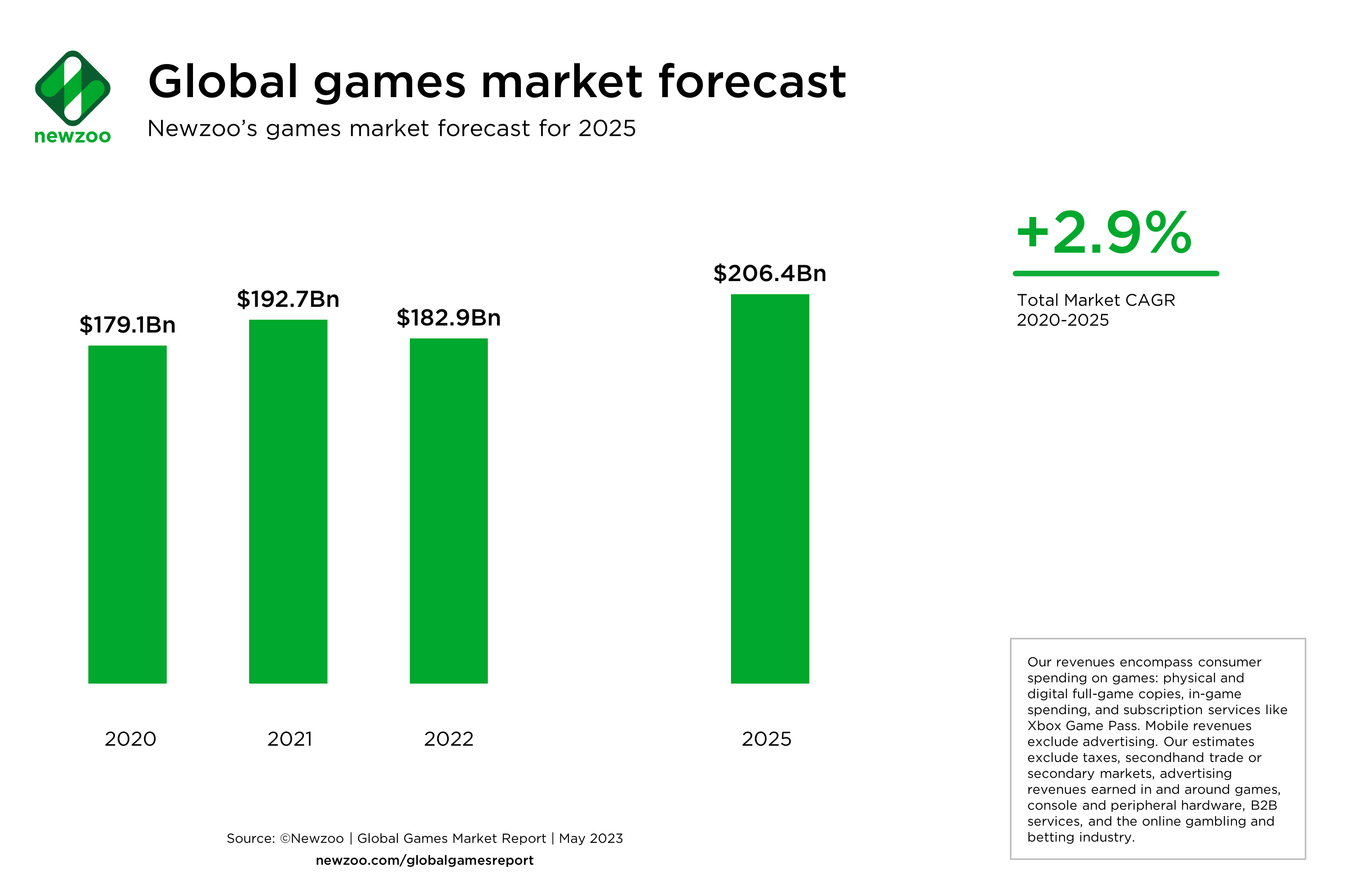
The mobile gaming market has been a powerful force in the app industry for quite some time now, but in spite of the fact that this is the case, even it is not immune to the economic setbacks that have been plaguing most industries around the world. Newzoo just released a report that shed some light on the factors that are at play here, and they have revealed some key insights about the state of the industry as of right now.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that the total revenue generated by the mobile gaming market in 2022 totalled to around $91.8 billion. While impressive, this is nonetheless a 6.7% decrease from the numbers that were seen last year, which indicates that the mobile gaming industry is earning less than might have been the case otherwise.
However, it bears mentioning that about 50% of the total apps that are available across various platforms are still mobile gaming apps. This reveals just how significant games are in this industry, and despite the revenue decline, they will continue to be a formidable force with all things having been considered and taken into account.
Around 49% of the total revenue that went towards these games came from China as well as the US. The Asia-Pacific region saw revenues decline by 8.9%, and North American revenues dropped by 2.5% year over year. This indicates that the two powerhouses for this industry are not providing quite as much cash as they used to in the past.
Meanwhile, Latin America composes the smallest share of this total revenue, coming up to just 5%. It was still able to see 3.3% growth year over year making it the one of two regions whose revenues went north instead of south.
The other region that showed a positive trend in terms of revenue was the Middle East, where revenues grew by 5.8% year over year. This brought the total mobile gaming revenue for this region up to just under $7 billion, or $6.8 billion to be precise.
Read next: Here Are the Biggest Philosophical Questions People Ask Google
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
"Mr Branding" is a blog based on RSS for everything related to website branding and website design, it collects its posts from many sites in order to facilitate the updating to the latest technology.
To suggest any source, please contact me: Taha.baba@consultant.com
Monday, June 19, 2023
A trillion-dollar global economic boost and new opportunities are expected from generative AI
In a world where generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is gaining significant traction, major companies across various industries are eagerly embracing this transformative technology. The impact of their moves on the global economy is poised to be substantial, with experts predicting a remarkable addition of trillions of dollars annually. According to a recent report by McKinsey and Company, GenAI has the potential to inject a staggering $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion into the global economy each year.
