The post Preloader Style 211 appeared first on Best jQuery.
by Admin via Best jQuery
"Mr Branding" is a blog based on RSS for everything related to website branding and website design, it collects its posts from many sites in order to facilitate the updating to the latest technology.
To suggest any source, please contact me: Taha.baba@consultant.com
In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to integrate Vue.js with a WordPress plugin to provide a modern UI experience to our WordPress users.
Vue.js is a very popular progressive JavaScript library for building modern and rich user interfaces similar to Angular and React in terms of popularity, performance and component-based architecture. We’ll dive into the entire process of building a very simple WordPress plugin with a Vue interface that interacts with the WordPress REST API through the JavaScript Fetch API.
We’ll create a shortcode that will allow us to add a latest published posts widget in our WordPress website. The UI of the widget is a Vue app which fetches the latest published posts via the /wp-json/wp/v2/posts?filter[orderby]=date WP-API endpoint.
This tutorial assumes some familiarity with Vue.js. We’ll see how to create a Vue instance, use life-cycle hooks like mounted(), and also the JavaScript Fetch API to interact with the WordPress REST API.
In this section, we’ll see how to create a WordPress plugin that registers a shortcode in a few steps.
wp-content/pluginsLet’s start by creating the back-end part of our plugin. Plugins live inside the wp-content/plugins folder. Navigate to this folder inside your WordPress installation folder and create a sub-folder for your plugin. Let’s call it vueplugin:
cd /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins
mkdir vueplugin
Inside your plugin folder, create a vueplugin.php file and add the initial content:
<?php
/*
Plugin Name: Latest Posts
Description: Latest posts shortcode
Version: 1.0
*/
These comments are used as meta information for the plugin. In our case, we simply provide a plugin name, description and version.
If you visit the plugins page in the admin interface you should be able to see your plugin listed:
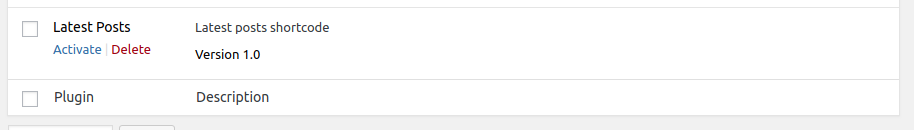
Shortcodes are used via WordPress plugins to enable users to add content to posts and pages. To register a shortcode you need to add the following minimal code in your plugin file:
function handle_shortcode() {
return 'My Latest Posts Widget';
}
add_shortcode('latestPosts', 'handle_shortcode');
We’re registering a shortcode named latestPosts.
WordPress provides the built-in add_shortcode() function to create the shortcode in your WordPress plugin. The function takes a name as the first parameter and the handler function that processes your shortcode logic and returns an output as a second parameter.
At this point, we’re only returning a static string from our shortcode, but shortcodes are more useful when used to insert dynamic content.
Now, let’s activate the plugin from the admin interface by clicking on the Activate link below the plugin name:
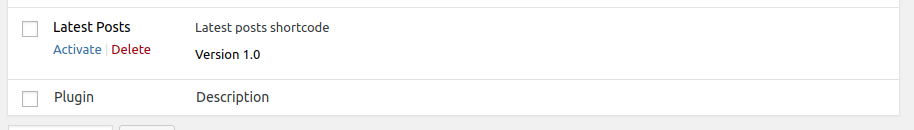
You can use a shortcode by enclosing it in square brackets — that is, [SHORTCODE_NAME]. The text inside the brackets is the name we passed as the first parameter to the add_shortcode() function. It gets replaced by the output returned by the PHP function passed as the second parameter.
To test if our shortcode is successfully registered, we can create a new post and add [latestPosts] in the post content:
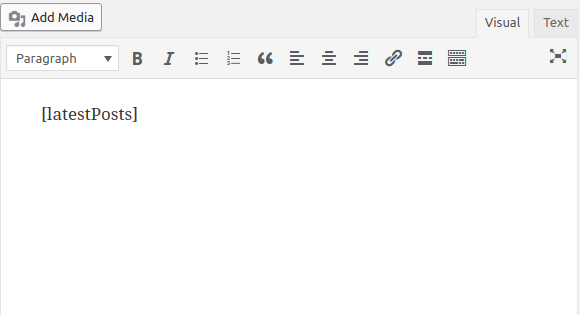
You should see My Latest Posts Widget sentence rendered:

