GPTZero has taken the academic world by storm, positioning itself as a frontrunner in transforming how professors identify the incorporation of AI in student assignments. Nevertheless, it encounters fierce competition from well-established players such as Turnitin, which has bolstered its anti-plagiarism tools by integrating AI content detection capabilities. The widespread use of AI-powered text generators has sparked an extensive debate on job applications, sales pitches, and the legitimacy of essays. This has prompted stakeholders in the education and business realms to actively seek methods to differentiate between content crafted by human beings and that generated by AI bots.
Since its introduction in January, GPTZero, created by a skilled undergraduate from Princeton University, has rapidly gained popularity. The platform experienced an astounding 5.5 M visits in April alone, and projections from Similarweb suggest that this number will surpass 5.9 M in May. These remarkable figures firmly establish GPTZero as the top contender in the realm of AI content detection, focusing solely on this specialized field.
In recent developments, Turnitin, a reputable academic tool, has expanded its offerings by incorporating AI detection tools for content alongside its existing anti-plagiarism features. The platform has experienced a notable surge in popularity, with an estimated visit count of more than 17 M in May, representing an 11.5 percent increase compared to the previous year. Furthermore, educational institutions are embracing AI content detection by integrating it into their learning management systems, underscoring the increasing significance of this technology in academia.
OpenAI, the mastermind behind the development of ChatGPT, has recently launched its own text classifier designed to distinguish between content generated by ChatGPT and other sources. Although it may not enjoy the same widespread adoption as certain commercial alternatives, OpenAI's solution garnered considerable attention in April and attracted a total of 861,700 visits predominantly from desktop web traffic.
Numerous online platforms provide AI content detection tools with the intention of supporting copywriters and content creators in harnessing the power of artificial intelligence. Interestingly, a significant portion of the traffic these websites receive is predominantly focused on their AI content detection pages. Noteworthy statistics reveal that approximately 61 percent to copyleaks.com, 80 percent of the traffic to writer.com, and 85 percent to contentatscale.ai is specifically driven by users seeking AI content detection capabilities.
In order to offer a comprehensive perspective, we analyze the top websites that provide AI content detection tools free of charge or on a trial basis, excluding Turnitin. One notable contender is GPTZero, a platform born out of the limited resources of a 22-year-old named Edward Tian. Initially, GPTZero's primary goal was to assist professors in detecting the use of AI in students' work. Over time, the company has expanded its team by recruiting AI Ph.Ds and has recently secured an impressive $3.5 million in funding.
While many of the domains listed are multi-service companies, GPTZero stands out as the exception, ranking highest among these emerging platforms focused solely on AI content detection. By examining desktop web traffic related to AI content detection, Writer emerges as the second most popular tool, garnering around 3 M visits in April, trailing closely behind GPTZero's estimated 5 M visits.
Turnitin, a widely recognized and long-standing academic tool, maintains a significantly higher level of user engagement compared to GPTZero, emphasizing its continued relevance and importance within the academic community.
AI text generators like ChatGPT have presented challenges in academic and professional contexts. Institutions are grappling with usage guidelines as students and professionals use AI to enhance their work, sometimes blurring ethical boundaries. However, these tools may mistakenly identify student work as AI-generated, especially for non-native English speakers.
Read next: OpenAI Website Sees Traffic Soar to Billion Mark
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
"Mr Branding" is a blog based on RSS for everything related to website branding and website design, it collects its posts from many sites in order to facilitate the updating to the latest technology.
To suggest any source, please contact me: Taha.baba@consultant.com
Monday, June 5, 2023
New Report Reveals 3.3 Billion Interconnected Devices Will Start Trading Money and Data by 2030
The Internet of Things refers to the various smart devices that are connected to each other to facilitate ease of use. There are a lot of benefits to this, but in spite of the fact that this is the case, many downsides can also be noted with all things having been considered and taken into account.
A new study that was just published by STL Partners suggests that nearly 3.3 billion devices will be connected through the Internet of Things by 2030. With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that these devices will regularly trade money as well as data with each other by the end of the decade.