Over 850 occupations and 2,100 employees from 47 nations were examined as part of a thorough examination by McKinsey, accounting for more than 80% of the world's workforce. The updated economic effect estimate is a significant improvement over their first projections from 2017, demonstrating the wide range of possible applications for GenAI products among both large and small firms.
While concerns about job losses due to automation arise, McKinsey's report offers a more nuanced perspective. Alex Sukharevsky, senior partner and global leader of QuantumBlack, McKinsey's in-house AI division and report co-author, highlights that GenAI has the potential to enhance job performance significantly, enabling tasks to be completed faster and with greater precision. Sukharevsky explains that instead of focusing on job replacement, GenAI empowers employees to be more productive and creative.
Although GenAI has captured the public's attention and imagination, McKinsey emphasises that other AI applications and technologies will also have a significant impact on how the world economy is reshaped. Differentiating generative AI from general AI, robotics, and automation technologies is essential. While other AI technologies find their strengths in physical jobs like manufacturing, construction, engineering, transportation, mining, and search and rescue, GenAI and large language models (LLMs) are particularly well suited for white-collar, knowledge-worker positions and duties.
According to the McKinsey analysis, GenAI is anticipated to have a major positive impact in four important areas: customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and research and development (R&D). In North America, computers, including AI, now handle around half of all customer interactions in customer operations, and GenAI has the potential to further cut down on human-serviced interactions by up to 50%.
GenAI-generated personalized and intelligent content might boost productivity in marketing and sales by 5–15% and 3–5%, respectively. GenAI is expected to boost productivity in software engineering by 20–45% by speeding up code creation, correction, and system design. GenAI can optimise designs in R&D, resulting in lower production and transport costs.
McKinsey's research pointed that, GenAI has the potential to revolutionize sectors by acting as a catalyst for new technologies and unleashing people' creative potential. The paper imagines a time of invention and creativity in which workers become creators and use AI technologies to improve their skills.
It's important to note that although some of the data for the study's analysis and collection was done by AI, human authors wrote the full research on the economic effect of AI.
As we advance, professionals from all industries continue to be motivated by the economic potential of GenAI. The annual injection of trillions of dollars into the world economy is expected to change sectors and produce new jobs and activities. Even while certain positions may change, this ground-breaking technology has the potential to unleash previously unheard-of levels of creativity and productivity, promoting a future where human intellect and AI will collaborate to drive economic development and innovation.
The emergence of GenAI has placed the global economy on the edge of a dynamic new era, one that will present opportunities that will have a lasting impact on our planet.
Read next: 15% of Employees Are Giving ChatGPT Their Data
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Over 850 occupations and 2,100 employees from 47 nations were examined as part of a thorough examination by McKinsey, accounting for more than 80% of the world's workforce. The updated economic effect estimate is a significant improvement over their first projections from 2017, demonstrating the wide range of possible applications for GenAI products among both large and small firms.
While concerns about job losses due to automation arise, McKinsey's report offers a more nuanced perspective. Alex Sukharevsky, senior partner and global leader of QuantumBlack, McKinsey's in-house AI division and report co-author, highlights that GenAI has the potential to enhance job performance significantly, enabling tasks to be completed faster and with greater precision. Sukharevsky explains that instead of focusing on job replacement, GenAI empowers employees to be more productive and creative.
Although GenAI has captured the public's attention and imagination, McKinsey emphasises that other AI applications and technologies will also have a significant impact on how the world economy is reshaped. Differentiating generative AI from general AI, robotics, and automation technologies is essential. While other AI technologies find their strengths in physical jobs like manufacturing, construction, engineering, transportation, mining, and search and rescue, GenAI and large language models (LLMs) are particularly well suited for white-collar, knowledge-worker positions and duties.
According to the McKinsey analysis, GenAI is anticipated to have a major positive impact in four important areas: customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and research and development (R&D). In North America, computers, including AI, now handle around half of all customer interactions in customer operations, and GenAI has the potential to further cut down on human-serviced interactions by up to 50%.
GenAI-generated personalized and intelligent content might boost productivity in marketing and sales by 5–15% and 3–5%, respectively. GenAI is expected to boost productivity in software engineering by 20–45% by speeding up code creation, correction, and system design. GenAI can optimise designs in R&D, resulting in lower production and transport costs.
McKinsey's research pointed that, GenAI has the potential to revolutionize sectors by acting as a catalyst for new technologies and unleashing people' creative potential. The paper imagines a time of invention and creativity in which workers become creators and use AI technologies to improve their skills.
It's important to note that although some of the data for the study's analysis and collection was done by AI, human authors wrote the full research on the economic effect of AI.
As we advance, professionals from all industries continue to be motivated by the economic potential of GenAI. The annual injection of trillions of dollars into the world economy is expected to change sectors and produce new jobs and activities. Even while certain positions may change, this ground-breaking technology has the potential to unleash previously unheard-of levels of creativity and productivity, promoting a future where human intellect and AI will collaborate to drive economic development and innovation.
The emergence of GenAI has placed the global economy on the edge of a dynamic new era, one that will present opportunities that will have a lasting impact on our planet.
Read next: 15% of Employees Are Giving ChatGPT Their Data
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Entry Level Smartphones See 22% Sales Surge in Chinese Markets
The smartphone industry is currently undergoing a significant period of strife, but in spite of the fact that this is the case, China is seeing some success in a surprising segment. While the overall smartphone market in China saw a 5% decrease, entry level phones that cost under $150 have seen their sales go up by 22% year over year.
The primary focus of most Chinese OEMs has been to create premium and flagship models because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up netting the highest profit per unit. With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that budget phones are now a 12% part of the total market, up from the 9% that was seen in the year prior.
This is still far lower than the 24% share that these phones had back in 2018, but it seems to suggest that economic woes are forcing buyers to look for cheaper options than might have been the case otherwise. One thing that might have led to this increase in sales for budget smartphones is the lowering of manufacturing costs with all things having been considered and taken into account.
