer, the box that usually appears in the search bar eventually stopped displaying. Instead, it shows web pages and videos related to online timers and stopwatches. You might have no idea about this feature as a user also reported noticing this tool after a long while. It is a simple feature that allows users to set a timer for instance 15 minutes and the timer would start ticking instantly. The timer helps people to take a mini break or distract themselves from the workload.
When the feature disappeared, some users suggested installing plugins, but not many people find it a good alternative. In addition, when users were looking for Google’s stopwatch they found it disgusting to visit certain websites to get just a minute of functionality. It was not known whether the removal of the stopwatch was made intentionally or it was a bug. Anyhow, Dany Sullivan, an analyst who better understands Google and helps people to notice news about Google and hears public feedback shared a tweet that says the Google timer started working again.
The feature is accessible now and you can immediately pull it up on the web. If you haven’t used this tool before, it is time to use this handy tool and get benefits from it. One way to do this is to visit Google’s homepage and in the search box type (Set a timer for Y minutes). When you provide the time, the timer will start counting down. Another way to use this functionality is to simply type the same thing on the URL bar in Google Chrome if you want to skip the lengthy part.
For the stopwatch, start instantly from Google’s homepage just like you do in case of a timer. Type Start a stopwatch in the search box. The stopwatch will instantly start ticking and you can easily stop or restart the stopwatch. Furthermore, you can also use the stopwatch functionality from the URL bar.
If you still have queries regarding the stopwatch and timer, make sure to ask on Twitter or take Google’s help.
Read next: A Global Overview of Internet Prices and Speed
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
A month ago, when people were searching for a stopwatch or timer, the box that usually appears in the search bar eventually stopped displaying. Instead, it shows web pages and videos related to online timers and stopwatches. You might have no idea about this feature as a user also reported noticing this tool after a long while. It is a simple feature that allows users to set a timer for instance 15 minutes and the timer would start ticking instantly. The timer helps people to take a mini break or distract themselves from the workload.
When the feature disappeared, some users suggested installing plugins, but not many people find it a good alternative. In addition, when users were looking for Google’s stopwatch they found it disgusting to visit certain websites to get just a minute of functionality. It was not known whether the removal of the stopwatch was made intentionally or it was a bug. Anyhow, Dany Sullivan, an analyst who better understands Google and helps people to notice news about Google and hears public feedback shared a tweet that says the Google timer started working again.
The feature is accessible now and you can immediately pull it up on the web. If you haven’t used this tool before, it is time to use this handy tool and get benefits from it. One way to do this is to visit Google’s homepage and in the search box type (Set a timer for Y minutes). When you provide the time, the timer will start counting down. Another way to use this functionality is to simply type the same thing on the URL bar in Google Chrome if you want to skip the lengthy part.
For the stopwatch, start instantly from Google’s homepage just like you do in case of a timer. Type Start a stopwatch in the search box. The stopwatch will instantly start ticking and you can easily stop or restart the stopwatch. Furthermore, you can also use the stopwatch functionality from the URL bar.
If you still have queries regarding the stopwatch and timer, make sure to ask on Twitter or take Google’s help.
Read next: A Global Overview of Internet Prices and Speed
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
How Safe Is Android 13? Concerns Arise As Malware Developers Bypass Its New ‘Restricted Setting’
Android 13 is out and the makers have promised better security enhancements including a special restricted setting feature.
But what if we told you that the promises made have failed to hold through as leading malware developers claim they’ve managed to create droppers to bypass the security feature outlined? Yes, developers say they’ve devised a system based on tactics to overcome the safety features.
The news is alarming and an apparent setback for those with high hopes. Remember, it’s only been a day or two since we last heard about the launch. This was seen across Google’s Pixel phones and AOSP’s source code.
Despite the news, you can’t deny how hard Google tried to disturb mobile malware that made attempts to enter the system using vital and powerful permissions like AccessbilityService.
This way, the malware was allowed to carry out their malicious threats to the systems, making it easy for the company to detect and disable them. But it seems their hard work couldn’t go all the way.
Thanks to a few research experts and tech analysts from Threat Fabric, a new report highlights how malware authors achieved success in creating Android-specific malware droppers that certainly go above and beyond such features.
They end up delivering results that make the most of the users’ devices, leaving them vulnerable to further attack while enjoying the highest privileges.