This new phenomenon is being dubbed the Economy of Things, and experts are predicting that it will be worth somewhere in the region of 10% of the total IoT economy. What’s more, this subset of the IoT will reportedly witness a CAGR of about 68%, which could lead to it possessing enormous influence across a wide array of product classes.
Current predictions estimate that around 88 million devices will be connected via the so called Economy of Things as of next year. Hence, in order to reach the 3.3 billion mark by 2030, this industry will require a whopping 3,750% growth rate in just six years. This astronomical growth rate might seem like it is far too high, but experts clearly feel like it is a likely outcome.
40% of these devices will likely be grid enabled smart devices. A further 700 million will have to do with supply chain related devices with the rest being distributed across various sectors.
The high CAGR will likely help it reach the 3.3 billion mark because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up compounding over time. It will be interesting to see how this impacts consumer welfare, since the privacy violations of the Internet of Things have become rather notorious and the Economy of Things could be orders of magnitude more harmful in that respect.
Read next: AI Searches on Google Soar to All-Time High
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
A new study that was just published by STL Partners suggests that nearly 3.3 billion devices will be connected through the Internet of Things by 2030. With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that these devices will regularly trade money as well as data with each other by the end of the decade.
This new phenomenon is being dubbed the Economy of Things, and experts are predicting that it will be worth somewhere in the region of 10% of the total IoT economy. What’s more, this subset of the IoT will reportedly witness a CAGR of about 68%, which could lead to it possessing enormous influence across a wide array of product classes.
Current predictions estimate that around 88 million devices will be connected via the so called Economy of Things as of next year. Hence, in order to reach the 3.3 billion mark by 2030, this industry will require a whopping 3,750% growth rate in just six years. This astronomical growth rate might seem like it is far too high, but experts clearly feel like it is a likely outcome.
40% of these devices will likely be grid enabled smart devices. A further 700 million will have to do with supply chain related devices with the rest being distributed across various sectors.
The high CAGR will likely help it reach the 3.3 billion mark because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up compounding over time. It will be interesting to see how this impacts consumer welfare, since the privacy violations of the Internet of Things have become rather notorious and the Economy of Things could be orders of magnitude more harmful in that respect.
Read next: AI Searches on Google Soar to All-Time High
