Apple has made a name for itself as a company that cares about privacy more than other companies in the same field. In spite of the fact that this is the case, it turns out that some of its default apps that come pre-loaded with brand new versions of phones might track you regardless of whether or not you have actually consented to this tracking. This information comes from a study conducted by researchers at Aalto University in Finland, and it involves apps such as Safari, iMessage, and Find My among others.
If we were to take the example of Siri, users have the option of setting it up later if they so choose. With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that Siri will still be collecting data in the background even if you haven’t set it up in the first place. It bears mentioning that this isn’t just an issue that has to do with Siri alone
Safari can collect information that is as sensitive as your credit card details, and iMessage along with Facetime both have the ability to access your call logs. As if that wasn't enough, they can also take a look at any and all apps that you have used at this current point in time. Some might read this and conclude that they can simply turn this tracking off in Settings, but that’s not quite how things work.
Even when a user switches off data sharing for particular apps, the information will still be sent to them with all things having been considered and taken into account. This data collection is happening in secret which is dangerous because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up compromising on something as basic as privacy.
The Family Sharing feature is yet another aspect of Apple products that might infringe on privacy. Your location and purchase history can be shared with family members, and this might be a serious privacy violation between partners as well as between children and their parents.
Image: DIW-AIgen
Read next: Meta's Active User Data Gap: Instagram's Individual Numbers Remain a Mystery
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
"Mr Branding" is a blog based on RSS for everything related to website branding and website design, it collects its posts from many sites in order to facilitate the updating to the latest technology.
To suggest any source, please contact me: Taha.baba@consultant.com
Wednesday, April 10, 2024
Meta's Active User Data Gap: Instagram's Individual Numbers Remain a Mystery
Meta has shared update about its number of users but it is not clear how many users each Meta app has individually. We already know that 3.065 billion people log in to Facebook every month but monthly users for Instagram are not known. 2022 was the last year when there was an update about Instagram's monthly users. According to that update, Instagram had 2 billion daily users and the number must have grown a lot in the last 2 years. We already know that Facebook has seen a decline in its daily users.
But last week, Meta had to show Instagram’s revenue figures because of Meta’s legal filing to FTC’s antitrust lawsuit. The lawsuit was asking Meta to sell WhatsApp and Instagram and Meta wanted to dismiss the lawsuit. The document that Meta showed to the court highlighted Instagram’s revenue. $11.3 billion were earned by Instagram in ad revenue in 2018 and $17.9 billion in 2019. It earned $22 billion and $32.4 billion revenue in 2020 and 2021 respectively. In the first half of 2022, Instagram earned $16.5 billion and earned more than $33 billion at the end of the same year.
30% of the total Meta's revenue was earned by Instagram in 2022, according to a report by Bloomberg. This suggests $40 billion of Meta's revenue was earned by Instagram in 2022. New app regulations by E.U also asks Meta to show its user count every six months. So according to the numbers given by Meta to E.U, there are 259 million monthly active users on Instagram in September 2023. Based on this, the US has approximately 175 million users and Asia has 750 million users, with India being Instagram’s biggest market. All these numbers total up to Instagram having about 2 billion users worldwide. These are not official numbers, but they provide an estimation based on the number of users Instagram has.
Image: DIW-AIgen
Read next: How Does the Tone of Your Prompts Impact LLM Output
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
But last week, Meta had to show Instagram’s revenue figures because of Meta’s legal filing to FTC’s antitrust lawsuit. The lawsuit was asking Meta to sell WhatsApp and Instagram and Meta wanted to dismiss the lawsuit. The document that Meta showed to the court highlighted Instagram’s revenue. $11.3 billion were earned by Instagram in ad revenue in 2018 and $17.9 billion in 2019. It earned $22 billion and $32.4 billion revenue in 2020 and 2021 respectively. In the first half of 2022, Instagram earned $16.5 billion and earned more than $33 billion at the end of the same year.
30% of the total Meta's revenue was earned by Instagram in 2022, according to a report by Bloomberg. This suggests $40 billion of Meta's revenue was earned by Instagram in 2022. New app regulations by E.U also asks Meta to show its user count every six months. So according to the numbers given by Meta to E.U, there are 259 million monthly active users on Instagram in September 2023. Based on this, the US has approximately 175 million users and Asia has 750 million users, with India being Instagram’s biggest market. All these numbers total up to Instagram having about 2 billion users worldwide. These are not official numbers, but they provide an estimation based on the number of users Instagram has.