When we look at Android versions from the past, it’s quite clear how most of them are related to making their way inside the device through apps found simply from Google’s Play Store. They appear legitimate but their true behavior is masqueraded.
At the time of making downloads, different malware apps force users to gain access to various permissions that authors dub risky. On the other end, they’re sideloading dangerous payloads by breaking through the device’s accessibility service.
The latter has been labeled as one of the most easily abused systems out there for Android. With simple touches and swipes, apps are allowed to perform tasks with ease and can even return to home screens with a single tap. And you guessed it, the user has zero clue of what’s really going on.
On usual occasions, the malware has the ability to give itself more permission than allowed. This way, the victim is stopped from making attempts to have the app deleted.
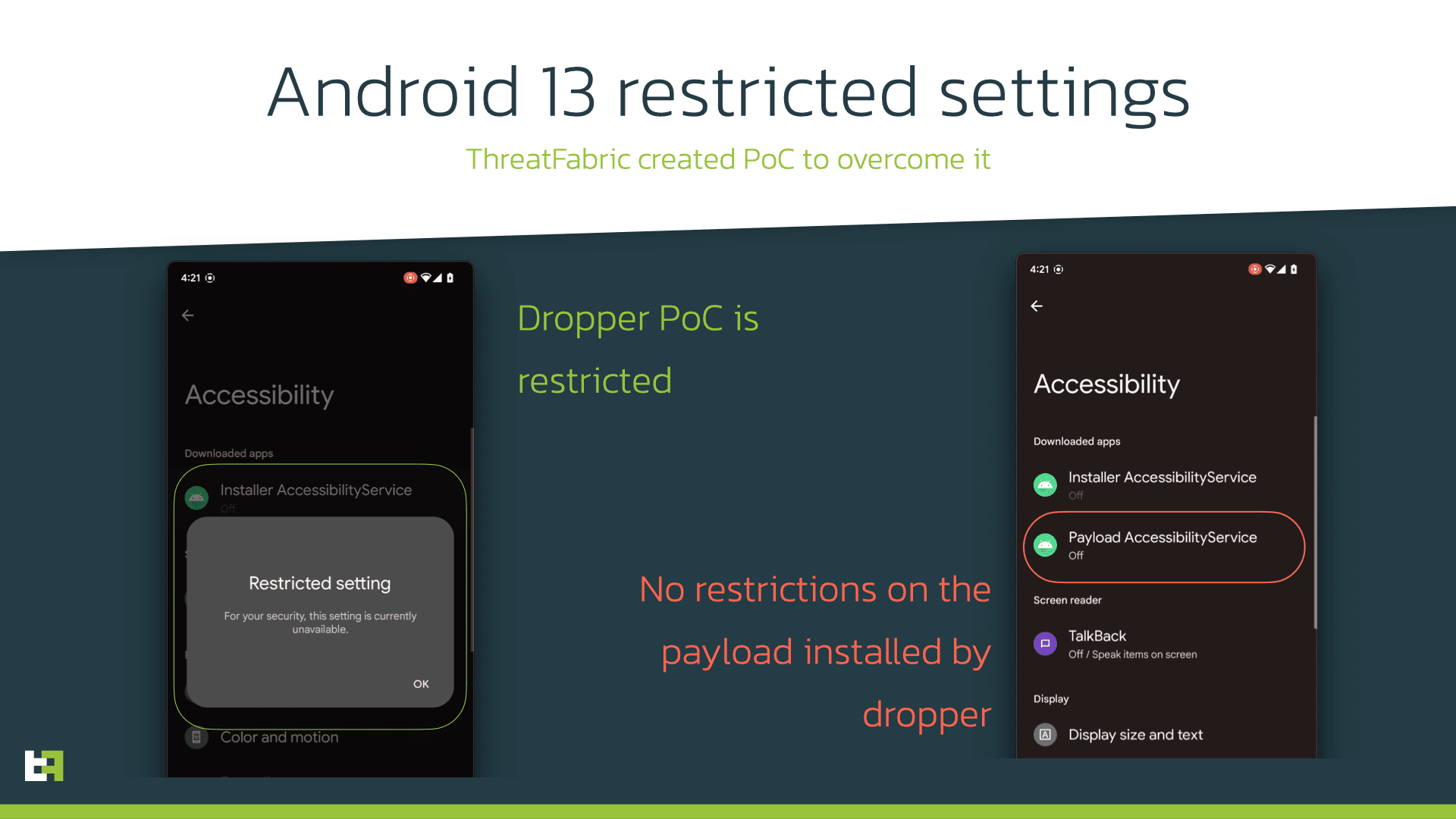
But what really surprises many is how engineers had boasted so much about the new restricted setting functionality. The purpose with which it was designed was to block sideloading from requesting permission from the Accessibility Service. This way, it would be limiting functions to just APKs from Google’s Play Store.