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Snapchat's Lucky Month this May as Revenue Soars to New Heights
May has proven to be a remarkable month for Snapchat, the widely-used social media platform among young users, as it achieved unprecedented growth in revenue. This notable upswing not only signifies a major achievement for the company but also demonstrates the sustained demand for Snapchat's services, thereby dispelling any previous doubts about its growth trajectory.
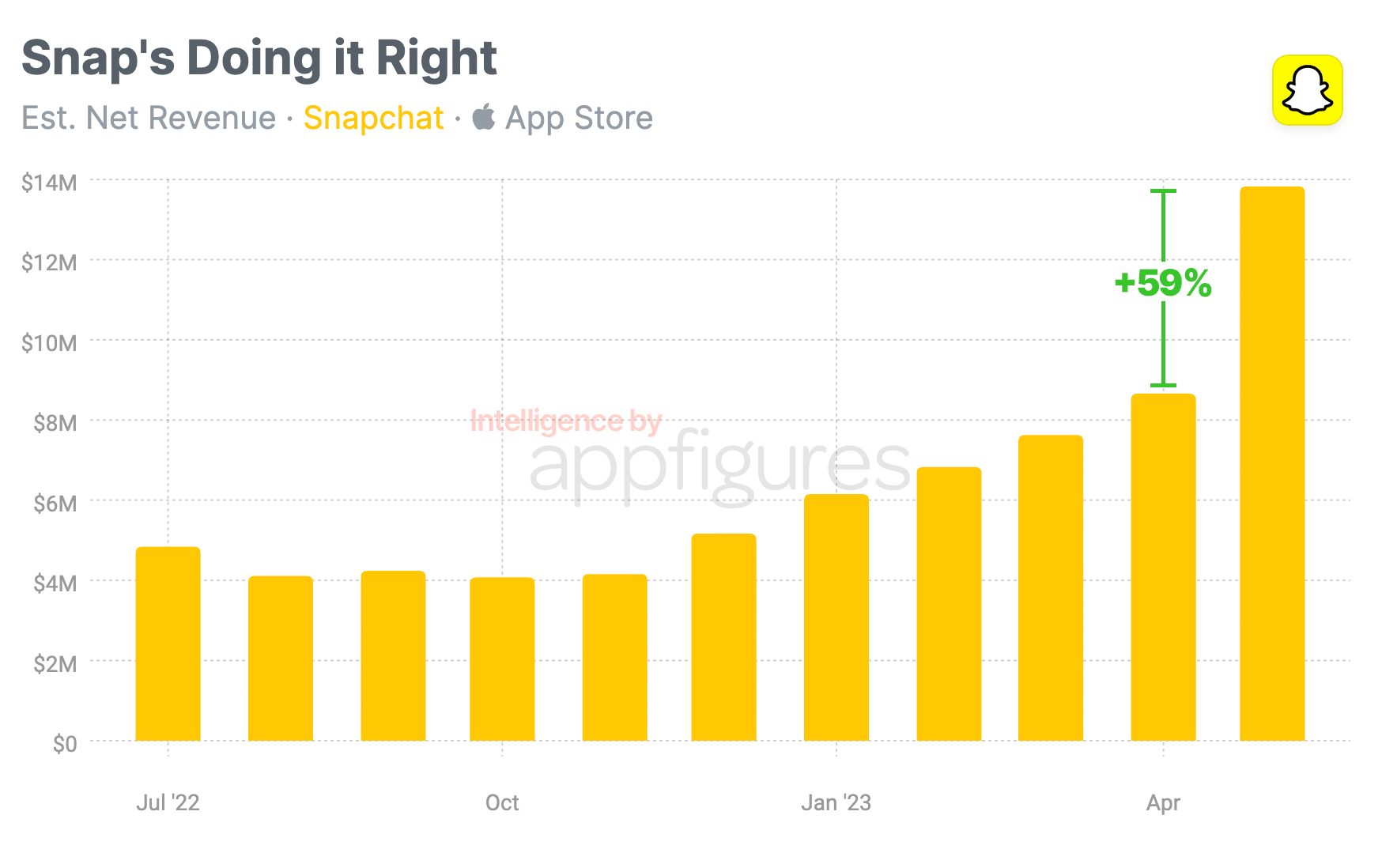
In May, Snapchat achieved a significant milestone in terms of net revenue generated from the App Store. According to App Intelligence by Appfigures, the popular social media platform recorded an impressive $13.9 million in net revenue, marking a remarkable 59% growth compared to the previous month, April. This outstanding performance has contributed to Snapchat's cumulative net revenue since its launch, which now stands at an impressive $70 million. It's worth noting that this figure represents the revenue retained by Snap after deducting Apple's share.
The revenue growth observed in May highlights the strong appeal of Snapchat's features among users. It contradicts earlier assertions that Snapchat's offering was insufficient and needed additional enhancements to sustain growth. These statistics indicate that Snapchat is thriving on its own, without the need for major external developments.
After delving into the distribution of revenue, it becomes clear that a substantial portion, accounting for 65.9%, of Snapchat's net revenue is generated by users in the United States. The remaining 34.1% originates from a diverse range of countries. Noteworthy among these contributors is the United Kingdom, occupying the second spot as a significant revenue generator. Following closely behind are Australia, Canada, and France, showcasing their importance in driving Snapchat's overall revenue.
Snapchat's revenue growth from paid features may still be trailing behind its advertising revenue, but the rapid expansion it has witnessed is truly remarkable, particularly considering its history of offering free services to users. This trend holds great promise for other platforms that rely on product-led revenue strategies, as it demonstrates the willingness of users to invest in and engage with paid features, even in a landscape dominated by free offerings.
Snapchat's ability to achieve substantial revenue growth on its own, without major external factors, highlights the strength and appeal of its core features, paving the way for other social media companies to explore innovative strategies and tap into the growing demand for enhanced experiences and premium features.
After witnessing Snapchat's impressive performance in May, experts in the industry are curious about which social media platform will be the next to achieve significant revenue growth. As the landscape of social media evolves, there is a growing trend toward product-led revenue models, making it intriguing to observe which platform will adopt a similar approach and achieve remarkable financial success.