Image: DIW-AIgen
Read next: How Does the Tone of Your Prompts Impact LLM Output
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Tuesday, April 9, 2024
How Does the Tone of Your Prompts Impact LLM Output
There are a number of ways in which you might go about submitting prompts to ChatGPT. Some might offer an elaborate framework in which the response must be formatted, others would start with a simple greeting, and others still might offer a metaphorical tip for the services that the LLM using chatbot is providing at this current point in time. It turns out that the manner in which you approach these prompts can vastly change the responses that one can receive.
According to Abel Salinas, who works at the USC Information Sciences Institute as a researcher, he and his team were eager to ascertain how various prompts can change output. He collaborated with Fred Morstatter, who leads the team at ISI and also works as the research Assistant Professor of computer science at the USC’s Viterbi School of Engineering, to find an answer to the question at hand. It is important to note that the prompts that they utilized were split into four basic categories.
The first category involved specifying the format of the response, such as requiring it to be in a list. Secondly, they analyzed how minor differences such as unnecessary spaces as well as various kinds of greetings would impact the type of response that they would end up receiving. The third type had to do with jailbreaks, such as asking the AI to answer like it was evil, and finally, the researchers tried offering tips to see how this would affect things.
The various prompts were then tested against 11 different benchmark texts that involved text classification. These are standardized tests that are quite commonplace in LLM research since they can help determine the overall efficiency of the Natural Language Processing of any given system.
The first test involved saying “Howdy!”, and researchers realized that it definitely improved responses with all things having been considered and taken into account. In fact, relatively tiny differences in the style of prompt could have extremely significant changes to the type of response that would be received, which just goes to show how much of an impact these things can end up having.
10% of predictions changed when the output format was specified, and jailbreaks created the biggest changes of all. In spite of the fact that this is the case, the scale of change was largely contingent on the type of jailbreak used. It will be interesting to see where things go from here on out, since studies like this are critical for shaping our understanding of LLMs and how they function in the here and now.
Image: DIW-Aigen
Read next: Google Rolls Out New Updates For Its Gemma AI Models But No Fix For Gemini In Sight Despite Controversy
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
According to Abel Salinas, who works at the USC Information Sciences Institute as a researcher, he and his team were eager to ascertain how various prompts can change output. He collaborated with Fred Morstatter, who leads the team at ISI and also works as the research Assistant Professor of computer science at the USC’s Viterbi School of Engineering, to find an answer to the question at hand. It is important to note that the prompts that they utilized were split into four basic categories.
The first category involved specifying the format of the response, such as requiring it to be in a list. Secondly, they analyzed how minor differences such as unnecessary spaces as well as various kinds of greetings would impact the type of response that they would end up receiving. The third type had to do with jailbreaks, such as asking the AI to answer like it was evil, and finally, the researchers tried offering tips to see how this would affect things.
The various prompts were then tested against 11 different benchmark texts that involved text classification. These are standardized tests that are quite commonplace in LLM research since they can help determine the overall efficiency of the Natural Language Processing of any given system.
The first test involved saying “Howdy!”, and researchers realized that it definitely improved responses with all things having been considered and taken into account. In fact, relatively tiny differences in the style of prompt could have extremely significant changes to the type of response that would be received, which just goes to show how much of an impact these things can end up having.
10% of predictions changed when the output format was specified, and jailbreaks created the biggest changes of all. In spite of the fact that this is the case, the scale of change was largely contingent on the type of jailbreak used. It will be interesting to see where things go from here on out, since studies like this are critical for shaping our understanding of LLMs and how they function in the here and now.
Image: DIW-Aigen
Read next: Google Rolls Out New Updates For Its Gemma AI Models But No Fix For Gemini In Sight Despite Controversy
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Google Gets Rid Of Its ‘Thumbs Down’ Feature After Arguments Over The Gaza-Israel War
Search engine giant Google has made a bold decision to say yes to a change across its internal message board.