This has allowed OEMs to start adding considerable upgrades to smartphones that were previously thought to be obsolete. It is now not entirely uncommon to find entry level smartphones that have been 5G enabled, thereby allowing users to stay active within a smartphone centric society like China’s without necessarily having to spend more than they can afford.
In the last few years, supply chain crunches forced OEMs to stop making entry level smartphones in large enough quantities. Now that the supply chain has normalized somewhat, it is expected that China’s budget smartphone sector will maintain its hold.
However, as the segment’s most dependable consumer class starts to disappear, namely that of low income earners, OEMs might begin to move away from budget smartphones too. The long replacement cycle of 40 months may put a further squeeze on this sector of the smartphone industry.
H/T: CPR
Read next: Global IoT Connections Grew by 29% in 2022
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
The primary focus of most Chinese OEMs has been to create premium and flagship models because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up netting the highest profit per unit. With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that budget phones are now a 12% part of the total market, up from the 9% that was seen in the year prior.
This is still far lower than the 24% share that these phones had back in 2018, but it seems to suggest that economic woes are forcing buyers to look for cheaper options than might have been the case otherwise. One thing that might have led to this increase in sales for budget smartphones is the lowering of manufacturing costs with all things having been considered and taken into account.
This has allowed OEMs to start adding considerable upgrades to smartphones that were previously thought to be obsolete. It is now not entirely uncommon to find entry level smartphones that have been 5G enabled, thereby allowing users to stay active within a smartphone centric society like China’s without necessarily having to spend more than they can afford.
In the last few years, supply chain crunches forced OEMs to stop making entry level smartphones in large enough quantities. Now that the supply chain has normalized somewhat, it is expected that China’s budget smartphone sector will maintain its hold.
However, as the segment’s most dependable consumer class starts to disappear, namely that of low income earners, OEMs might begin to move away from budget smartphones too. The long replacement cycle of 40 months may put a further squeeze on this sector of the smartphone industry.
H/T: CPR
Read next: Global IoT Connections Grew by 29% in 2022
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Analyzing the Performance of the ChatGPT Application and Third-Party Applications
The introduction of ChatGPT has sparked extensive discussions regarding the future of third-party applications. With the official ChatGPT app having been released for several weeks now, it provides an opportunity to delve deeper into its influence on the existing app landscape. By examining the market dynamics and user preferences, we can gain valuable insights into the potential impact of ChatGPT on third-party app developers and their offerings.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the environment in which ChatGPT was introduced, a thorough examination was carried out by AF on the leading third-party ChatGPT applications, namely Genie, Ask AI, and Chat AI. The main objective of this investigation was to monitor the weekly revenue generated by these applications, both before and after the introduction of ChatGPT. It is crucial to highlight that this evaluation exclusively pertains to ChatGPT not being presently accessible on the Android platform, limiting its availability to the App Store.
Before ChatGPT was officially launched in early May, the three apps in question were generating an estimated weekly revenue of $92,000, $511,000, and $805,000. These numbers indicate the net revenue, which signifies the amount of earnings developers retained after Apple's share was subtracted.
Ask AI emerges as the frontrunner in the AI app market, showcasing impressive revenue figures. It is important to bear in mind that these figures represent weekly earnings, highlighting the competitiveness of all three apps in the market. Upon its release, ChatGPT made a notable entrance by generating a respectable $164,000 in its inaugural week. Notably, the rival apps maintained a relatively steady performance during this period. However, the subsequent week witnessed a substantial increase in ChatGPT's net revenue, surpassing the previous figures and reaching an impressive $446,000. In contrast, competitors experienced a decline in their revenue, although the magnitude of the decrease varied. Ask AI observed a minor decrease in earnings, whereas Genie encountered a more significant
drop in its revenue stream.
As time passed, the rate of ChatGPT's expansion started to decelerate. The initial enthusiasm waned, resulting in intriguing changes in the figures observed in the final week.
The revenue of Ask AI showed a significant increase, reaching $847,000, signifying its ability to withstand challenges and maintain a trajectory of growth. Conversely, Genie faced a decline in revenue even prior to the launch of ChatGPT, and this trend persisted in the following weeks, with its revenue plummeting to $296,000. Chat AI experienced a slight rise, reaching $98,000, while ChatGPT's revenue stabilized at $278,000.
After carefully examining the extensive data available, it becomes clear that third-party apps remain relevant and have not become outdated. The general public has not fully connected ChatGPT's official app with the considerable excitement surrounding the remarkable functionalities of the mobile application ChatGPT. This paradox is clearly evident when observing the revenue figures.
Except for Genie, which had been experiencing a decline in performance even before ChatGPT entered the scene, the market for AI apps remains on a steady growth trajectory. This reiterates a previous observation that, despite the remarkable capabilities of ChatGPT, there is still a lack of familiarity among users regarding its effective utilization. As a result, emphasis should be placed on the development of innovative tools that harness the full potential of ChatGPT, rather than solely relying on the capabilities of ChatGPT itself.
In summary, the release of ChatGPT's official app has not rendered third-party apps obsolete. These apps continue to demonstrate resilience and maintain growth in the face of ChatGPT's entry into the market. The true potential of ChatGPT lies in its integration into innovative tools that leverage its capabilities, ultimately expanding its reach and impact on users' experiences.
Read next: 67% of Marketing Firms Increase Funding for Influencers
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the environment in which ChatGPT was introduced, a thorough examination was carried out by AF on the leading third-party ChatGPT applications, namely Genie, Ask AI, and Chat AI. The main objective of this investigation was to monitor the weekly revenue generated by these applications, both before and after the introduction of ChatGPT. It is crucial to highlight that this evaluation exclusively pertains to ChatGPT not being presently accessible on the Android platform, limiting its availability to the App Store.
Before ChatGPT was officially launched in early May, the three apps in question were generating an estimated weekly revenue of $92,000, $511,000, and $805,000. These numbers indicate the net revenue, which signifies the amount of earnings developers retained after Apple's share was subtracted.