Read next: 78% of Americans Are Rethinking Their Investments, Here’s Why
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
In May, Snapchat achieved a significant milestone in terms of net revenue generated from the App Store. According to App Intelligence by Appfigures, the popular social media platform recorded an impressive $13.9 million in net revenue, marking a remarkable 59% growth compared to the previous month, April. This outstanding performance has contributed to Snapchat's cumulative net revenue since its launch, which now stands at an impressive $70 million. It's worth noting that this figure represents the revenue retained by Snap after deducting Apple's share.
The revenue growth observed in May highlights the strong appeal of Snapchat's features among users. It contradicts earlier assertions that Snapchat's offering was insufficient and needed additional enhancements to sustain growth. These statistics indicate that Snapchat is thriving on its own, without the need for major external developments.
After delving into the distribution of revenue, it becomes clear that a substantial portion, accounting for 65.9%, of Snapchat's net revenue is generated by users in the United States. The remaining 34.1% originates from a diverse range of countries. Noteworthy among these contributors is the United Kingdom, occupying the second spot as a significant revenue generator. Following closely behind are Australia, Canada, and France, showcasing their importance in driving Snapchat's overall revenue.
Snapchat's revenue growth from paid features may still be trailing behind its advertising revenue, but the rapid expansion it has witnessed is truly remarkable, particularly considering its history of offering free services to users. This trend holds great promise for other platforms that rely on product-led revenue strategies, as it demonstrates the willingness of users to invest in and engage with paid features, even in a landscape dominated by free offerings.
Snapchat's ability to achieve substantial revenue growth on its own, without major external factors, highlights the strength and appeal of its core features, paving the way for other social media companies to explore innovative strategies and tap into the growing demand for enhanced experiences and premium features.
After witnessing Snapchat's impressive performance in May, experts in the industry are curious about which social media platform will be the next to achieve significant revenue growth. As the landscape of social media evolves, there is a growing trend toward product-led revenue models, making it intriguing to observe which platform will adopt a similar approach and achieve remarkable financial success.
Read next: 78% of Americans Are Rethinking Their Investments, Here’s Why
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
Decoding the Data Monopoly: AI Giants Anthropic, OpenAI, and Google Keep Their Data Locked Away While Using Others' Content
As the origin of productive Artificial Intelligence unfolds, big tech giants adopt a perplexing mantra: "Speak, but don't imitate." They support the ethical use of online content while confidentially diverging from their own principles, blurring the line between innovation and hypocrisy. In this mysterious landscape, the digital world sees a contradiction that begs the question: Can these giants truly practice what they preach?
In a realm dominated by artificial intelligence, the union of OpenAI supported by Microsoft, and Anthropic, supported by Google, stands accused of silently utilizing digital content crafted by the business to fuel their artificial intelligence models. This dubious practice, covered in debate, ignites a legal storm that will shape the destiny of the web and redefine the application of copyright legislation within this brave unexplored world. As action lines are drawn, the future awaits its ruling, balanced on the bluff of a digital revolution.
As the technology enterprise finds itself embroiled in a debate over adequate use, the question arises: Shouldn't these influential giants practice what they preach? While they strongly safeguard their own content from being utilized by other artificial intelligence models, they walk a fine line by leveraging everyone else's innovations without specific consent. It's a double standard that appeals to a fair and unbiased resolution in this evolving landscape.
Delving into Claude's service agreement, a clear-cut limitation emerges: Users are prohibited from using the platform to create rival products or services, including the expansion or training of AI algorithms or models. This strict guideline raises intriguing questions about competition, creation, and the extent of control exercised by Anthropic over the AI terrain. As the fine print unfolds, the limitations of technological exploration and the need for dominance come into sharp focus.
Google's terms strictly forbid utilizing the support for creating AI algorithms or similar technologies, posing fascinating restrictions on user invention and technical exploration.
Further, OpenAI's policy firmly states that users are prohibited from employing the Services' outcome to create competing models, posing limitations on the utilization of ChatGPT's abilities.
A wave of realization dawns upon different businesses as they discover the reality of their data's significance in artificial intelligence prototype training. Reddit, a long-standing resource, now intends to introduce bills for accessing its valuable corpus. Reddit's Chief Executive Officer asserts that they no longer wish to lose the full of this value to the world's biggest corporations without reaping the benefits.