The tech giant has opted to eliminate the tone-down feature found on a platform where employees have long been sharing memes for more than ten years. This is right after the workers ended up getting into heated debates with each other on the subject of the Israel-Palestine war in the Gaza Strip.
These changes as confirmed in a recently published report by The New York Times spoke of getting rid of options for thumbs-down on every post.
For those who might not be aware, the popular Memegen was a top spot for workers to laugh and joke about both the organization and those in charge of its leadership. Moreover, this popular meme generator is quite often utilized to put out the sentiments of employees who might not be able to do so elsewhere.
This particular meme generator had people often complaining about matters such as too much corporate work or overload and even mocking the figure for AI models which every firm has rolled out too.
This feature is awfully similar to the Reddit app and it has ended up upvoting memes and therefore pushing them at the forefront while downvoting memes that were not as popular. For example, such corporate overlords would entail layoffs in January and that got plenty of upvotes as predicted and shown by media outlet, The Verge.
Additionally, getting rid of thumbs down means saying hello to Google ridding matters like metrics that display a certain post’s popularity.
A few workers were concerned about changes ruining a certain texting board which Googlers have tried long and hard to speak freely and so candidly regarding some firm. Moreover, a certain employee was getting close to 8000 likes across a post where they would ask for changes like killing Memegen.
Another rep for Google added how the team is working toward its goal of conducting experiments with similarly trending industry practices which are in line with what is witnessed across various internal and external social media apps.
The changes are all set to take center stage this year so that means soon. And it’s actually happening because Google really takes feedback from all of its employees very seriously. It also reiterated how a thumbs down is a gesture that could end up making people feel so awful about themselves.
Media outlet The Times also mentioned how a memo sent internally through Google had some moderators agreeing with the decision that these kinds of gestures were more linked to bullying than anything else.
For now, Google is yet to roll out any requests for comments but these actions are proof about how strongly it feels. After all, the Israel-Palestinian war has been a source of massive controversy for so long at the company.
If you go back to the year 2021, nearly 250 employees called the firm to get rid of contracts generated with Israel after the latter’s forces conducted strikes in the Gaza Strip.
We even saw one staffer at Google quit and added how so many were being forced to suffer for showing support to Palestine so openly. A moment after that, more than 100 Google workers gathered to show their opposition to the company’s Project Nimbus which is the term reserved for a $1.2 billion contract featuring cloud computing with links to Israel.
Speaking to The Times in the past, Google workers did agree that tensions and slowly rising in the firm and many had serious issues with the growing figures of antisemitic posts while others felt they couldn’t let their voice or opinion out on the controversial topic.
In the past month, Google fired one of its workers who carried out a protest in Israel at the company’s NYC conference linked to Project Nimbus. The worker’s contract was terminated because he ended up disrupting another fellow colleague’s presentation.
Image: AIgen
Read next: Research Finds 54 Billion Cookies for Sale on the Dark Web
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
The tech giant has opted to eliminate the tone-down feature found on a platform where employees have long been sharing memes for more than ten years. This is right after the workers ended up getting into heated debates with each other on the subject of the Israel-Palestine war in the Gaza Strip.
These changes as confirmed in a recently published report by The New York Times spoke of getting rid of options for thumbs-down on every post.
For those who might not be aware, the popular Memegen was a top spot for workers to laugh and joke about both the organization and those in charge of its leadership. Moreover, this popular meme generator is quite often utilized to put out the sentiments of employees who might not be able to do so elsewhere.
This particular meme generator had people often complaining about matters such as too much corporate work or overload and even mocking the figure for AI models which every firm has rolled out too.
This feature is awfully similar to the Reddit app and it has ended up upvoting memes and therefore pushing them at the forefront while downvoting memes that were not as popular. For example, such corporate overlords would entail layoffs in January and that got plenty of upvotes as predicted and shown by media outlet, The Verge.
Additionally, getting rid of thumbs down means saying hello to Google ridding matters like metrics that display a certain post’s popularity.
A few workers were concerned about changes ruining a certain texting board which Googlers have tried long and hard to speak freely and so candidly regarding some firm. Moreover, a certain employee was getting close to 8000 likes across a post where they would ask for changes like killing Memegen.