Now, there’s clear proof thanks to Threat Fabric how the system is being fooled easily and bypassed for malicious means into the Accessibility Service.
The malware dropper manages to include some different types of features so it bypasses restricted settings in place.
It’s called BugDrop and while it’s still in its early stage of development, it’s doing a pretty fine job as a novel entity.
The code featured is very similar to that observed with Brox. This is another name provided to malware making its way to different hacking platforms.
With Android 13, search giant Google thought it would be good to restrict entry into the Accessibility Services, other than the Notification Listener to apps getting installed via the session-based method only.
Therefore, if BugDrop was actually using this method for sideloading, it would be detected through the new Android protection system as proven by the malware developers.
For now, BugDrop is in its early creation phase. But soon, it’s going to be ready for further deployment, wreaking havoc across Android devices by the masses.
Read next: New Survey Proves 49% Of Android Users Prefer Switching To iPhones Because It’s Safer
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
But what if we told you that the promises made have failed to hold through as leading malware developers claim they’ve managed to create droppers to bypass the security feature outlined? Yes, developers say they’ve devised a system based on tactics to overcome the safety features.
The news is alarming and an apparent setback for those with high hopes. Remember, it’s only been a day or two since we last heard about the launch. This was seen across Google’s Pixel phones and AOSP’s source code.
Despite the news, you can’t deny how hard Google tried to disturb mobile malware that made attempts to enter the system using vital and powerful permissions like AccessbilityService.
This way, the malware was allowed to carry out their malicious threats to the systems, making it easy for the company to detect and disable them. But it seems their hard work couldn’t go all the way.
Thanks to a few research experts and tech analysts from Threat Fabric, a new report highlights how malware authors achieved success in creating Android-specific malware droppers that certainly go above and beyond such features.
They end up delivering results that make the most of the users’ devices, leaving them vulnerable to further attack while enjoying the highest privileges.
When we look at Android versions from the past, it’s quite clear how most of them are related to making their way inside the device through apps found simply from Google’s Play Store. They appear legitimate but their true behavior is masqueraded.
At the time of making downloads, different malware apps force users to gain access to various permissions that authors dub risky. On the other end, they’re sideloading dangerous payloads by breaking through the device’s accessibility service.
The latter has been labeled as one of the most easily abused systems out there for Android. With simple touches and swipes, apps are allowed to perform tasks with ease and can even return to home screens with a single tap. And you guessed it, the user has zero clue of what’s really going on.
On usual occasions, the malware has the ability to give itself more permission than allowed. This way, the victim is stopped from making attempts to have the app deleted.
But what really surprises many is how engineers had boasted so much about the new restricted setting functionality. The purpose with which it was designed was to block sideloading from requesting permission from the Accessibility Service. This way, it would be limiting functions to just APKs from Google’s Play Store.
Now, there’s clear proof thanks to Threat Fabric how the system is being fooled easily and bypassed for malicious means into the Accessibility Service.
The malware dropper manages to include some different types of features so it bypasses restricted settings in place.
It’s called BugDrop and while it’s still in its early stage of development, it’s doing a pretty fine job as a novel entity.
The code featured is very similar to that observed with Brox. This is another name provided to malware making its way to different hacking platforms.
With Android 13, search giant Google thought it would be good to restrict entry into the Accessibility Services, other than the Notification Listener to apps getting installed via the session-based method only.
Therefore, if BugDrop was actually using this method for sideloading, it would be detected through the new Android protection system as proven by the malware developers.
For now, BugDrop is in its early creation phase. But soon, it’s going to be ready for further deployment, wreaking havoc across Android devices by the masses.
Read next: New Survey Proves 49% Of Android Users Prefer Switching To iPhones Because It’s Safer
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
Netflix Might Limit Offline Downloads In Its Ad-Free Versions Of The Streaming Service
If you thought the ad-supported tier of popular streaming service Netflix was the same as before, except for the addition of a few commercials, well, you’re wrong.