In a bold move, Elon Musk publicly blamed Microsoft, OpenAI's primary supporter, for unlawfully leveraging data from Twitter to train models for artificial intelligence. Musk's tweet indicated a potential lawful action, evoking a reaction from a Microsoft representative who dismissed the claim, stating that this notion is so flawed that I have no idea where I should start.
The Chief Executive Officer of Open AI embraces a more considerate approach by developing AI models that honor copyright, ensuring creators receive compensation for their content or style being utilized.
A retired executive of MS brings attention to the perceived flaw in the current artificial intelligence approach, asserting that it damages the web. By highlighting the lack of value given to innovators and copyright keepers through data harvesting and model training, he raises thought-provoking worries about the growing dynamics between content, technology, and ownership.
Read next: Android 13 vs. Android 11: Data Reveal Surprising Shifts in Google-Owned OS Adoption
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
In a realm dominated by artificial intelligence, the union of OpenAI supported by Microsoft, and Anthropic, supported by Google, stands accused of silently utilizing digital content crafted by the business to fuel their artificial intelligence models. This dubious practice, covered in debate, ignites a legal storm that will shape the destiny of the web and redefine the application of copyright legislation within this brave unexplored world. As action lines are drawn, the future awaits its ruling, balanced on the bluff of a digital revolution.
As the technology enterprise finds itself embroiled in a debate over adequate use, the question arises: Shouldn't these influential giants practice what they preach? While they strongly safeguard their own content from being utilized by other artificial intelligence models, they walk a fine line by leveraging everyone else's innovations without specific consent. It's a double standard that appeals to a fair and unbiased resolution in this evolving landscape.
Delving into Claude's service agreement, a clear-cut limitation emerges: Users are prohibited from using the platform to create rival products or services, including the expansion or training of AI algorithms or models. This strict guideline raises intriguing questions about competition, creation, and the extent of control exercised by Anthropic over the AI terrain. As the fine print unfolds, the limitations of technological exploration and the need for dominance come into sharp focus.
Google's terms strictly forbid utilizing the support for creating AI algorithms or similar technologies, posing fascinating restrictions on user invention and technical exploration.
Further, OpenAI's policy firmly states that users are prohibited from employing the Services' outcome to create competing models, posing limitations on the utilization of ChatGPT's abilities.
A wave of realization dawns upon different businesses as they discover the reality of their data's significance in artificial intelligence prototype training. Reddit, a long-standing resource, now intends to introduce bills for accessing its valuable corpus. Reddit's Chief Executive Officer asserts that they no longer wish to lose the full of this value to the world's biggest corporations without reaping the benefits.
In a bold move, Elon Musk publicly blamed Microsoft, OpenAI's primary supporter, for unlawfully leveraging data from Twitter to train models for artificial intelligence. Musk's tweet indicated a potential lawful action, evoking a reaction from a Microsoft representative who dismissed the claim, stating that this notion is so flawed that I have no idea where I should start.
The Chief Executive Officer of Open AI embraces a more considerate approach by developing AI models that honor copyright, ensuring creators receive compensation for their content or style being utilized.
A retired executive of MS brings attention to the perceived flaw in the current artificial intelligence approach, asserting that it damages the web. By highlighting the lack of value given to innovators and copyright keepers through data harvesting and model training, he raises thought-provoking worries about the growing dynamics between content, technology, and ownership.
Read next: Android 13 vs. Android 11: Data Reveal Surprising Shifts in Google-Owned OS Adoption
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Sunday, June 4, 2023
Android 13 vs. Android 11: Data Reveal Surprising Shifts in Google-Owned OS Adoption
Freshly released data from Google unveils that Android 13 has achieved a presence on around 15 percent of active devices globally. Notwithstanding the progress of this latest version, Android 11 remains firmly entrenched as the leading Android version in terms of widespread usage.
Google collects data periodically on a global scale to track Android devices that have accessed the Play Store within a week's time. This data is then made available to developers through Android Studio, empowering them to analyze the distribution of Android versions across devices. This information plays a crucial role in determining the minimum Android version that an app should support. Interestingly, Apple has also utilized similar data to highlight the rapid adoption of iOS updates among its users.