Ask AI emerges as the frontrunner in the AI app market, showcasing impressive revenue figures. It is important to bear in mind that these figures represent weekly earnings, highlighting the competitiveness of all three apps in the market. Upon its release, ChatGPT made a notable entrance by generating a respectable $164,000 in its inaugural week. Notably, the rival apps maintained a relatively steady performance during this period. However, the subsequent week witnessed a substantial increase in ChatGPT's net revenue, surpassing the previous figures and reaching an impressive $446,000. In contrast, competitors experienced a decline in their revenue, although the magnitude of the decrease varied. Ask AI observed a minor decrease in earnings, whereas Genie encountered a more significant
drop in its revenue stream.
As time passed, the rate of ChatGPT's expansion started to decelerate. The initial enthusiasm waned, resulting in intriguing changes in the figures observed in the final week.
The revenue of Ask AI showed a significant increase, reaching $847,000, signifying its ability to withstand challenges and maintain a trajectory of growth. Conversely, Genie faced a decline in revenue even prior to the launch of ChatGPT, and this trend persisted in the following weeks, with its revenue plummeting to $296,000. Chat AI experienced a slight rise, reaching $98,000, while ChatGPT's revenue stabilized at $278,000.
After carefully examining the extensive data available, it becomes clear that third-party apps remain relevant and have not become outdated. The general public has not fully connected ChatGPT's official app with the considerable excitement surrounding the remarkable functionalities of the mobile application ChatGPT. This paradox is clearly evident when observing the revenue figures.
Except for Genie, which had been experiencing a decline in performance even before ChatGPT entered the scene, the market for AI apps remains on a steady growth trajectory. This reiterates a previous observation that, despite the remarkable capabilities of ChatGPT, there is still a lack of familiarity among users regarding its effective utilization. As a result, emphasis should be placed on the development of innovative tools that harness the full potential of ChatGPT, rather than solely relying on the capabilities of ChatGPT itself.
In summary, the release of ChatGPT's official app has not rendered third-party apps obsolete. These apps continue to demonstrate resilience and maintain growth in the face of ChatGPT's entry into the market. The true potential of ChatGPT lies in its integration into innovative tools that leverage its capabilities, ultimately expanding its reach and impact on users' experiences.
Read next: 67% of Marketing Firms Increase Funding for Influencers
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
Seven Outdated Software Development Methodologies to Leave Behind
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, the software development industry finds itself at a crossroads. As the demand for cutting-edge applications and systems intensifies, clinging to outdated methodologies becomes a hindrance rather than a virtue. It's time to break free from the shackles of the past and embrace a new era of innovation, efficiency, and forward-thinking methodologies. In this piece, we'll touch upon seven approaches that no longer align with the needs of today's digital landscape.
The number of businesses vulnerable to attacks is impressive. As reported by Statista, the United States alone experienced 1802 data compromises in the year 2022. FEMA states that 40% of businesses affected by data loss end up closing.
Waterfall implies a linear progression, where each SDLC stage flows in a rigid sequence. The sequential nature, once considered a strength, now stifles innovation and adaptability.
Among the glaring pitfalls of Waterfall is its inflexibility to accommodate changes. Modifications or additions to requirements are hard to implement once a particular phase is over. This lack of adaptability often leads to rigid workflows that struggle to keep up with evolving project needs, leading to missed opportunities and compromised outcomes. When working linearly, the phases usually take a long time since each one needs to be done before moving on.
In contrast, the Agile approach is a transformative force in the entire industry. It prioritizes flexibility, collaboration, and incremental progress. Its emphasis on close collaboration and frequent communication fosters a shared understanding of project goals and encourages stakeholders to actively participate in the process.
BDUF, as its name suggests, advocates for extensive upfront planning and design before any code is written. The intention is to foresee and address potential challenges and requirements in a comprehensive manner. However, this approach often leads to analysis paralysis, where works are delayed while specialists laboriously attempt to predict every conceivable scenario.
A major issue with BDUF is that it assumes the requirements for a project must be accurately identified and completely understood before the work on it begins. In reality, the IT sector is dynamic, and requirements evolve as stakeholders gain deeper insights and feedback from users. By fixating on a rigid set of initial requirements, organizations risk building a product that no longer aligns with the evolving needs of the market and end-users.
In contrast, iterative and incremental approaches, such as Agile and Lean, have gained prominence by embracing a more adaptive mindset. They advocate for smaller, iterative cycles. Thus, specialists can gather feedback and introduce important changes in a timely manner.
This process is called this way due to the form it creates, with development and testing tasks moving forward in tandem yet in a methodical and sequential fashion. Every step of the V-model ties in with a certain stage in the SDLC. The aim of this tactic is to make sure that every step is finished before going on to the following one.
However, this rigid structure poses challenges in an environment where requirements are subject to change, market demands shift, and customer expectations grow. The fact that it is linear makes it hard to adjust to modifications after a phase is finished, which can cause setbacks, extra work, and a lack of ability to respond to urgent demands without delay.
A major issue is that testing is mainly done at the end of the development process. QA activities usually take place at the tail end of the procedure, meaning any issues or defects may not be detected until late in the process, which can make it costlier and time-consuming to correct them.
By shifting from the rigidity of the V-model to the Agile methodology, businesses can unlock numerous benefits. Adopting modern approaches provides a pathway, allowing organizations to manage complexity, react to alteration, and provide top-notch custom solutions that answer the continually changing needs of users and the market.
RUP suggests a set of repetitive and gradual cycles, each including stages such as inception, elaboration, construction, and transition. They help establish a good roadmap, define requirements, design the system, create software components, and ensure proper deployment and maintenance. Its strength lies in its ability to provide structure and guidance throughout the SDLC.
However, the heavyweight and documentation-centric nature of RUP can introduce challenges in today's software industry. The extensive documentation requirements can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, diverting valuable effort away from actual development and impeding responsiveness to changing customer needs. The rigid phase-based approach of RUP can limit adaptability, making it difficult to address changing requirements.
While RUP provided valuable insights into software creation processes, it no longer aligns with the need for speed, adaptability, and responsiveness in today's IT industry. Agile alternatives, such as Scrum and Extreme Programming (XP), offer a compelling solution, enabling organizations to streamline their workflows and deliver custom software solutions that clients find efficient.