Another rep for Google added how the team is working toward its goal of conducting experiments with similarly trending industry practices which are in line with what is witnessed across various internal and external social media apps.
The changes are all set to take center stage this year so that means soon. And it’s actually happening because Google really takes feedback from all of its employees very seriously. It also reiterated how a thumbs down is a gesture that could end up making people feel so awful about themselves.
Media outlet The Times also mentioned how a memo sent internally through Google had some moderators agreeing with the decision that these kinds of gestures were more linked to bullying than anything else.
For now, Google is yet to roll out any requests for comments but these actions are proof about how strongly it feels. After all, the Israel-Palestinian war has been a source of massive controversy for so long at the company.
If you go back to the year 2021, nearly 250 employees called the firm to get rid of contracts generated with Israel after the latter’s forces conducted strikes in the Gaza Strip.
We even saw one staffer at Google quit and added how so many were being forced to suffer for showing support to Palestine so openly. A moment after that, more than 100 Google workers gathered to show their opposition to the company’s Project Nimbus which is the term reserved for a $1.2 billion contract featuring cloud computing with links to Israel.
Speaking to The Times in the past, Google workers did agree that tensions and slowly rising in the firm and many had serious issues with the growing figures of antisemitic posts while others felt they couldn’t let their voice or opinion out on the controversial topic.
In the past month, Google fired one of its workers who carried out a protest in Israel at the company’s NYC conference linked to Project Nimbus. The worker’s contract was terminated because he ended up disrupting another fellow colleague’s presentation.
Image: AIgen
Read next: Research Finds 54 Billion Cookies for Sale on the Dark Web
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
Research Finds 54 Billion Cookies for Sale on the Dark Web
Pretty much anything can be found for sale on the Dark Web, and this goes for cookies just as much as anything else. Researchers working at Nord VPN uncovered a dataset containing a whopping 54 billion cookies for sale on the Dark Web, and it’s just one of the many listings of this nature that can be found. As a result of the fact that this is the case, these researchers sought to analyze where these cookies came from, how they were stolen, as well as the type of information that they contained at this current point in time.
It is important to note that there are four types of cookies that must be discussed in the here and now. The first type are called first party cookies, and they’re basically created whenever you visit a particular website. This allows the site to store your log in details for easy access, as well as to customize the site based on your own personal preferences. These cookies can be used to steal sensitive information from you by malicious actors.
Another type of cookie worth mentioning are third party cookies. They’re used by sites other than the one you’re currently browsing, and they provide inter-site tracking as well as analytical data with all things having been considered and taken into account. This data can include things like your age, gender, sexual orientation, and other private information that can do a lot of harm if it ends up in the wrong hands. They can also result in you getting tracked in some way, shape or form.
And then there is the category of Super Cookies, which many people don’t know the first thing about. They are similar to standard cookies, except that they are a great deal more intrusive than might have been the case otherwise. They’re exceptionally challenging to locate let alone remove, which is quite different from first and third party cookies that are usually relatively easy to delete. They’re generally implemented by ISPs and can create a complete picture of who someone is.
Finally, there’s the classification of so-called “zombie” cookies. These are a subcategory of super cookies that replaces deleted cookies through stored information from places other than the dedicated cookie area within the web browser. The main issue with them is that they can allow hackers to scrape your data and also allow for a concerningly high amount of tracking.
As for how these cookies end up getting stolen, oftentimes it has to do with the use of malware. The three most prevalent forms of malware that are used for the purposes of stealing cookies are keyloggers, trojans, as well as info stealers. The most commonplace malware of all was the info stealer and keylogger called Redline of which there have been 30 billion instances 9 billion of which are currently active.
As per researchers, sellers tagged cookies with keywords indicating data type. Popular keywords included "assigned ID" (10.5B), "session ID" (739M), "authentication" (154M), and "login" (37M). These cookies often store personal data like names, emails, and addresses, posing a risk of cyberattacks. Active cookies could enable cybercriminals to access personal accounts and launch targeted attacks.
It bears mentioning that this malware is available as a service for the price of $100 per month, which just goes to show how easy it has become to use malware to steal cookies and for other nefarious purposes. More work must be done to prevent these cookies from ending up in the wrong hands.