In the past few years, Google has been less frequent in updating the distribution chart, typically doing so on a quarterly basis. However, this year has been an exception with updates provided in January, April, and now June. The latest distribution chart, which is dated May 30, 2023, has been included in the latest version of Android Studio.
According to the latest data from Google, Android 13 now occupies approximately 15 percent of active devices globally, marking a steady rise from 12.1 percent in April. However, Android 11 continues to dominate as the most widely adopted Android version, installed on 23.1 percent of devices worldwide. The distribution figures, collected from devices connected to the Play Store within a specific seven-day period, provide valuable insights to developers through Android Studio. These statistics aid developers in determining the minimum Android version to support their apps. The consistent growth of Android 13 indicates its increasing acceptance among users, while the enduring popularity of Android 11 showcases its resilience and widespread usage.
Remarkably, Android Oreo stands out as the sole Android version that experienced an increase in adoption between April and June, rising from 6.7 percent to 8.3 percent. It is important to highlight that this growth is still lower than its 9.5 percent share recorded in January, indicating a slight overall decline. The factors contributing to this unexpected surge in adoption during the specified timeframe remain uncertain and warrant further investigation.
The data suggests a steady increase in adoption for the latest Android version, Android 13, although Android 11 continues to dominate the market. As Android development progresses, developers can utilize this information to make informed decisions regarding the Android versions they support. It will be interesting to observe future updates and see how the distribution landscape evolves in the coming months.
In conclusion, the latest data from Google sheds light on the distribution of Android versions among active devices worldwide. Android 13 has witnessed a steady increase in adoption, while Android 11 maintains its position as the dominant version. This valuable information, gathered from devices connected to the Play Store, empowers developers to make informed decisions about the minimum Android version they should support. The unexpected growth of Android Oreo between April and June presents an intriguing phenomenon that warrants further investigation. As the Android landscape evolves, developers can leverage this data to navigate the ever-changing market, and it will be fascinating to observe how distribution trends unfold in the future.
H/T: 9to5G
Read next: Google Expands Its Workspace Labs With New Features Including Innovative Image Generation
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
Google collects data periodically on a global scale to track Android devices that have accessed the Play Store within a week's time. This data is then made available to developers through Android Studio, empowering them to analyze the distribution of Android versions across devices. This information plays a crucial role in determining the minimum Android version that an app should support. Interestingly, Apple has also utilized similar data to highlight the rapid adoption of iOS updates among its users.
In the past few years, Google has been less frequent in updating the distribution chart, typically doing so on a quarterly basis. However, this year has been an exception with updates provided in January, April, and now June. The latest distribution chart, which is dated May 30, 2023, has been included in the latest version of Android Studio.
According to the latest data from Google, Android 13 now occupies approximately 15 percent of active devices globally, marking a steady rise from 12.1 percent in April. However, Android 11 continues to dominate as the most widely adopted Android version, installed on 23.1 percent of devices worldwide. The distribution figures, collected from devices connected to the Play Store within a specific seven-day period, provide valuable insights to developers through Android Studio. These statistics aid developers in determining the minimum Android version to support their apps. The consistent growth of Android 13 indicates its increasing acceptance among users, while the enduring popularity of Android 11 showcases its resilience and widespread usage.
Remarkably, Android Oreo stands out as the sole Android version that experienced an increase in adoption between April and June, rising from 6.7 percent to 8.3 percent. It is important to highlight that this growth is still lower than its 9.5 percent share recorded in January, indicating a slight overall decline. The factors contributing to this unexpected surge in adoption during the specified timeframe remain uncertain and warrant further investigation.
The data suggests a steady increase in adoption for the latest Android version, Android 13, although Android 11 continues to dominate the market. As Android development progresses, developers can utilize this information to make informed decisions regarding the Android versions they support. It will be interesting to observe future updates and see how the distribution landscape evolves in the coming months.