Risk management plays a significant role within the Spiral model. The process is divided into four phases: setting the goal, assessing the risk and engineering, creating and validating, and planning the next cycle. Each phase involves iterative cycles where the software evolves through repeated prototyping and refinement. However, it has certain limitations that hinder its effectiveness. Its focus on risk management can sometimes lead to excessive planning and documentation, resulting in a slower pace. Additionally, the model assumes that risks can be adequately identified and managed in the early stages, which may not always hold true.
To address these limitations, more adaptive approaches have gained popularity. The iterative and incremental development of Scrum and Kanban gives us the ability to have shorter feedback loops and greater collaboration with stakeholders. They prioritize building software in increments, which helps professionals gather feedback early and incorporate changes as they arise.
In a traditional monolithic architecture, the entire application is developed as a single, tightly integrated unit. This approach often leads to challenges such as a lack of modularity, difficulties in scaling specific components independently, and increased complexity in making changes or introducing new features. As the demands of modern applications and user expectations continue to evolve, organizations are recognizing the limitations of monolithic architectures and seeking alternatives that can better address these challenges.
Microservices architecture offers a paradigm shift by segmenting the application into a collection of smaller, autonomous services that interact through well-defined APIs. Every service is directed at a certain business capability, permitting teams to autonomously create, deploy, and expand various components. This modular approach enables faster cycles, as specialists of various profiles work simultaneously.
Additionally, microservices make it easier to be agile and creative by allowing organizations to incorporate new technologies and frameworks without causing disruption to the entire system. Teams can opt for the most fitting technology stack for every service, making use of the strengths of distinct programming languages, frameworks, and databases. Organizations can take advantage of this flexibility to keep improving, try new methods, and quickly change to fit the changing market.
In many cases, extensive requirements documents, detailed design specifications, and comprehensive user manuals become outdated quickly, fail to reflect changing project needs and act as barriers to rapid development and iterative improvement.
The shift towards Agile documentation practices emphasizes the value of simplicity, collaboration, and adaptability. Instead of lengthy and exhaustive documents, development teams strive to create concise and targeted artifacts that serve immediate project needs. This approach creates an environment of frequent communication, feedback, and collaboration between stakeholders, helping them to stay aligned and make sound decisions.
The seven outdated methodologies listed above have served their purpose in the past but now hinder the agility and efficiency that modern custom solutions demand. By embracing more iterative, adaptive, and user-centric approaches such as Agile, Lean, and microservices, organizations can unlock new levels of productivity, collaboration, and responsiveness in their software products.
About Author: This post is written by Valentin Kuzmenko, who "works in close cooperation with customers to define, craft, and improve high-performing software solutions across numerous industries".
by Web Desk via Digital Information World
Risks associated with outdated methodologies
As technology relentlessly propels forward, clinging to obsolete software development methodologies can cast a long shadow of risks over organizations. These can inflict serious damage on both operational efficiency and overall business success. And here is why:Stagnant security mechanisms
Outdated methodologies are akin to leaving your organization's digital assets vulnerable to unrelenting cyber threats. With every passing day, hackers refine their techniques, exploiting the weaknesses and unpatched vulnerabilities prevalent in outdated technologies. The consequences can range from sensitive data breaches and customer privacy violations to reputational damage and financial loss.The number of businesses vulnerable to attacks is impressive. As reported by Statista, the United States alone experienced 1802 data compromises in the year 2022. FEMA states that 40% of businesses affected by data loss end up closing.
Poor compatibility
As hardware and software advance, clinging to outdated methodologies breeds a dissonance that fragments operational harmony. Legacy systems struggle to integrate with modern tools and platforms, hindering collaboration, data sharing, and interoperability. The resulting rifts impede the seamless flow of information, stifling productivity and eroding the competitive edge.Poor support
Over time, support for outdated software becomes weaker and weaker. As vendors shift their focus towards newer technologies and order innovative custom solutions, older systems are no longer properly maintained.Lower performance
Like an aging athlete unable to keep pace with their younger counterparts, outdated methodologies suffer from diminishing performance momentum. As modern approaches surge forward with optimized efficiency and streamlined workflows, legacy systems lumber under the weight of outdated processes, slower response times, and reduced productivity.Budgetary burdens and opportunity costs
The price of stagnation reaches beyond the confines of inefficiency, stretching into the realm of financial burdens and opportunity costs. Outdated software may demand specialized hardware, costly infrastructure maintenance, and labor-intensive workarounds that drain resources and strain budgets. Moreover, the opportunity cost of missed innovation, delayed product launches, and the inability to seize emerging market trends can prove far more expensive in the long run.Regulatory and compliance issues
As regulations change to keep pace with technological advancements, old-school methodologies turn into a regulatory minefield. Failure to comply with industry standards and data protection requirements exposes organizations to legal issues, hefty fines, and damage to reputations. Companies must ensure their custom software aligns with current regulations.Rigidity amidst Agile disruption
The rigidity of old approaches stands in stark contrast to the Agile mindset that powers innovation in the digital age. With an inability to address changing market demands and embrace emerging technologies and methodologies, businesses clinging to the past find themselves unable to adapt to current circumstances while their competitors surge forward.Waterfall
In the annals of software development, the Waterfall methodology stands as a relic of the past, a testament to a bygone era. Originating from a time when predictability and stability were highly valued, it offered a sense of order and structure. However, as the IT sector advances at an exponential pace, the limitations and inherent risks of this methodology become increasingly apparent.Waterfall implies a linear progression, where each SDLC stage flows in a rigid sequence. The sequential nature, once considered a strength, now stifles innovation and adaptability.
Among the glaring pitfalls of Waterfall is its inflexibility to accommodate changes. Modifications or additions to requirements are hard to implement once a particular phase is over. This lack of adaptability often leads to rigid workflows that struggle to keep up with evolving project needs, leading to missed opportunities and compromised outcomes. When working linearly, the phases usually take a long time since each one needs to be done before moving on.