Read next: Price Of Hacking Tools That Can Break Into Top Devices And Apps Soar As Companies Step Up Security
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
It is important to note that there are four types of cookies that must be discussed in the here and now. The first type are called first party cookies, and they’re basically created whenever you visit a particular website. This allows the site to store your log in details for easy access, as well as to customize the site based on your own personal preferences. These cookies can be used to steal sensitive information from you by malicious actors.
Another type of cookie worth mentioning are third party cookies. They’re used by sites other than the one you’re currently browsing, and they provide inter-site tracking as well as analytical data with all things having been considered and taken into account. This data can include things like your age, gender, sexual orientation, and other private information that can do a lot of harm if it ends up in the wrong hands. They can also result in you getting tracked in some way, shape or form.
And then there is the category of Super Cookies, which many people don’t know the first thing about. They are similar to standard cookies, except that they are a great deal more intrusive than might have been the case otherwise. They’re exceptionally challenging to locate let alone remove, which is quite different from first and third party cookies that are usually relatively easy to delete. They’re generally implemented by ISPs and can create a complete picture of who someone is.
Finally, there’s the classification of so-called “zombie” cookies. These are a subcategory of super cookies that replaces deleted cookies through stored information from places other than the dedicated cookie area within the web browser. The main issue with them is that they can allow hackers to scrape your data and also allow for a concerningly high amount of tracking.
As for how these cookies end up getting stolen, oftentimes it has to do with the use of malware. The three most prevalent forms of malware that are used for the purposes of stealing cookies are keyloggers, trojans, as well as info stealers. The most commonplace malware of all was the info stealer and keylogger called Redline of which there have been 30 billion instances 9 billion of which are currently active.
As per researchers, sellers tagged cookies with keywords indicating data type. Popular keywords included "assigned ID" (10.5B), "session ID" (739M), "authentication" (154M), and "login" (37M). These cookies often store personal data like names, emails, and addresses, posing a risk of cyberattacks. Active cookies could enable cybercriminals to access personal accounts and launch targeted attacks.
It bears mentioning that this malware is available as a service for the price of $100 per month, which just goes to show how easy it has become to use malware to steal cookies and for other nefarious purposes. More work must be done to prevent these cookies from ending up in the wrong hands.
Read next: Price Of Hacking Tools That Can Break Into Top Devices And Apps Soar As Companies Step Up Security
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Monday, April 8, 2024
Price Of Hacking Tools That Can Break Into Top Devices And Apps Soar As Companies Step Up Security
Zero-day exploit tools are designed to help hackers of the government break into all sorts of leading apps such as WhatsApp as well as Android and iOS phones. But just when you thought this was the ideal means of 'hacking' comes some very interesting news.
You can now delve into famous software present on both Chrome and Safari browsers as well as messaging platforms through such means but at a much higher cost than before. And it's not quite what regulators wish to hear for obvious reasons.
But wait, the pricing has soared to a new high, multiplying several folds in the past couple of years. And today, such tools come at a staggering cost of millions of dollars. The reason is simple, companies are making it harder for such tools to combat serious security barriers.
So at the end of the day, it’s getting much harder to actually do what the tool promises to do and that is hack various leading platforms.
We saw tech giant Crowdefense recently rolled out its new and improved pricing list featuring hacking tools. These rely on all kinds of unpatched vulnerabilities found in the software that aren’t even known by the software’s makers.
Plenty of firms other than Crowdefense and its leading competitor are said to have acquired the tools to resell them to other top companies.
In most instances, it’s the government firms or contractors that keep on mentioning how they require the tools for spying or for tracking those breaking the law.