Thanks to a leading developer named Steve Moser, we’re getting some more information about how things are about to change.
Moser shared with Bloomberg how Netflix plans on introducing a few changes that entail limiting the number of offline downloads on the ad-free version.
At the moment, Netflix has a total of three different versions or tiers that are up for grabs. For starters, the standard version costs $9.99 per month. This enables users to watch content on only one screen at a single time.
Those who sign up for the $14.99 package a month can avail of HD quality and the chance to watch content on any two screens in one go. And those who want a little something extra can opt for the $19.99 deal where users get the chance to watch content on at least four different screens at once.
If you ask us, we certainly don’t see the move as a huge surprise for obvious reasons. Netflix trying to guard users against making offline downloads on the ad-free version certainly is sensible. After all, those who pay more should certainly get more.
This past year, we saw the company’s co-CEO mention boldly how the ad-supported version of the streaming service was not going to entail the same offerings as the one without ads. Moreover, he elaborated further on how those that support ads were designed to be the true gateway of great benefits at lower price tags.
Remember, it’s not simple to serve ads when you’re offline. We don’t believe the mission is impossible but it’s certainly not easy. As it is, the company is putting plenty of things behind payment barriers that we feel should be standard for everyone.
Keeping in mind records from the past, Netflix is yet to treat the ideology behind offline downloads as one that’s seen as a major benefit. The feature was launched back in the year 2016. At that time, the firm had only just begun enabling the concept of making downloads offline.
The whole idea was centered around providing support to those places where wi-fi connections weren’t performing at their best. And truth be told, Netflix was quite behind other archrivals who were already providing the benefit.
For instance, Amazon Prime allowed users to download content and then carry on watching it later for so long.
The news comes after we last heard from the famous content streaming service platform joining hands with Microsoft. Yes, the latter would now be seen as its leading tech, sales, and marketing partner as the duo collaborated, leaving behind so many others who had hopes of the same.
This is what has allowed for the ad-support version of Netflix to arise essentially. We’re going to see the probable launch of the new variants with ads in 2023 and until then, enjoy the platform as much as you can.
Read next: 7 in 10 consumers feel uncomfortable if their online activity gets leaked to someone they are familiar with
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
Thanks to a leading developer named Steve Moser, we’re getting some more information about how things are about to change.
Moser shared with Bloomberg how Netflix plans on introducing a few changes that entail limiting the number of offline downloads on the ad-free version.
At the moment, Netflix has a total of three different versions or tiers that are up for grabs. For starters, the standard version costs $9.99 per month. This enables users to watch content on only one screen at a single time.
Those who sign up for the $14.99 package a month can avail of HD quality and the chance to watch content on any two screens in one go. And those who want a little something extra can opt for the $19.99 deal where users get the chance to watch content on at least four different screens at once.
If you ask us, we certainly don’t see the move as a huge surprise for obvious reasons. Netflix trying to guard users against making offline downloads on the ad-free version certainly is sensible. After all, those who pay more should certainly get more.
This past year, we saw the company’s co-CEO mention boldly how the ad-supported version of the streaming service was not going to entail the same offerings as the one without ads. Moreover, he elaborated further on how those that support ads were designed to be the true gateway of great benefits at lower price tags.
Remember, it’s not simple to serve ads when you’re offline. We don’t believe the mission is impossible but it’s certainly not easy. As it is, the company is putting plenty of things behind payment barriers that we feel should be standard for everyone.
Keeping in mind records from the past, Netflix is yet to treat the ideology behind offline downloads as one that’s seen as a major benefit. The feature was launched back in the year 2016. At that time, the firm had only just begun enabling the concept of making downloads offline.
The whole idea was centered around providing support to those places where wi-fi connections weren’t performing at their best. And truth be told, Netflix was quite behind other archrivals who were already providing the benefit.
For instance, Amazon Prime allowed users to download content and then carry on watching it later for so long.
The news comes after we last heard from the famous content streaming service platform joining hands with Microsoft. Yes, the latter would now be seen as its leading tech, sales, and marketing partner as the duo collaborated, leaving behind so many others who had hopes of the same.
This is what has allowed for the ad-support version of Netflix to arise essentially. We’re going to see the probable launch of the new variants with ads in 2023 and until then, enjoy the platform as much as you can.
Read next: 7 in 10 consumers feel uncomfortable if their online activity gets leaked to someone they are familiar with
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)