Now, instead of displaying the static My Latest Posts Widget string, let’s display the latest posts using Vue.js.
The post Building a WordPress Plugin with Vue appeared first on SitePoint.
We received a lot of great entries in our recent competition to find the best tip for making the most out of Alibaba Cloud services. It was a fun but challenging task for our judges to pick the winners amongst so many helpful and interesting entries. But alas after fiery deliberations and heated debates they've decided that the second prize of the competition goes to Nhi Nam Ha. His winning tip is a part of a series on serverless app architecture on Alibaba Cloud, and it covers several Alibaba products.
This tutorial will show you how to deploy a MongoDB database on Alibaba Cloud and use Function Compute to develop a back-end API system to interact with the database.
Relational databases have been selected as the primary system to manage data in software development for a long time. Its ACID principals promote the data persistency, transaction integrity and concurrency control. Over the last few years, NoSQL (Not only SQL) has become popular. This model solves the impedance mismatch between the relational data structures (tables, rows, fields) and the in-memory data structures of the application (objects). Most importantly, NoSQL is designed to scale horizontally which makes it an excellent choice for modern web applications.
NoSQL could be categorized into 4 groups:
MongoDB is the most popular system within the document database group. As defined on mongodb.com,
A record in MongoDB is a document, which is a data structure composed of field and value pairs. MongoDB documents are similar to JSON objects. The values of fields may include other documents, arrays, and arrays of documents.
MongoDB databases can be deployed on Alibaba Cloud via its ApsaraDB for MongoDB service. Users can select among 3 pricing schemes:
Replication and sharding refers to the data distribution models:
In the Alibaba Cloud console, click on Products and you will see ApsaraDB for MongoDB under the ApsaraDB group. Alternatively, you can use the search box to filter the desired service.
Select the pricing scheme, the region, the server specification, and set a password for your database. Alibaba Cloud will tell you how much the service cost you based on what you chose.
More info about the instance parameters is here.
Note: if you are using a free trial account, remember to select a subscription instance. PAYG instances do not include in the trial program.
To ensure database security Alibaba Cloud automatically block all access to the database. You have to specify IP addresses in the whitelist to gain access to the target instance.

After you set your IP whitelist, click on “Database Connection” to see the connection parameters

Use this connection string to connect to the database in your Node.js code.
Function Compute lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. This service prepares computing resources for you and runs your codes on your behalf elastically and reliably. You only pay for resources actually consumed when running the codes. If your code isn’t executed, you don’t pay.
Function Compute runs your code in response to events. When the event source service triggers an event, the associated function is automatically called to process the event.
From the Alibaba Cloud console, select Function Compute and click on the “+” icon to create a new service

In the newly created service, click on the “+” icon to create a new function. You will go through a multi-step wizard to select options for your function.
For Function Template, select “Empty Function”

In the “Configure Triggers” step, select “HTTP Trigger” and give it a name. Other settings are as the image below

In the “Configure Function Settings” step, set a name for your function and select “nodejs6” as runtime

Click “Next” in the last two steps to finish the wizard and create the fucntion.
Click on the function you have just created and click on the “Code” tab. This is where you provide your code for the function to run

Use the connection string from your MongoDB server.
Also in this screen you can view the HTTP trigger that will invoke your function. You can also run the trigger to test you function here.

In this tutorial we have learnt about NoSQL database with MongoDB as a popular example. Alibaba Cloud provides its ApsaraDB for MongoDB service to those who want to run MongoDB servers on its cloud. The tutorial then moves to discuss the Function Compute service as a new way to build your application following the emerging Serverless architecture. It shows an example of a Node.js function triggered by an HTTP request to connect to the MongoDB database and perform an “insert” command.
The post Building a Serverless REST API with Function Compute and MongoDB appeared first on SitePoint.