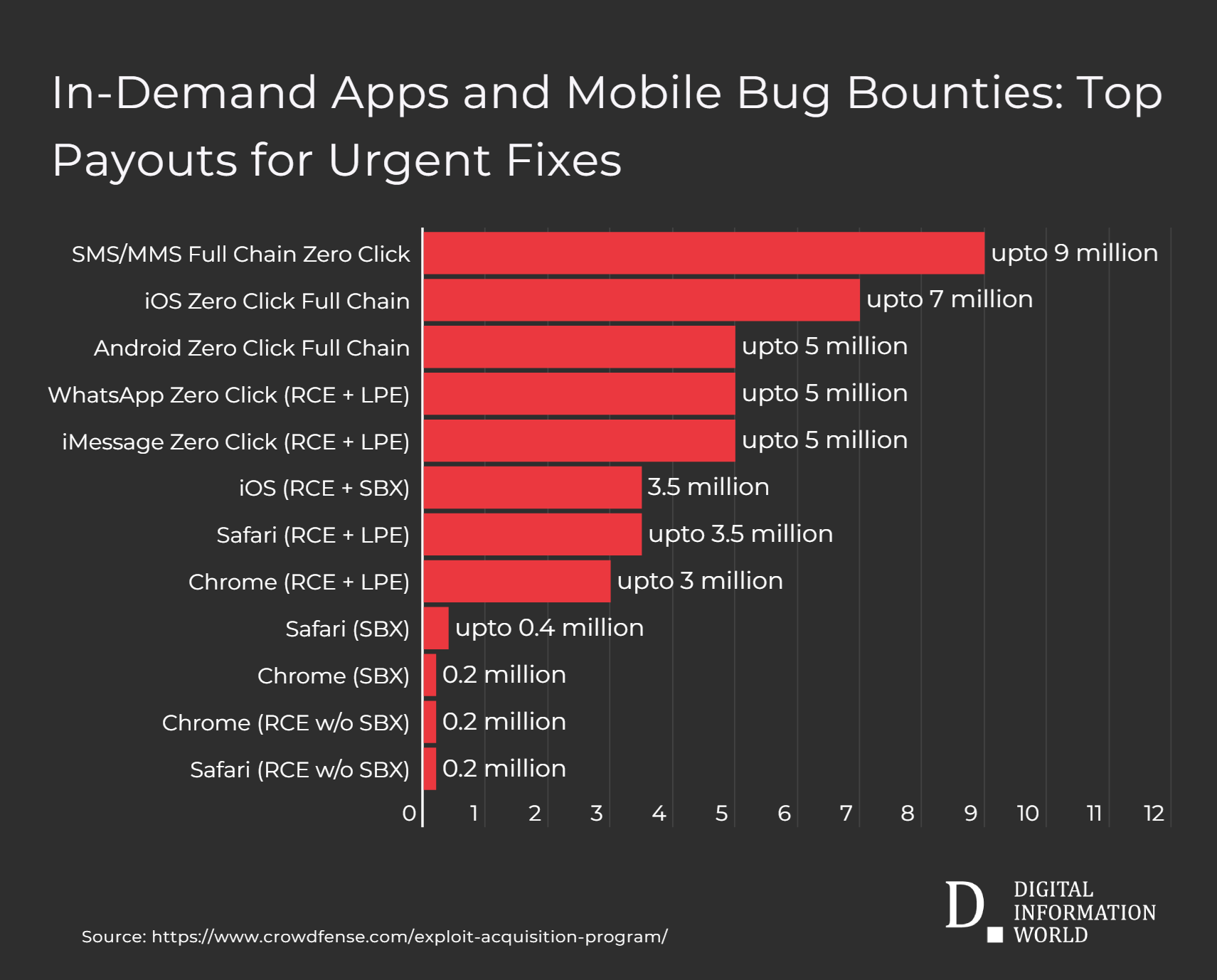
Today, Crowdfense offers around $5 to $7 million for the tools to get into devices, setting up close to $5 million for Android, and $3 million for browsers like Chrome and even Safari. The same is true for leading apps like WhatsApp or iMessage.
Another price list was rolled out in the past where it mentioned how Crowdfense was giving out $3 million for all devices in return for zero-day exploits.
The surge in pricing arrives when top tech giants such as Apple, Microsoft, and even Google are making it so much harder to enter devices through apps so in this manner, people stay more protected with time.
Year after year, it’s getting a little harder to exploit software on devices as companies do pay researchers to get the tools who then report them further to other organizations impacted with a simple goal. And that is to have the vulnerability fixed.
As more vulnerabilities continue to arise as we speak, intelligence agencies are putting in more effort toward ensuring how more platforms can improve and therefore adding greater security barriers.
So the effort that was once required by a hacker is now much greater, not to mention how much longer it would take for another sophisticated attack to arise.