In contrast, the Agile approach is a transformative force in the entire industry. It prioritizes flexibility, collaboration, and incremental progress. Its emphasis on close collaboration and frequent communication fosters a shared understanding of project goals and encourages stakeholders to actively participate in the process.
Big design up front
Big design up front once reigned as the holy grail of meticulous planning and exhaustive documentation. The allure of comprehensive blueprints and iron-clad specifications seemed irresistible. However, as the industry evolves and the need for agility and responsiveness grows, the drawbacks and limitations of BDUF become increasingly evident.BDUF, as its name suggests, advocates for extensive upfront planning and design before any code is written. The intention is to foresee and address potential challenges and requirements in a comprehensive manner. However, this approach often leads to analysis paralysis, where works are delayed while specialists laboriously attempt to predict every conceivable scenario.
A major issue with BDUF is that it assumes the requirements for a project must be accurately identified and completely understood before the work on it begins. In reality, the IT sector is dynamic, and requirements evolve as stakeholders gain deeper insights and feedback from users. By fixating on a rigid set of initial requirements, organizations risk building a product that no longer aligns with the evolving needs of the market and end-users.
In contrast, iterative and incremental approaches, such as Agile and Lean, have gained prominence by embracing a more adaptive mindset. They advocate for smaller, iterative cycles. Thus, specialists can gather feedback and introduce important changes in a timely manner.
V-model
This model has long been synonymous with conventional linear project execution. With its emphasis on meticulous planning and stage-by-stage strategy, it instilled a sense of order and control. However, as the software realm is getting more dynamic, the limitations of the V-model are becoming increasingly apparent.This process is called this way due to the form it creates, with development and testing tasks moving forward in tandem yet in a methodical and sequential fashion. Every step of the V-model ties in with a certain stage in the SDLC. The aim of this tactic is to make sure that every step is finished before going on to the following one.
However, this rigid structure poses challenges in an environment where requirements are subject to change, market demands shift, and customer expectations grow. The fact that it is linear makes it hard to adjust to modifications after a phase is finished, which can cause setbacks, extra work, and a lack of ability to respond to urgent demands without delay.
A major issue is that testing is mainly done at the end of the development process. QA activities usually take place at the tail end of the procedure, meaning any issues or defects may not be detected until late in the process, which can make it costlier and time-consuming to correct them.
By shifting from the rigidity of the V-model to the Agile methodology, businesses can unlock numerous benefits. Adopting modern approaches provides a pathway, allowing organizations to manage complexity, react to alteration, and provide top-notch custom solutions that answer the continually changing needs of users and the market.
Rational unified process
The rational unified process appeared as a prominent software development methodology in the late 1990s. It offered a structured and disciplined approach to building applications. It gained popularity for its emphasis on comprehensive documentation, phased cycles, and strict roles and responsibilities. However, modern organizations are seeking more flexible and adaptive alternatives to streamline their workflows.RUP suggests a set of repetitive and gradual cycles, each including stages such as inception, elaboration, construction, and transition. They help establish a good roadmap, define requirements, design the system, create software components, and ensure proper deployment and maintenance. Its strength lies in its ability to provide structure and guidance throughout the SDLC.
However, the heavyweight and documentation-centric nature of RUP can introduce challenges in today's software industry. The extensive documentation requirements can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, diverting valuable effort away from actual development and impeding responsiveness to changing customer needs. The rigid phase-based approach of RUP can limit adaptability, making it difficult to address changing requirements.
While RUP provided valuable insights into software creation processes, it no longer aligns with the need for speed, adaptability, and responsiveness in today's IT industry. Agile alternatives, such as Scrum and Extreme Programming (XP), offer a compelling solution, enabling organizations to streamline their workflows and deliver custom software solutions that clients find efficient.
Spiral model
This model, proposed by Barry Boehm in 1986, allows for risk-driven and iterative software development. It brings together the stages of the Waterfall model and the cyclical nature of prototyping, to create an approach that allows for changes to be made and risks to be identified and solved early on. While it has its merits, the ever-changing software industry calls for more adaptive and responsive software development methodologies.Risk management plays a significant role within the Spiral model. The process is divided into four phases: setting the goal, assessing the risk and engineering, creating and validating, and planning the next cycle. Each phase involves iterative cycles where the software evolves through repeated prototyping and refinement. However, it has certain limitations that hinder its effectiveness. Its focus on risk management can sometimes lead to excessive planning and documentation, resulting in a slower pace. Additionally, the model assumes that risks can be adequately identified and managed in the early stages, which may not always hold true.
To address these limitations, more adaptive approaches have gained popularity. The iterative and incremental development of Scrum and Kanban gives us the ability to have shorter feedback loops and greater collaboration with stakeholders. They prioritize building software in increments, which helps professionals gather feedback early and incorporate changes as they arise.
Traditional monolithic architecture
Once dominant, traditional monolithic architecture is now facing problems in meeting the demands of modern applications and dynamic business environments. Companies are moving towards microservices and modular development to achieve higher scalability, flexibility, and maintainability.In a traditional monolithic architecture, the entire application is developed as a single, tightly integrated unit. This approach often leads to challenges such as a lack of modularity, difficulties in scaling specific components independently, and increased complexity in making changes or introducing new features. As the demands of modern applications and user expectations continue to evolve, organizations are recognizing the limitations of monolithic architectures and seeking alternatives that can better address these challenges.
Microservices architecture offers a paradigm shift by segmenting the application into a collection of smaller, autonomous services that interact through well-defined APIs. Every service is directed at a certain business capability, permitting teams to autonomously create, deploy, and expand various components. This modular approach enables faster cycles, as specialists of various profiles work simultaneously.
Additionally, microservices make it easier to be agile and creative by allowing organizations to incorporate new technologies and frameworks without causing disruption to the entire system. Teams can opt for the most fitting technology stack for every service, making use of the strengths of distinct programming languages, frameworks, and databases. Organizations can take advantage of this flexibility to keep improving, try new methods, and quickly change to fit the changing market.