In conclusion, the latest data from Google sheds light on the distribution of Android versions among active devices worldwide. Android 13 has witnessed a steady increase in adoption, while Android 11 maintains its position as the dominant version. This valuable information, gathered from devices connected to the Play Store, empowers developers to make informed decisions about the minimum Android version they should support. The unexpected growth of Android Oreo between April and June presents an intriguing phenomenon that warrants further investigation. As the Android landscape evolves, developers can leverage this data to navigate the ever-changing market, and it will be fascinating to observe how distribution trends unfold in the future.
H/T: 9to5G
Read next: Google Expands Its Workspace Labs With New Features Including Innovative Image Generation
by Ayesha Hasnain via Digital Information World
Microsoft Windows 11’s Growth Rate Slowed Down in May 2023
The monthly progress report for Windows has recently been released by StatCounter, an analyst company. The report for May 2023 highlighted the market share of Windows, including Windows 7, 8, 10, and the latest one, Windows 11.
As per the analysis, currently Windows 10 is leading the chart with almost seventy-two percent (or 71.9% to be exact) market share after it gained 0.5 points. However, the latest Windows version, which is Windows 11, was found to be far behind Windows 10. Windows 11 held a share of around 23 percent after losing 0.16 points last month.
Several factors may have contributed to the slowdown in Windows 11’s growth rate. Firstly, the initial surge of early adopters and tech enthusiasts who eagerly upgraded to the new operating system has likely subsided. This early wave of adopters tends to be more proactive and open to change, while the general public may take a more cautious approach.
Additionally, some users may be reluctant to upgrade to Windows 11 due to compatibility issues. Unlike previous versions of Windows, Windows 11 has stricter hardware requirements, which means older devices may not be able to run the new OS smoothly. This limitation could deter some users from making the switch.
Moreover, the ongoing chip shortage affecting the tech industry has resulted in supply constraints for new computers. As a result, many individuals and businesses may be holding off on purchasing new devices, which consequently slows down the adoption of Windows 11.Ever since it was announced that those who were using Windows 7 wouldn’t be able to receive the latest security updates, it has lost around 0.17 points with a share of 3.6 percent. Whereas Windows 8 and 8.1 were found to be at the bottom with a share of around 0.7 percent and 0.3 percent, respectively. It was also revealed that almost 0.3 percent of the users had Windows XP on their systems.
Despite the temporary setback, Windows 11 remains a significant update with new features and enhancements. As more users become aware of the benefits and as the hardware landscape evolves, it is likely that Windows 11’s growth rate will regain momentum.
Read next: The Quest for Public Attention Intensifies as AI vs Bitcoin Search Battle Continues
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
As per the analysis, currently Windows 10 is leading the chart with almost seventy-two percent (or 71.9% to be exact) market share after it gained 0.5 points. However, the latest Windows version, which is Windows 11, was found to be far behind Windows 10. Windows 11 held a share of around 23 percent after losing 0.16 points last month.
Several factors may have contributed to the slowdown in Windows 11’s growth rate. Firstly, the initial surge of early adopters and tech enthusiasts who eagerly upgraded to the new operating system has likely subsided. This early wave of adopters tends to be more proactive and open to change, while the general public may take a more cautious approach.
Additionally, some users may be reluctant to upgrade to Windows 11 due to compatibility issues. Unlike previous versions of Windows, Windows 11 has stricter hardware requirements, which means older devices may not be able to run the new OS smoothly. This limitation could deter some users from making the switch.
Moreover, the ongoing chip shortage affecting the tech industry has resulted in supply constraints for new computers. As a result, many individuals and businesses may be holding off on purchasing new devices, which consequently slows down the adoption of Windows 11.Ever since it was announced that those who were using Windows 7 wouldn’t be able to receive the latest security updates, it has lost around 0.17 points with a share of 3.6 percent. Whereas Windows 8 and 8.1 were found to be at the bottom with a share of around 0.7 percent and 0.3 percent, respectively. It was also revealed that almost 0.3 percent of the users had Windows XP on their systems.
Despite the temporary setback, Windows 11 remains a significant update with new features and enhancements. As more users become aware of the benefits and as the hardware landscape evolves, it is likely that Windows 11’s growth rate will regain momentum.