Meanwhile, more studies are speaking about how it’s getting harder with each passing day for anyone to hack into a software or system. It’s hard to exploit a vulnerability, something that was unheard of in the past.
One security analyst by the name of David Manoucheri also added how targets arising from the likes of big names in the industry like Apple and Google really do realize that zero exploit tools are on the rise so they’re working effectively to combat them. This means saying hello to a trade that increases in complexity and transforms into something that is super time-consuming.
See, the little amendments that vendors are adding are actually working. It’s a big trade and something that goes above and beyond in regards to complexity. This is later on reflected in regards to greater costs.
We’ve got teams of researchers working hard, day and night, to crack the code in terms of how to enter the system. Prices keep soaring and the demand is there so it’s a never-ending vicious cycle.
The companies offering the greatest prices in public today are certainly those located right outside Russia. Russian prices might appear greater due to the current war carried out against Ukraine, not to mention the great number of sanctions that simply discourage and stop people from having relations with Russians.
So the tool is mighty, having multiple uses, and therefore as long as it gets the job done, people are willing to pay.
Read next: App Spending Soars to $288 Billion by 2030, 2.9 Trillion Downloads Expected
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
You can now delve into famous software present on both Chrome and Safari browsers as well as messaging platforms through such means but at a much higher cost than before. And it's not quite what regulators wish to hear for obvious reasons.
But wait, the pricing has soared to a new high, multiplying several folds in the past couple of years. And today, such tools come at a staggering cost of millions of dollars. The reason is simple, companies are making it harder for such tools to combat serious security barriers.
So at the end of the day, it’s getting much harder to actually do what the tool promises to do and that is hack various leading platforms.
We saw tech giant Crowdefense recently rolled out its new and improved pricing list featuring hacking tools. These rely on all kinds of unpatched vulnerabilities found in the software that aren’t even known by the software’s makers.
Plenty of firms other than Crowdefense and its leading competitor are said to have acquired the tools to resell them to other top companies.
In most instances, it’s the government firms or contractors that keep on mentioning how they require the tools for spying or for tracking those breaking the law.
Today, Crowdfense offers around $5 to $7 million for the tools to get into devices, setting up close to $5 million for Android, and $3 million for browsers like Chrome and even Safari. The same is true for leading apps like WhatsApp or iMessage.
Another price list was rolled out in the past where it mentioned how Crowdfense was giving out $3 million for all devices in return for zero-day exploits.
| Vulnerability Type | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| SMS/MMS Full Chain Zero Click | upto 9 million |
| iOS Zero Click Full Chain | upto 7 million |
| Android Zero Click Full Chain | upto 5 million |
| WhatsApp Zero Click (RCE + LPE) | upto 5 million |
| iMessage Zero Click (RCE + LPE) | upto 5 million |
| iOS (RCE + SBX) | 3.5 million |
| Safari (RCE + LPE) | upto 3.5 million |
| Chrome (RCE + LPE) | upto 3 million |
| Safari (SBX) | upto 0.4 million |
| Chrome (SBX) | 0.2 million |
| Chrome (RCE w/o SBX) | 0.2 million |
| Safari (RCE w/o SBX) | 0.2 million |
The surge in pricing arrives when top tech giants such as Apple, Microsoft, and even Google are making it so much harder to enter devices through apps so in this manner, people stay more protected with time.
Year after year, it’s getting a little harder to exploit software on devices as companies do pay researchers to get the tools who then report them further to other organizations impacted with a simple goal. And that is to have the vulnerability fixed.
As more vulnerabilities continue to arise as we speak, intelligence agencies are putting in more effort toward ensuring how more platforms can improve and therefore adding greater security barriers.
So the effort that was once required by a hacker is now much greater, not to mention how much longer it would take for another sophisticated attack to arise.
Meanwhile, more studies are speaking about how it’s getting harder with each passing day for anyone to hack into a software or system. It’s hard to exploit a vulnerability, something that was unheard of in the past.
One security analyst by the name of David Manoucheri also added how targets arising from the likes of big names in the industry like Apple and Google really do realize that zero exploit tools are on the rise so they’re working effectively to combat them. This means saying hello to a trade that increases in complexity and transforms into something that is super time-consuming.