Heavyweight documentation
In traditional software development methodologies, heavyweight documentation has long been regarded as a necessary evil. Extensive documents, often outdated and hard to handle, have burdened developers and hindered flexibility and cooperation. But with Agile, companies are reevaluating the role of documentation and embracing flexible practices to improve efficiency and enhance the overall development process.In many cases, extensive requirements documents, detailed design specifications, and comprehensive user manuals become outdated quickly, fail to reflect changing project needs and act as barriers to rapid development and iterative improvement.
The shift towards Agile documentation practices emphasizes the value of simplicity, collaboration, and adaptability. Instead of lengthy and exhaustive documents, development teams strive to create concise and targeted artifacts that serve immediate project needs. This approach creates an environment of frequent communication, feedback, and collaboration between stakeholders, helping them to stay aligned and make sound decisions.
Conclusion
By leaving behind outdated methodologies and embracing more modern and effective alternatives, businesses can position themselves for success in the ever-evolving world of custom software solutions development. Therefore, present-day organizations should reassess their approach to the development process and adapt to the changing needs of the industry.The seven outdated methodologies listed above have served their purpose in the past but now hinder the agility and efficiency that modern custom solutions demand. By embracing more iterative, adaptive, and user-centric approaches such as Agile, Lean, and microservices, organizations can unlock new levels of productivity, collaboration, and responsiveness in their software products.
About Author: This post is written by Valentin Kuzmenko, who "works in close cooperation with customers to define, craft, and improve high-performing software solutions across numerous industries".
by Web Desk via Digital Information World
Sunday, June 18, 2023
Zoom Surpasses Remarkable Milestone in Mobile Revenue Generation
Zoom, a popular video conferencing app, has reached a significant achievement in generating revenue through its mobile platform. Following a surge in downloads during the pandemic, Zoom has successfully transformed these downloads into a large customer base consisting of paying users.
Last year in July, Zoom unveiled Zoom One Pro, an extensive package of advanced features designed to enhance the app's capabilities. Although it took a while for the app to gain popularity, it ended May on a high note, achieving its highest monthly revenue thus far and reaching a significant milestone in Zoom's progress. To put it succinctly, Zoom's triumph can be likened to a rapid rise reminiscent of its very name.
The achievement Zoom reached in May is truly impressive. The revenue generated within the app itself on the App Store surpassed the one million dollar mark, marking a significant milestone since the introduction of the new subscription. According to valuable data from App Intelligence, Zoom's net revenue for that month was a remarkable $1.2 million, which reflects the amount that Zoom retained after subtracting Apple's share.
During April, Zoom's net revenue came tantalizingly close to the one-million-dollar mark, estimated at $975,000. However, in May, it experienced an outstanding 23% surge, successfully crossing the newly established milestone.
Since the unveiling of Zoom One Pro in July 2022, Zoom has accumulated a substantial net revenue of $4.6 million from the App Store alone. Notably, this revenue is a result of global usage, with the United States accounting for only 34% of the total. While this contribution remains significant, it is lower than anticipated for a productivity and business-focused tool like Zoom. Preliminary expectations suggested a higher figure, but the diverse global distribution of revenue showcases Zoom's wide-reaching user base and its adoption across numerous regions.
The top five countries contributing to Zoom's revenue, alongside the United States, are Japan, the United Arab Emirates, Canada, and Brazil. Collectively, these nations represent slightly over 50% of Zoom's net revenue, amounting to approximately $2.5 million.
Interestingly, Zoom's revenue distribution extends beyond the top-performing countries, encompassing diverse markets such as Nepal and Yemen. Although the revenue contribution from these markets is relatively small, when combined, they contributed approximately $1,000 to Zoom's revenue.
Such a unique revenue distribution pattern on the App Store is not commonly observed. However, given Zoom's widespread popularity and extensive usage, it comes as no surprise. The broad global reach of Zoom's revenue signifies the app's wide user base and the successful adoption of the platform in various regions.
In summary, Zoom has achieved an impressive milestone in mobile revenue, with its net revenue in May surpassing the one-million-dollar mark. Despite the decline in downloads following the peak of the pandemic, Zoom has effectively monetized its substantial user base, resulting in a significant revenue stream. As the app continues to evolve and expand its offerings, Zoom remains a dominant force in the realm of video conferencing and remote collaboration, shaping the way individuals and businesses communicate worldwide.
Read next: Global IoT Connections Grew by 29% in 2022
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
Last year in July, Zoom unveiled Zoom One Pro, an extensive package of advanced features designed to enhance the app's capabilities. Although it took a while for the app to gain popularity, it ended May on a high note, achieving its highest monthly revenue thus far and reaching a significant milestone in Zoom's progress. To put it succinctly, Zoom's triumph can be likened to a rapid rise reminiscent of its very name.
The achievement Zoom reached in May is truly impressive. The revenue generated within the app itself on the App Store surpassed the one million dollar mark, marking a significant milestone since the introduction of the new subscription. According to valuable data from App Intelligence, Zoom's net revenue for that month was a remarkable $1.2 million, which reflects the amount that Zoom retained after subtracting Apple's share.
During April, Zoom's net revenue came tantalizingly close to the one-million-dollar mark, estimated at $975,000. However, in May, it experienced an outstanding 23% surge, successfully crossing the newly established milestone.
Since the unveiling of Zoom One Pro in July 2022, Zoom has accumulated a substantial net revenue of $4.6 million from the App Store alone. Notably, this revenue is a result of global usage, with the United States accounting for only 34% of the total. While this contribution remains significant, it is lower than anticipated for a productivity and business-focused tool like Zoom. Preliminary expectations suggested a higher figure, but the diverse global distribution of revenue showcases Zoom's wide-reaching user base and its adoption across numerous regions.
The top five countries contributing to Zoom's revenue, alongside the United States, are Japan, the United Arab Emirates, Canada, and Brazil. Collectively, these nations represent slightly over 50% of Zoom's net revenue, amounting to approximately $2.5 million.
Interestingly, Zoom's revenue distribution extends beyond the top-performing countries, encompassing diverse markets such as Nepal and Yemen. Although the revenue contribution from these markets is relatively small, when combined, they contributed approximately $1,000 to Zoom's revenue.