Read next: The Quest for Public Attention Intensifies as AI vs Bitcoin Search Battle Continues
by Arooj Ahmed via Digital Information World
Americans With Side Hustles Are Now Earning Over $800 a Month on Average
Starting up a side hustle has become increasingly important because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up helping people pay their bills. According to a recent survey conduced by Bankrate, 39% of Americans say that they have a side hustle. 44% even said that they will always need one since a single job no longer pays enough to help them stay ahead of their expenses.
33% of the people that participated in this survey stated that they need their side hustles for basic living expenses, with 27% using their side hustle to get some discretionary money for expenses other than necessities. 25% of survey respondents indicated that they use this side hustle money to save for the future, and 12% are compelled to start a side hustle in order to make their debts easier to pay off than might have been the case otherwise.
It is unsurprising that a large chunk of people with side hustles are low income and hail from more recent generations. 53% of Gen Z and 50% of Millennials said that they have side hustles, and 42% of people that bring in under $50,000 a year stated that they need side hustles in order to keep the lights on. However, 45% of people that earn over $100,000 per year said that they have side hustles as well, indicating that this practice is not the sole purview of low income groups.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that the average monthly income that people can bring from their side hustles is around $810. In spite of the fact that this is the case, this number might be skewed by those that bring in far more than this on a monthly basis.
Around 28% of the people that currently have side hustles bring in just $1 to $50 on a monthly basis, with 14% earning between $51 and $100. 11% admitted to earning between $101 to $200, 6% mentioned $200 to $300 and 14% are currently bringing in around $301 to $500 per month with all things having been considered and taken into account.
12% of survey respondents did mention monthly incomes that range from $501 to $1,000, however. What’s more, 7% of the people with side hustles that answered questions in this survey referenced monthly incomes that exceed $1,001 and reach up to $2,000. 7% even said that they earn over $2,000 on a monthly basis.
If we were to zero in on this data on a generational basis, Millennial seem to be earning more than any other cohort. They bring in around $1,022 per month on average, with Gen Z earning $753 per month, Gen X earning around $670 and Baby Boomers coming in dead last with $636 in monthly earnings.
All in all, side hustles have become a popular way for people to make ends meet. While this says a lot about the state of the economy, it also reveals that the modern world is offering new avenues for people to bolster their revenue streams and diversify so that they can meet their needs.
Read next: This Survey Reveals the Generational Gap in AI Acceptance
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
33% of the people that participated in this survey stated that they need their side hustles for basic living expenses, with 27% using their side hustle to get some discretionary money for expenses other than necessities. 25% of survey respondents indicated that they use this side hustle money to save for the future, and 12% are compelled to start a side hustle in order to make their debts easier to pay off than might have been the case otherwise.
It is unsurprising that a large chunk of people with side hustles are low income and hail from more recent generations. 53% of Gen Z and 50% of Millennials said that they have side hustles, and 42% of people that bring in under $50,000 a year stated that they need side hustles in order to keep the lights on. However, 45% of people that earn over $100,000 per year said that they have side hustles as well, indicating that this practice is not the sole purview of low income groups.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that the average monthly income that people can bring from their side hustles is around $810. In spite of the fact that this is the case, this number might be skewed by those that bring in far more than this on a monthly basis.
Around 28% of the people that currently have side hustles bring in just $1 to $50 on a monthly basis, with 14% earning between $51 and $100. 11% admitted to earning between $101 to $200, 6% mentioned $200 to $300 and 14% are currently bringing in around $301 to $500 per month with all things having been considered and taken into account.
12% of survey respondents did mention monthly incomes that range from $501 to $1,000, however. What’s more, 7% of the people with side hustles that answered questions in this survey referenced monthly incomes that exceed $1,001 and reach up to $2,000. 7% even said that they earn over $2,000 on a monthly basis.
If we were to zero in on this data on a generational basis, Millennial seem to be earning more than any other cohort. They bring in around $1,022 per month on average, with Gen Z earning $753 per month, Gen X earning around $670 and Baby Boomers coming in dead last with $636 in monthly earnings.
All in all, side hustles have become a popular way for people to make ends meet. While this says a lot about the state of the economy, it also reveals that the modern world is offering new avenues for people to bolster their revenue streams and diversify so that they can meet their needs.
Read next: This Survey Reveals the Generational Gap in AI Acceptance
by Zia Muhammad via Digital Information World
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)