See, the little amendments that vendors are adding are actually working. It’s a big trade and something that goes above and beyond in regards to complexity. This is later on reflected in regards to greater costs.
We’ve got teams of researchers working hard, day and night, to crack the code in terms of how to enter the system. Prices keep soaring and the demand is there so it’s a never-ending vicious cycle.
The companies offering the greatest prices in public today are certainly those located right outside Russia. Russian prices might appear greater due to the current war carried out against Ukraine, not to mention the great number of sanctions that simply discourage and stop people from having relations with Russians.
So the tool is mighty, having multiple uses, and therefore as long as it gets the job done, people are willing to pay.
Read next: App Spending Soars to $288 Billion by 2030, 2.9 Trillion Downloads Expected
by Dr. Hura Anwar via Digital Information World
App Spending Soars to $288 Billion by 2030, 2.9 Trillion Downloads Expected
According to a new report by Data.ai, the app spending in app stores will grow about 267% in this decade (2020-2023) and there will be an increase in app downloads too. The data shows that $288 billion are going to be spent on apps in 2030 alone which suggests that 2.9 trillion apps and games are going to be downloaded within these ten years. This will ultimately result in advancement and usage of mobile devices. Consumers all over the world spend an average 16 billion hours on mobile phones but these numbers are going to reach 58 trillion in this decade.
The apps on mobile phones have direct spending revenue of $2.2 trillion, excluding the amount earned by in-app spendings, which was $362 billion in just 2023. The report shows that the app economy has declined by 2% in the last 15 years and there are various factors that became the reason for it. Inflation, limited income, privacy changes and global pandemic are some to name. Even with this slight decline, apps generated $171 billion in consumer dollars in 2023. This is because the mobile users are increasing and apps are making the experience of users on mobile phones more useful and interesting.
If we talk about what the rest of this decade is going to bring to the app market, it is expected that apps are going to earn more than games. Previously, games were the top contributors in the app market but by 2030, apps are going to contribute 50.3% to the market as compared to 37% in 2023. The apps containing streaming and short video will make 18% of the annual apps spend by 2030. These apps will grow 120% from 2023 to 2030. Streaming app called IQIYI surpassed $3 billion in player spending globally in 2023 and made it to the $3 billion club alongside Max, Tencent Video and Disney+. But even these streaming apps cannot compete with video apps like TikTok, Instagram and YouTube. The social and entertainment apps including these three are expected to reach 4.8 trillion hours in 2030.
Countries like the United States, Japan, China and Korea will make two-thirds of consumer spending by 2030 but major growth is expected to be seen from other countries from Central America (12.0%), South America (10.9%) and Africa (10.8%). In conclusion, this decade is going to be the turning point for the app market all over the world.
Read next: How Much Do Tech Workers Earn? Here’s How It Varies From City to City
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
The apps on mobile phones have direct spending revenue of $2.2 trillion, excluding the amount earned by in-app spendings, which was $362 billion in just 2023. The report shows that the app economy has declined by 2% in the last 15 years and there are various factors that became the reason for it. Inflation, limited income, privacy changes and global pandemic are some to name. Even with this slight decline, apps generated $171 billion in consumer dollars in 2023. This is because the mobile users are increasing and apps are making the experience of users on mobile phones more useful and interesting.
If we talk about what the rest of this decade is going to bring to the app market, it is expected that apps are going to earn more than games. Previously, games were the top contributors in the app market but by 2030, apps are going to contribute 50.3% to the market as compared to 37% in 2023. The apps containing streaming and short video will make 18% of the annual apps spend by 2030. These apps will grow 120% from 2023 to 2030. Streaming app called IQIYI surpassed $3 billion in player spending globally in 2023 and made it to the $3 billion club alongside Max, Tencent Video and Disney+. But even these streaming apps cannot compete with video apps like TikTok, Instagram and YouTube. The social and entertainment apps including these three are expected to reach 4.8 trillion hours in 2030.
Countries like the United States, Japan, China and Korea will make two-thirds of consumer spending by 2030 but major growth is expected to be seen from other countries from Central America (12.0%), South America (10.9%) and Africa (10.8%). In conclusion, this decade is going to be the turning point for the app market all over the world.
Read next: How Much Do Tech Workers Earn? Here’s How It Varies From City to City
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)