Such a unique revenue distribution pattern on the App Store is not commonly observed. However, given Zoom's widespread popularity and extensive usage, it comes as no surprise. The broad global reach of Zoom's revenue signifies the app's wide user base and the successful adoption of the platform in various regions.
In summary, Zoom has achieved an impressive milestone in mobile revenue, with its net revenue in May surpassing the one-million-dollar mark. Despite the decline in downloads following the peak of the pandemic, Zoom has effectively monetized its substantial user base, resulting in a significant revenue stream. As the app continues to evolve and expand its offerings, Zoom remains a dominant force in the realm of video conferencing and remote collaboration, shaping the way individuals and businesses communicate worldwide.
Read next: Global IoT Connections Grew by 29% in 2022
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
Telegram Revenue Grows and Hits $14 Million Mark Since Initiating Monetization
Telegram, a popular messaging app, has entered its first year of monetization, following the footsteps of other social platforms such as Snapchat and Twitter. To bolster their revenue streams, these platforms have initiated the practice of imposing charges on users for supplementary features, aiming to capitalize on their existing user base that primarily avails services for free.
Although Telegram is not traditionally considered a social platform, it has a significant user base that is accustomed to accessing everything for free, placing it in a similar category. While May did not mark Telegram's best month in terms of revenue, it still performed quite well. Based on Appfigures estimates, Telegram earned approximately $1.9 million in net revenue from the App Store during that month. This represents a slight increase compared to April and a substantial improvement compared to the previous year.
In the month of February, Telegram experienced a notable surge in revenue, marking a significant milestone in its financial trajectory. During this period, the net revenue generated from the App Store reached an impressive $2.3 million. It's important to highlight that this figure reflects the amount of revenue that Telegram retained after Apple's share was deducted. This remarkable boost in revenue not only distinguished Telegram from its competitors but also signaled a turning point in its monetization strategy. Since then, Telegram has been steadily progressing, surpassing its financial performance from the previous year.
As a result, within a span of just one year, Telegram has amassed an impressive $14 million in revenue from the App Store. It's worth mentioning that while a substantial portion of this revenue originated from Russia, Telegram's home country, the United States closely followed in terms of revenue contribution. This success underscores Telegram's ability to effectively monetize its large user base and establish a global presence in the messaging landscape.
Based on these estimates, Telegram has generated a substantial $14 million in revenue from the App Store within a span of one year. Russia emerged as the primary source of this revenue, with the United States closely following suit. Moreover, Ukraine, Hong Kong, and China rank among the top five countries in terms of their contributions to Telegram's revenue stream. This impressive financial achievement highlights Telegram's ability to attract a global user base and generate significant revenue from its services.
Out of all the three platforms that have been under observation, Snapchat has emerged as the undisputed frontrunner, achieving impressive monthly revenue figures in the millions throughout the month of May. On the other hand, Telegram still has considerable potential for expansion before it can attain similar levels of financial success. However, it is making consistent strides toward that goal, steadily moving in the right direction.
In conclusion, Telegram's strategic move to monetize its app has yielded impressive results, with significant revenue generated in a relatively brief timeframe. This success can be attributed to Telegram's ability to adapt and continuously introduce new features that entice users to invest in enhanced functionality. As Telegram further refines its offerings and expands its user base, it has the potential to emerge as a formidable player in the realm of app monetization. By striking a balance between providing value to its users and generating revenue, Telegram is well-positioned for future growth and continued success.
Read next: Big Tech Firms Know UK Citizens Prioritize Other Things Over Online Security And They’re Exploiting Them
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
Although Telegram is not traditionally considered a social platform, it has a significant user base that is accustomed to accessing everything for free, placing it in a similar category. While May did not mark Telegram's best month in terms of revenue, it still performed quite well. Based on Appfigures estimates, Telegram earned approximately $1.9 million in net revenue from the App Store during that month. This represents a slight increase compared to April and a substantial improvement compared to the previous year.
In the month of February, Telegram experienced a notable surge in revenue, marking a significant milestone in its financial trajectory. During this period, the net revenue generated from the App Store reached an impressive $2.3 million. It's important to highlight that this figure reflects the amount of revenue that Telegram retained after Apple's share was deducted. This remarkable boost in revenue not only distinguished Telegram from its competitors but also signaled a turning point in its monetization strategy. Since then, Telegram has been steadily progressing, surpassing its financial performance from the previous year.
As a result, within a span of just one year, Telegram has amassed an impressive $14 million in revenue from the App Store. It's worth mentioning that while a substantial portion of this revenue originated from Russia, Telegram's home country, the United States closely followed in terms of revenue contribution. This success underscores Telegram's ability to effectively monetize its large user base and establish a global presence in the messaging landscape.
Based on these estimates, Telegram has generated a substantial $14 million in revenue from the App Store within a span of one year. Russia emerged as the primary source of this revenue, with the United States closely following suit. Moreover, Ukraine, Hong Kong, and China rank among the top five countries in terms of their contributions to Telegram's revenue stream. This impressive financial achievement highlights Telegram's ability to attract a global user base and generate significant revenue from its services.
Out of all the three platforms that have been under observation, Snapchat has emerged as the undisputed frontrunner, achieving impressive monthly revenue figures in the millions throughout the month of May. On the other hand, Telegram still has considerable potential for expansion before it can attain similar levels of financial success. However, it is making consistent strides toward that goal, steadily moving in the right direction.
In conclusion, Telegram's strategic move to monetize its app has yielded impressive results, with significant revenue generated in a relatively brief timeframe. This success can be attributed to Telegram's ability to adapt and continuously introduce new features that entice users to invest in enhanced functionality. As Telegram further refines its offerings and expands its user base, it has the potential to emerge as a formidable player in the realm of app monetization. By striking a balance between providing value to its users and generating revenue, Telegram is well-positioned for future growth and continued success.
Read next: Big Tech Firms Know UK Citizens Prioritize Other Things Over Online Security And They’re Exploiting Them
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)